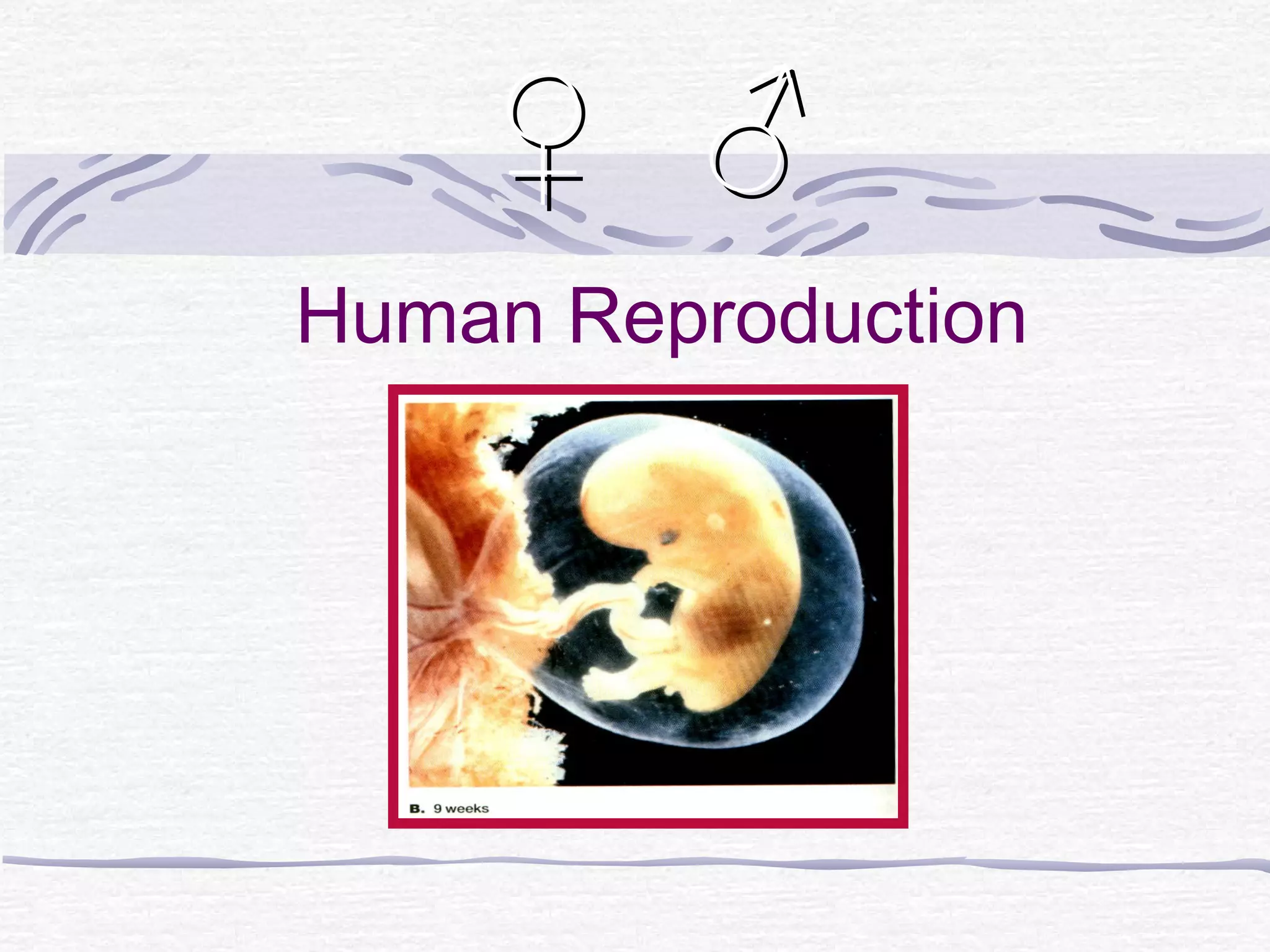
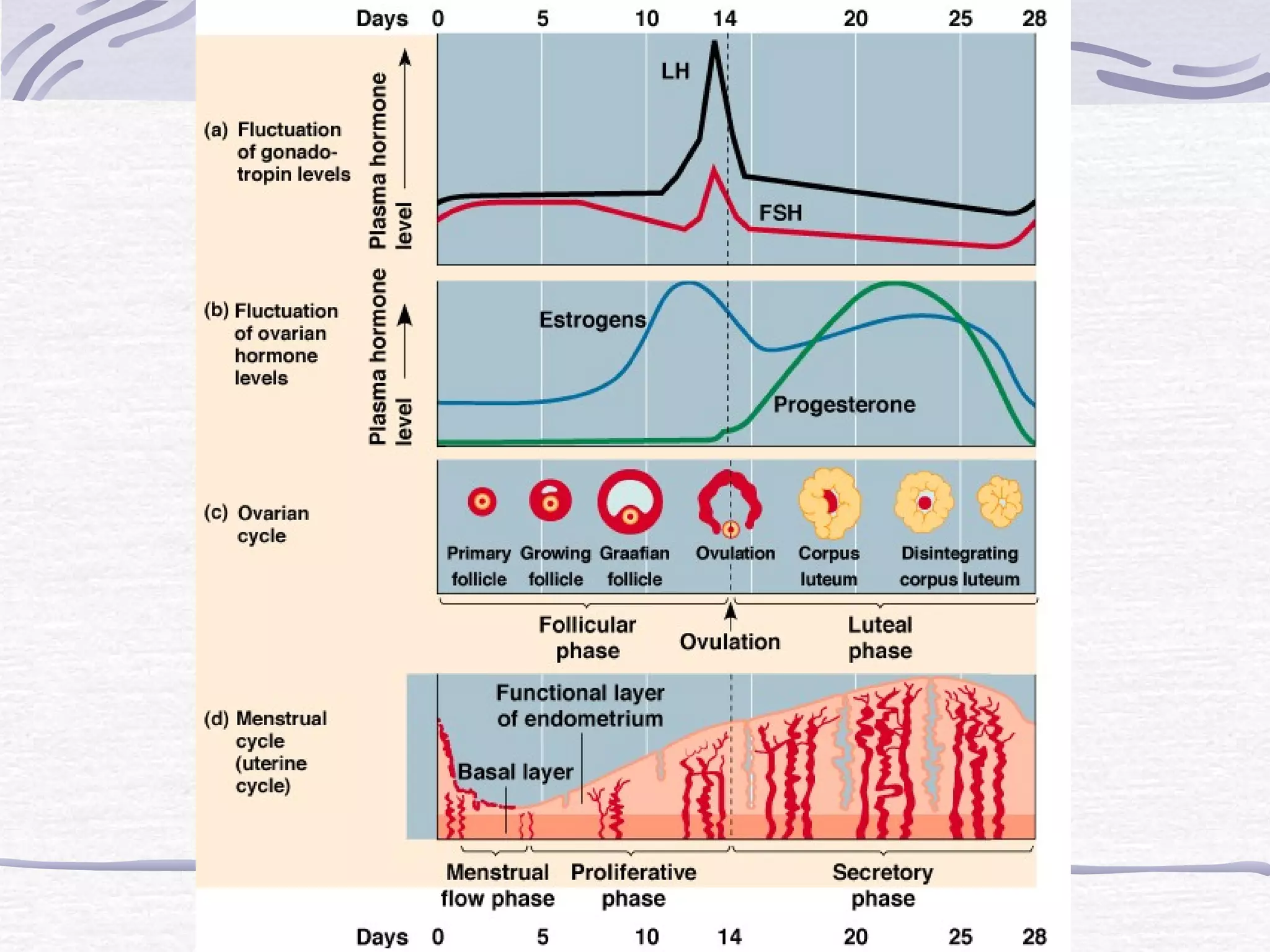
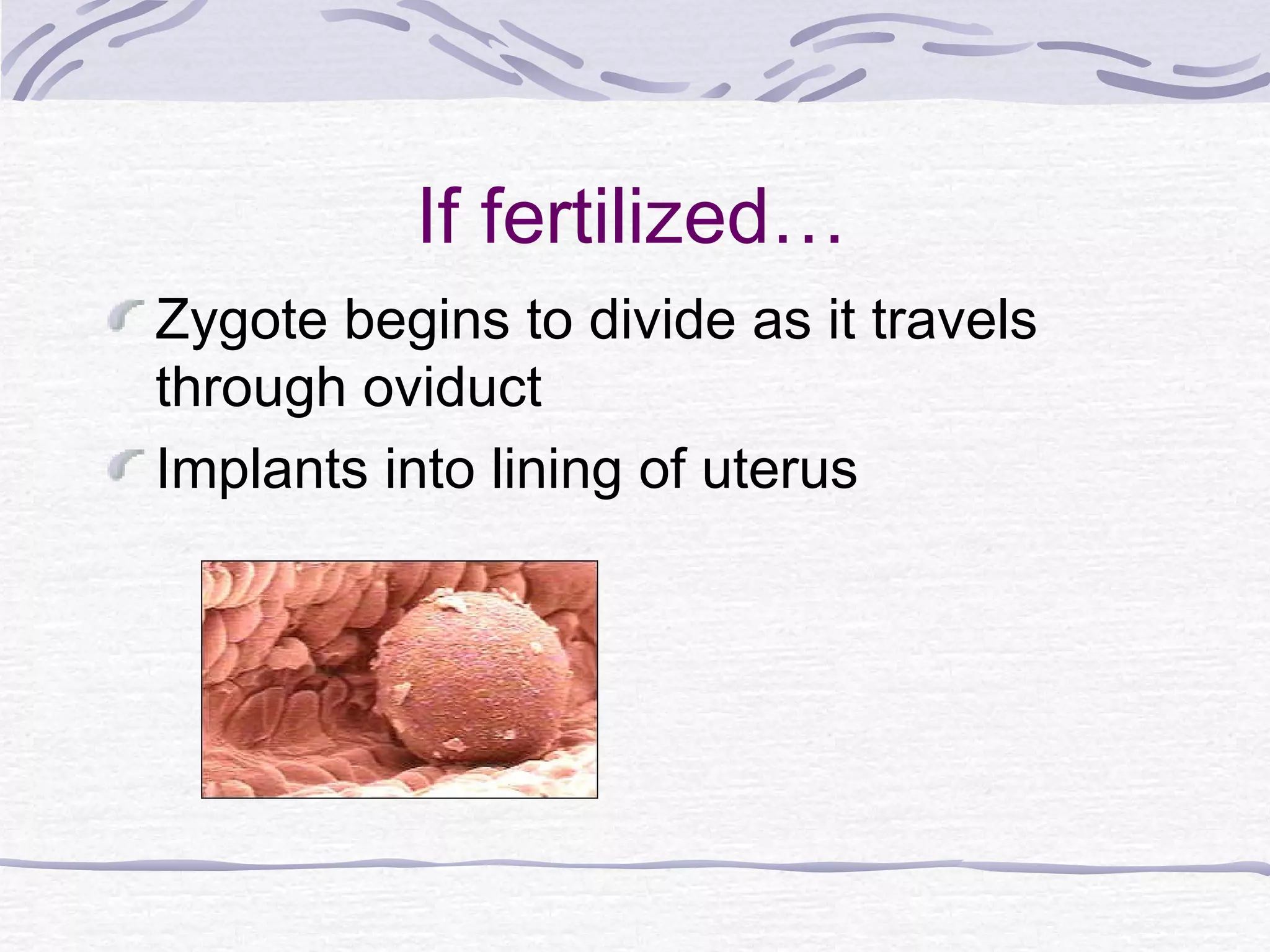
