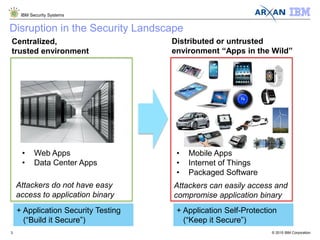
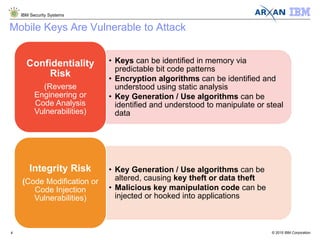
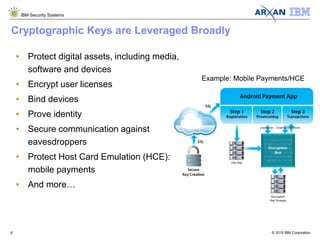
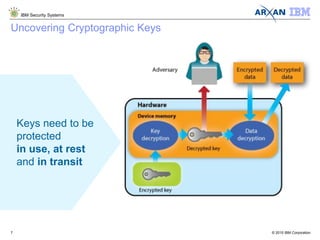
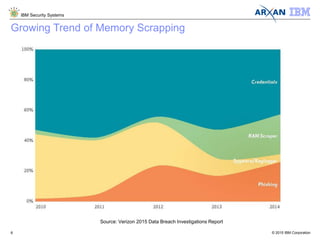
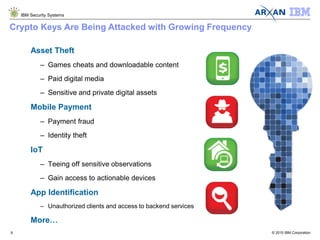
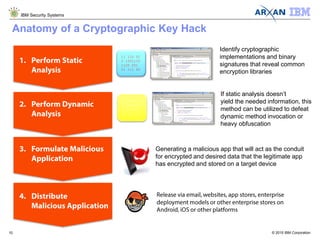
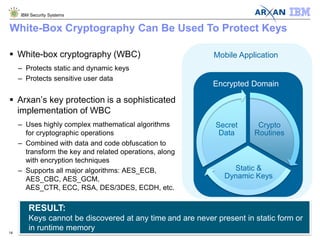
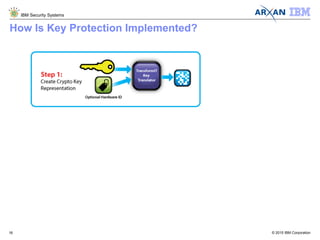
The document discusses the vulnerabilities associated with cryptographic keys, detailing methods of key theft through static and dynamic analysis. It emphasizes the growing frequency of attacks on cryptographic keys and outlines ways to mitigate these risks using advanced protection techniques like white-box cryptography. Furthermore, it promotes Arxan's key protection solutions integrated with IBM's security offerings to safeguard sensitive data against such threats.