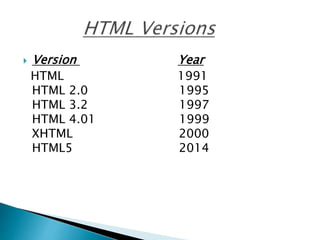
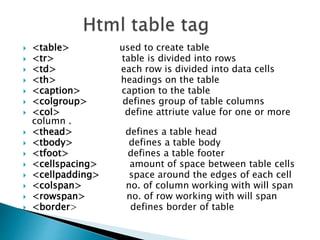
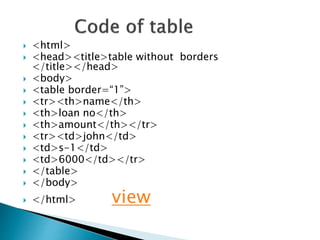
The document provides a comprehensive overview of HTML, including its structure, basic tags, and various versions. It covers elements like headings, text formatting, links, images, tables, and form controls, along with examples for practical understanding. Additionally, it introduces CSS and modern HTML5 elements to enhance web page design.