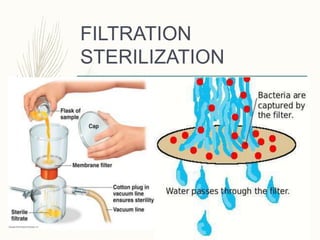
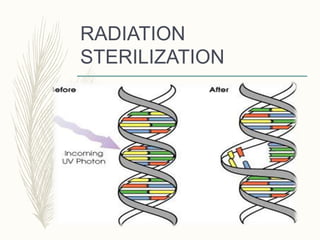
Small volume parenterals are sterile preparations intended for injection that have volumes between 1-30 mL. They include ampules, vials, dry powders, and prefilled syringes. Key considerations for their formulation include using water for injection, appropriate solutes, added substances like antimicrobial agents or antioxidants, and ensuring sterility through various techniques like moist heat sterilization, filtration, or radiation. Their quality must be assured through testing for leaks, sterility, clarity, and presence of pyrogens.