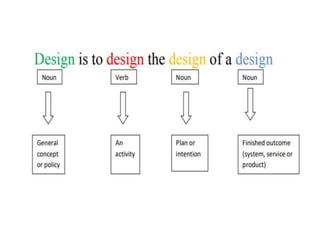
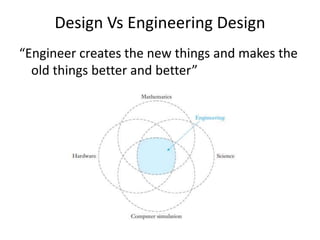
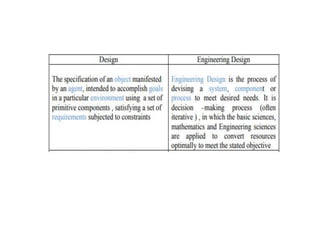
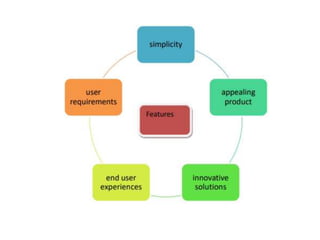
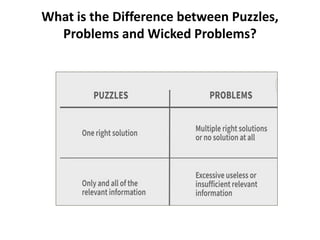
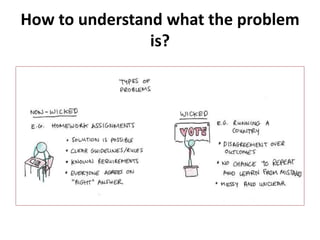
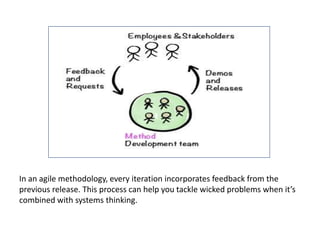
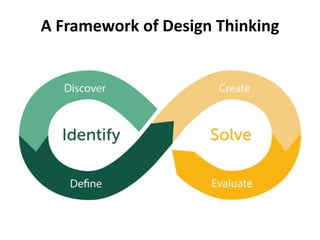
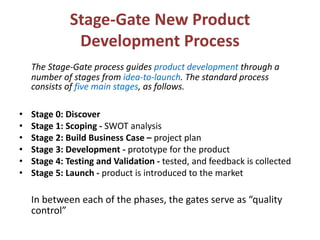
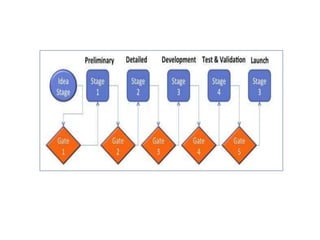
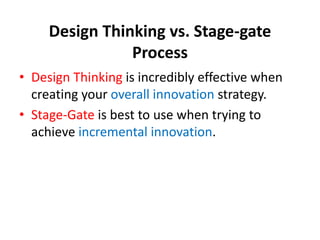
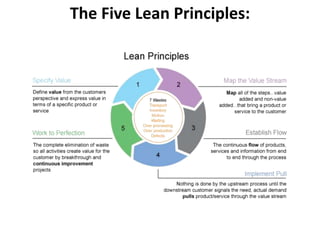
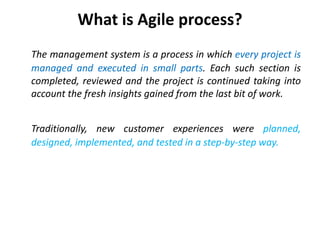
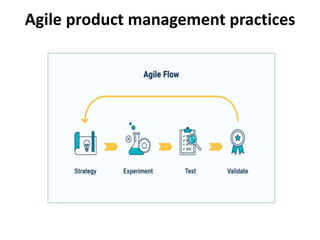
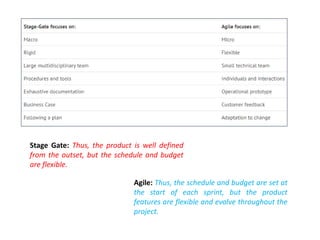
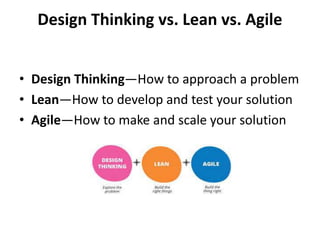
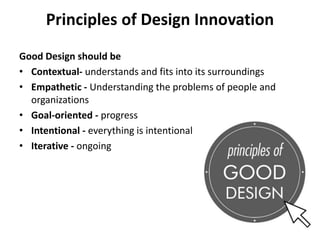
The document provides an extensive overview of design thinking, highlighting its role as a systematic and collaborative approach to problem identification and creative solution development. It contrasts design thinking with engineering and methodologies like agile and lean, emphasizing its iterative nature and focus on user-centered solutions to complex 'wicked problems.' Additionally, it outlines the phases of design thinking and its applications in new product development, underscoring the benefits of combining various methodologies for effective problem-solving.