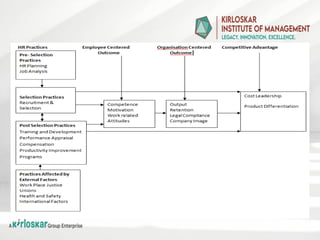
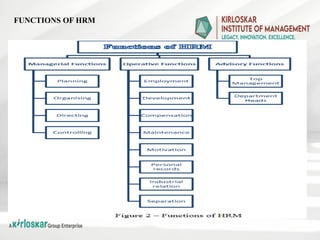
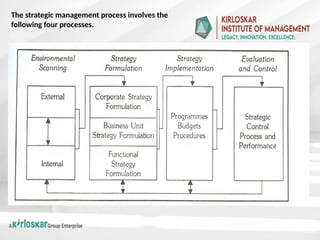
Human capital refers to the collective skills, knowledge, experience, and attributes that individuals possess, which contribute to their economic productivity and societal development. It is an intangible asset that encompasses education, training, health, intelligence, creativity, and social skills, all of which enhance an individual's ability to perform tasks efficiently and contribute to an organization's or nation's economic growth.
The concept of human capital is rooted in the idea that investments in people, such as education and skill development, yield long-term benefits by increasing productivity and innovation. A well-educated and skilled workforce is often seen as a driving force behind economic progress, technological advancement, and overall competitiveness in a globalized economy. Organizations that prioritize human capital development through continuous training programs, employee engagement, and well-being initiatives tend to experience higher levels of performance, job satisfaction, and retention.
In economic terms, human capital is often considered just as important as physical capital, such as machinery and infrastructure, because it directly influences labor efficiency and economic output. Countries with high human capital indices tend to have stronger economies, as their workforce is equipped to adapt to new technologies, improve processes, and drive entrepreneurial ventures. Conversely, a lack of investment in human capital can lead to stagnation, skill gaps, and reduced economic potential.
Moreover, human capital is not limited to professional competencies alone. Emotional intelligence, leadership abilities, problem-solving skills, and adaptability are also critical components that shape an individual's effectiveness in personal and professional settings. As the world shifts toward a knowledge-based economy, the value of human capital continues to rise, making lifelong learning and skill enhancement essential for career growth and national progress.
In the modern workplace, companies recognize human capital as a strategic asset, leading to the development of human resource management practices focused on talent acquisition, employee development, and performance optimization. Organizations that cultivate a strong human capital base through diversity, inclusion, and leadership development often gain a competitive advantage by fostering innovation and resilience in an ever-changing business environment.
In conclusion, human capital plays a pivotal role in shaping the economic and social fabric of societies. It is a key determinant of productivity, innovation, and sustainable growth, making it imperative for individuals, businesses, and governments to invest in education, skills training, and well-being initiatives to maximize its potential.