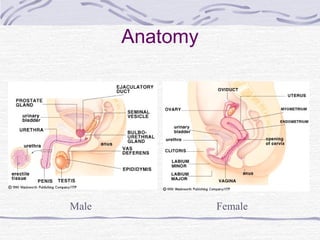
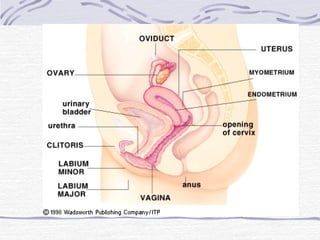
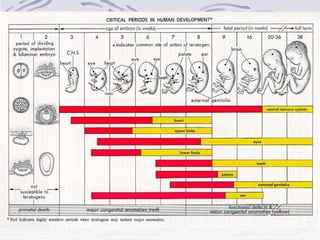
1. Human reproduction involves both similarities and differences between males and females. While anatomy initially develops similarly, hormones direct development towards either male or female anatomy by the 7th week of gestation.
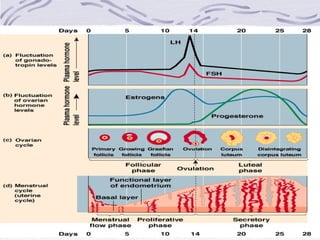
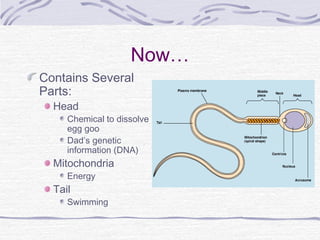
2. The female reproductive cycle is highly complex and regulated by hormones to coordinate the monthly maturation and release of a single egg, while the male system continuously produces millions of sperm daily.
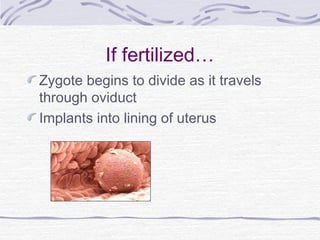
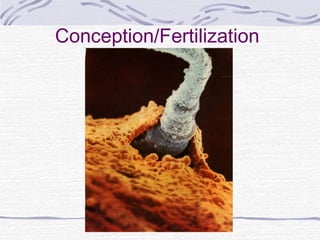
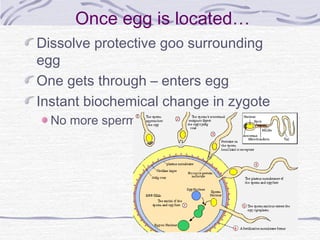
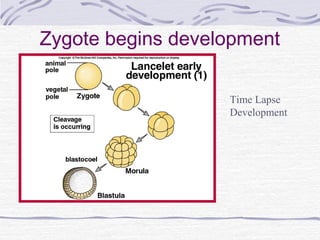
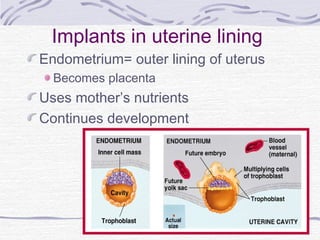
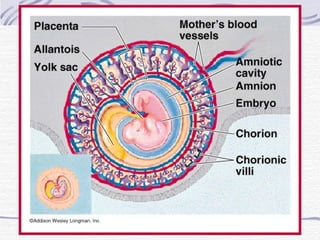
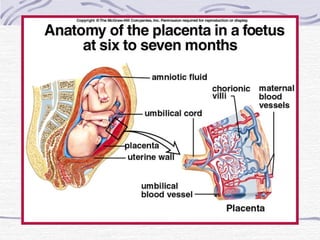
3. Fertilization occurs if sperm successfully navigates the female reproductive tract and one unites with an egg, initiating cell division and implantation in the uterine wall. Development then proceeds through gestation, culminating in birth.