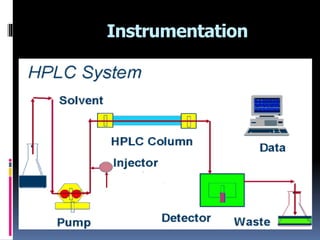
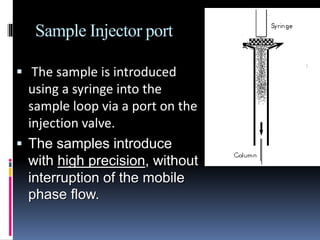
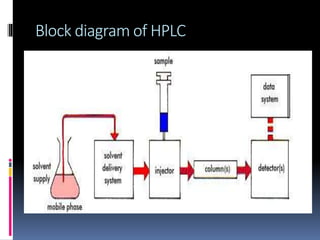
HPLC is an advanced form of liquid chromatography that uses pumps to force a pressurized liquid solvent containing a sample mixture through a column filled with adsorbent material. Each component interacts slightly differently with the adsorbent, leading to separation as components flow out the column at different rates. Key components of an HPLC system include solvent reservoirs, pumps that maintain high pressure, an injector port for samples, a column packed with porous silica or other material, and various detectors to monitor the separated components emerging from the column. HPLC is used to separate, identify, and quantify individual components in a mixture through differential partitioning between a mobile and stationary phase under high pressure.