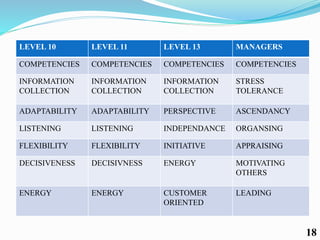
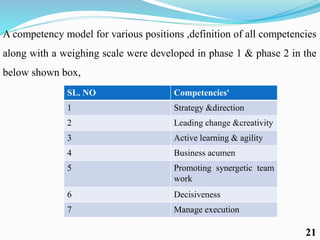
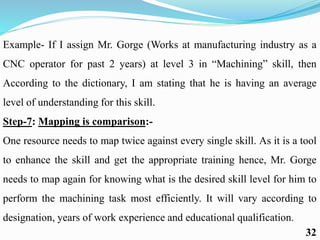
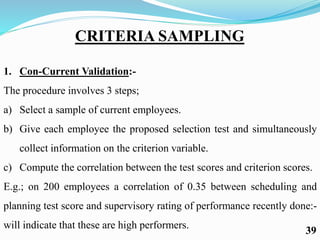
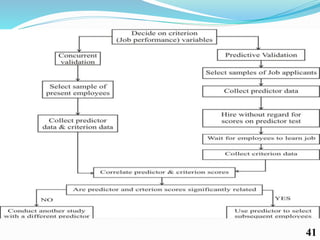
Competency mapping is a systematic process that identifies and evaluates key competencies necessary for employees to perform jobs effectively. It involves understanding behaviors, skills, knowledge, and other traits that contribute to successful performance. Various methods such as interviews, assessment centers, and psychometric tests are used to assess competencies and align them with organizational goals.