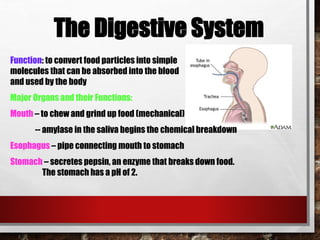
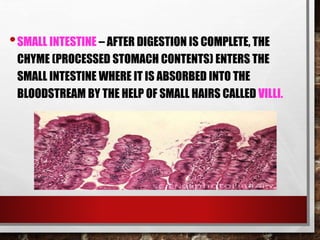
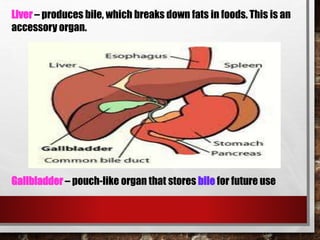
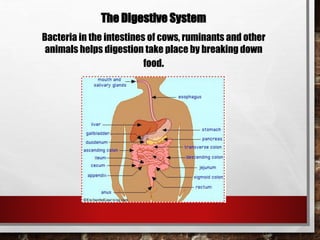
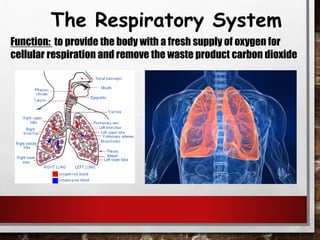
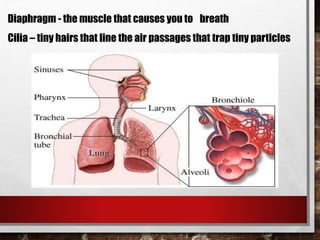
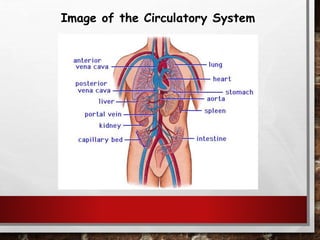
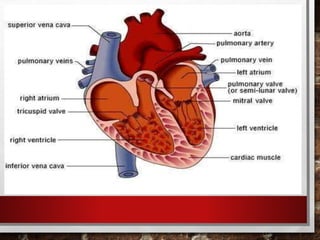
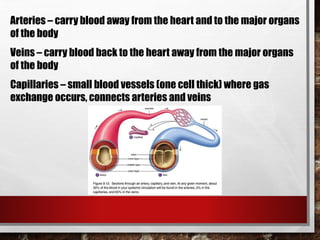
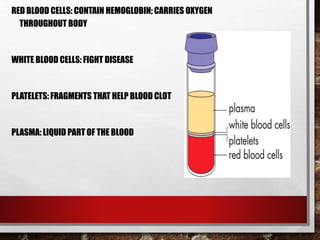
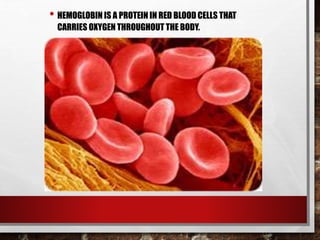
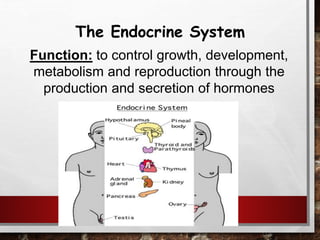
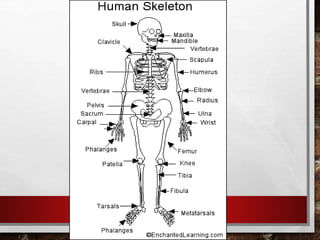
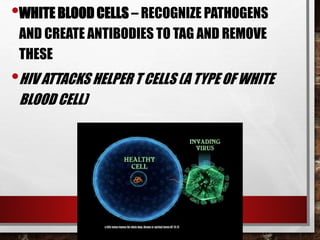
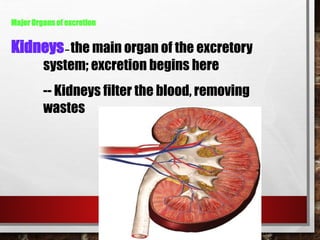
The excretory system relies on the circulatory system to transport waste products from tissues to the kidneys for filtration from the blood. It also works with the integumentary system as sweat glands aid in waste removal through the skin. The digestive system produces waste that