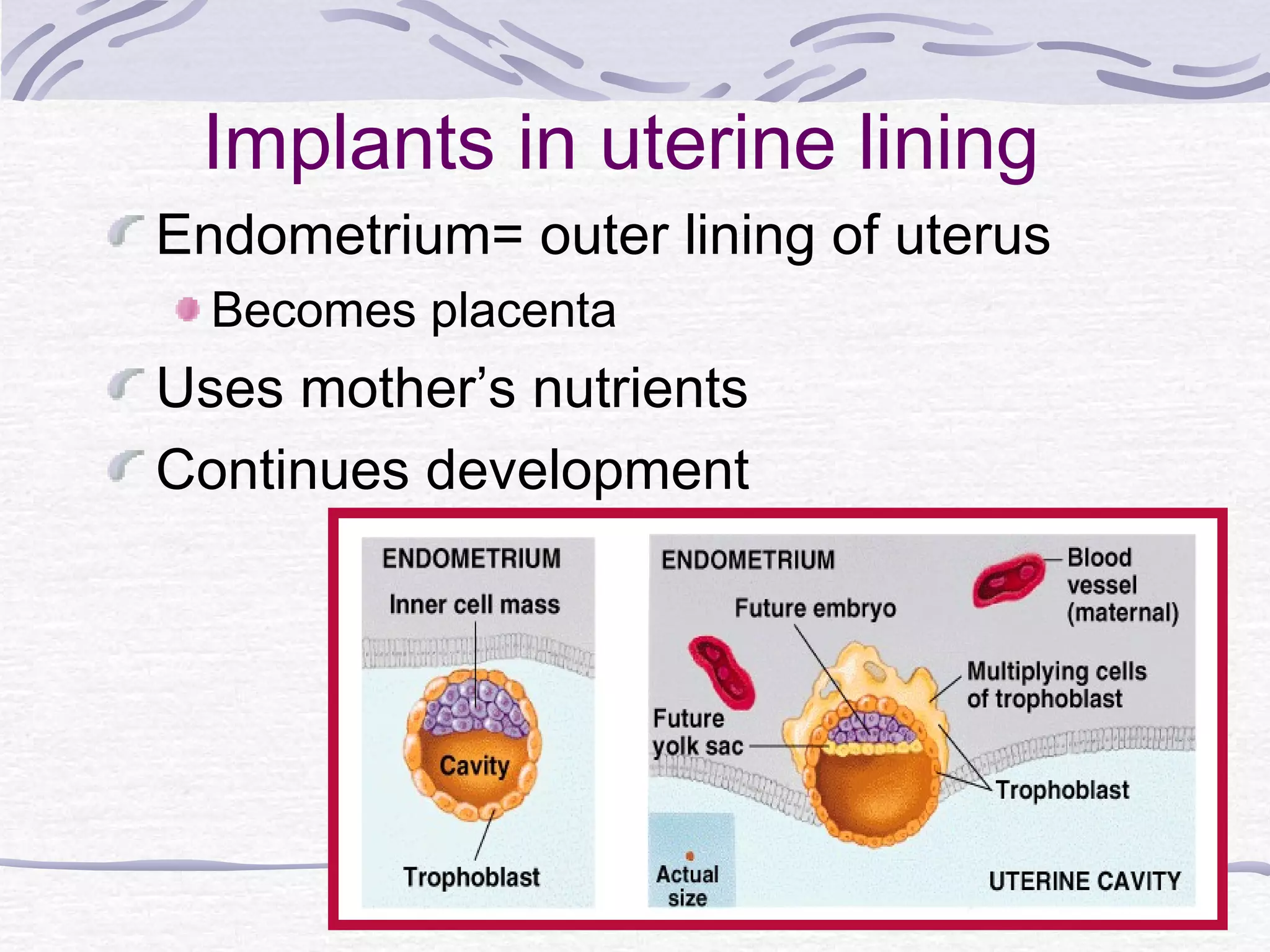
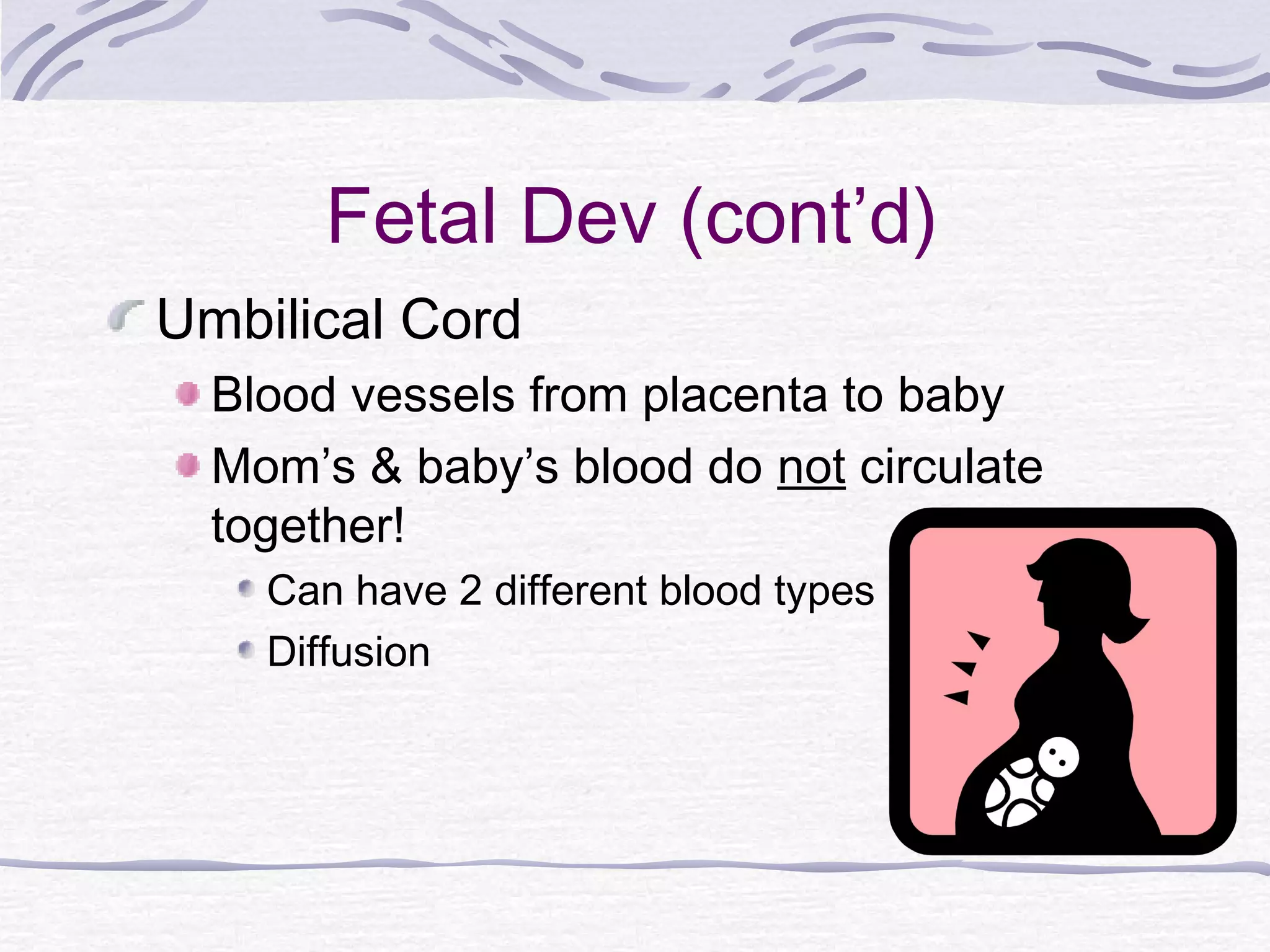
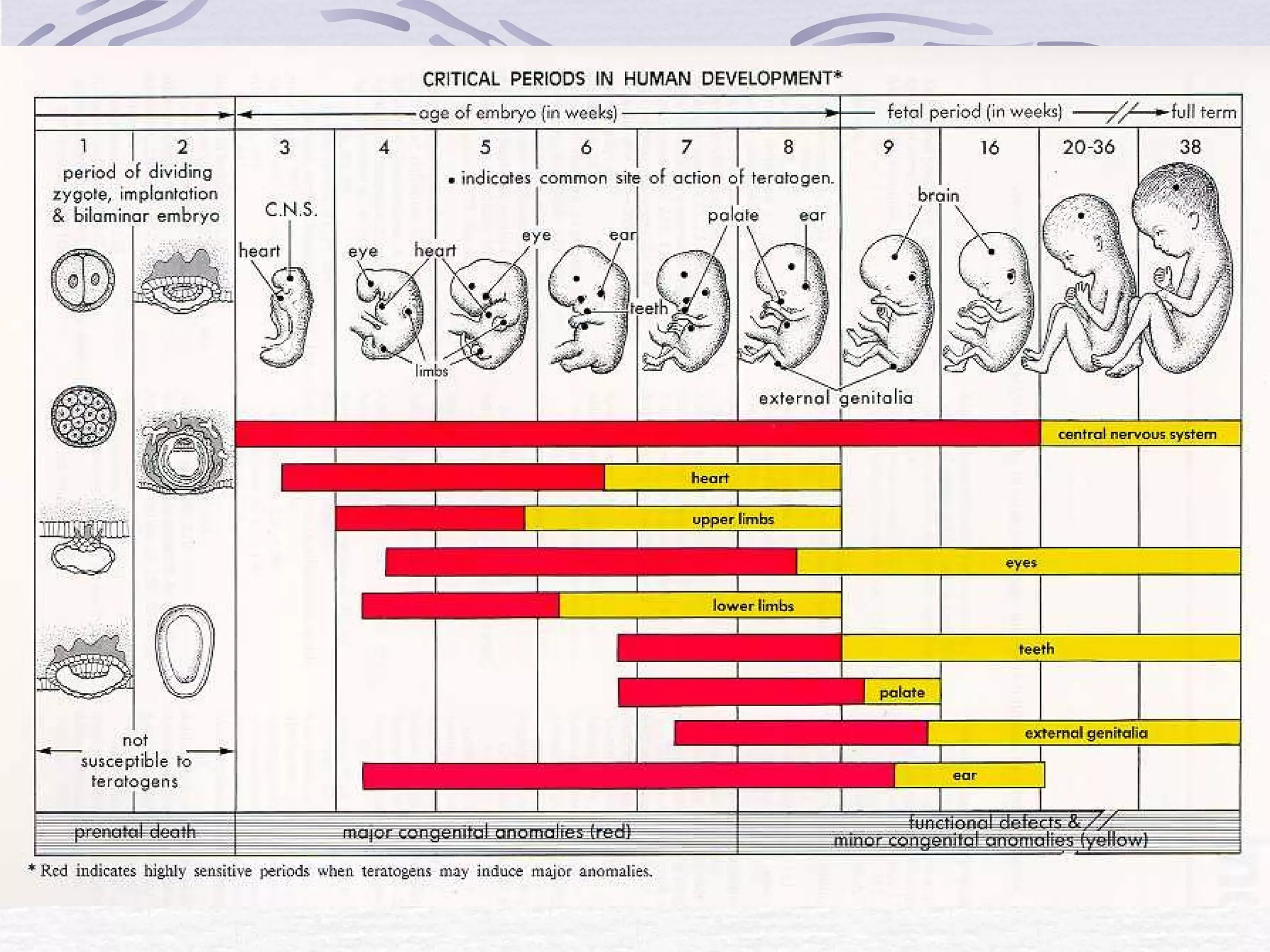
The document discusses human reproduction, examining the differences and similarities in male and female anatomy, the processes of ovulation and sperm production, and the mechanics of conception and birth. It highlights the hormonal control over reproductive functions and explores sexually transmitted infections (STIs), their symptoms, treatments, and preventive measures. The conclusion emphasizes that abstinence is the best method to prevent STIs and that condoms do not offer complete protection against all STIs.