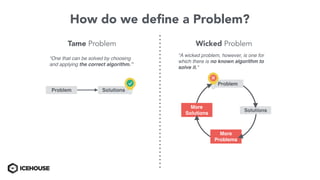
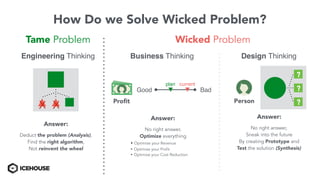
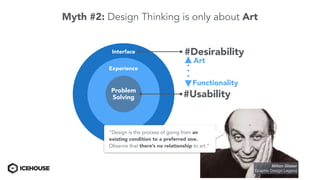
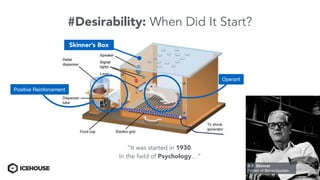
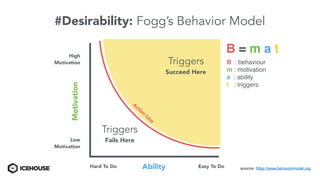
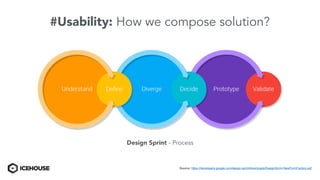
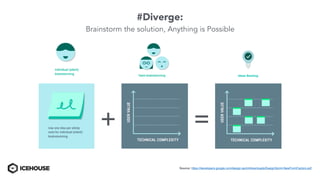
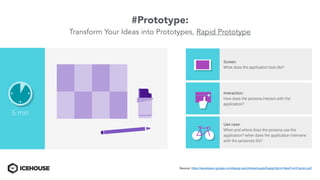
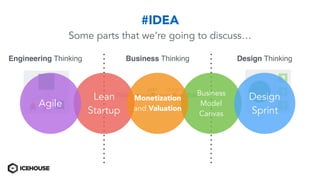
The document discusses solving "wicked problems" using a human-centric approach like design thinking. It explains that wicked problems have no clear solution and their understanding evolves over time as potential solutions are tested. In contrast, "tame problems" can be solved through deductive reasoning and established algorithms. The document then outlines design thinking techniques like defining user personas, brainstorming solutions, rapid prototyping, and validating ideas with users to iteratively understand and address wicked problems. It proposes an "Ice House Design Dojo" workshop series bringing together different thinking approaches to solve challenges.