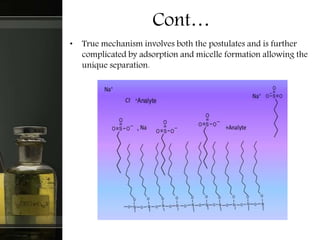
Ion pair chromatography is a reversed-phase liquid chromatography technique used to separate ionized and partly ionized organic compounds. It utilizes reversed-phase columns and mobile phases with an added ion pair reagent that interacts with the analytes to change their retention times. The technique has advantages over ion exchange chromatography like higher efficiency columns and ability to use water-rich mobile phases. It has wide applications in analysis of biomolecules, food, drugs and more.



![lon Pair Reagent
• Added to mobile phase at low concentration (usually
0.05M) and is itself ionized.
• lon pair reagent are molecules containing a hydrophobic
region and an ionizable functioality.
• •One ion of the reagent is retained by the stationary phase
providing the otherwise neutral stationary phase with its
charge.
• •This charged stationary phase can then retain and separate
organic solute ions of the opposite charge by forming a
reversible ion pair complex with the ionized sample.
Example –
RCOO- + R4N+ ---→ [R4N+-OOCR] ion pair](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ion-pairreversedpairliquidchromatography-201020045553/85/Ion-pair-reversed-pair-liquid-chromatography-4-320.jpg)