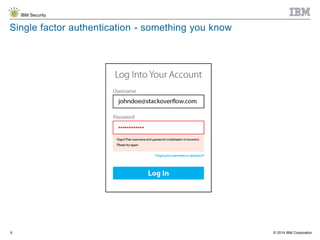
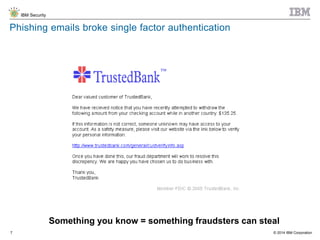
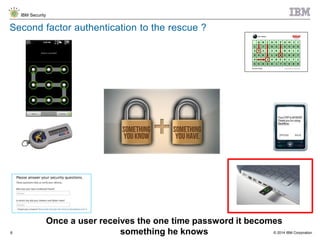
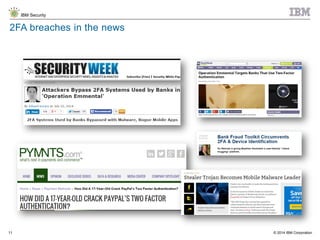
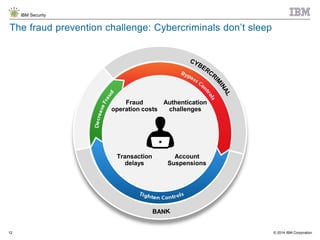
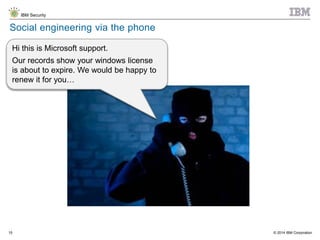
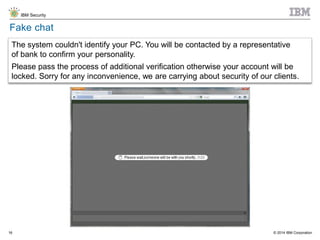
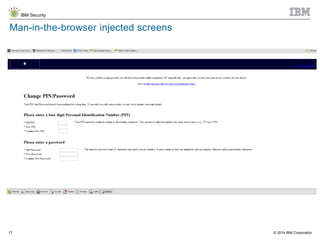
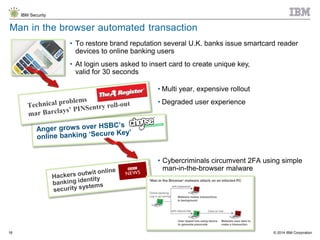
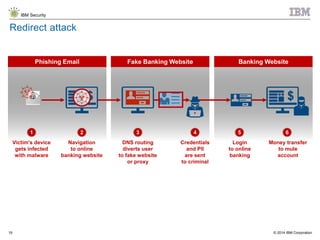
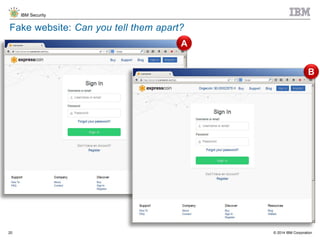
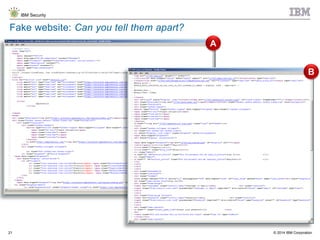
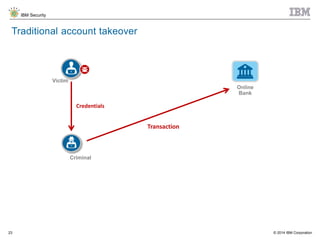
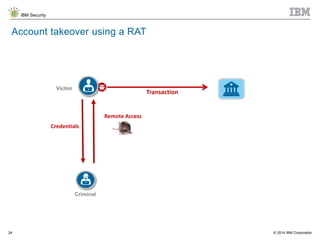
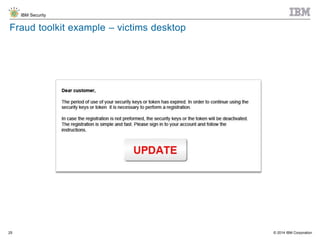
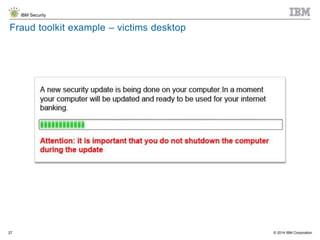
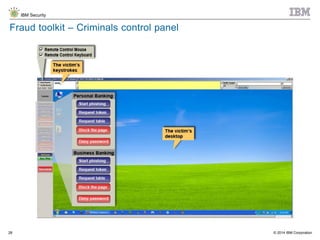
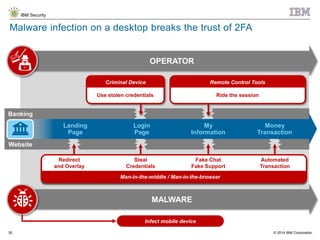
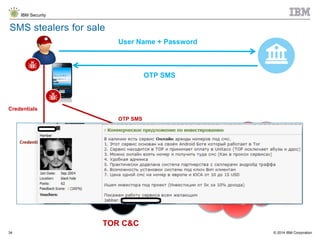
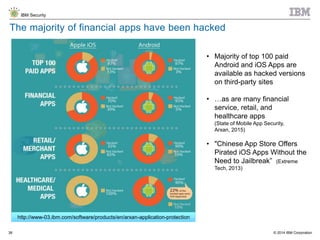
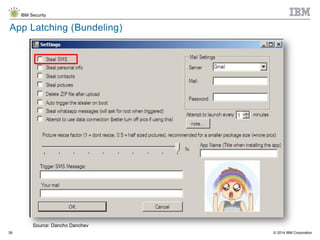
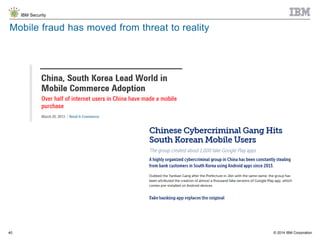
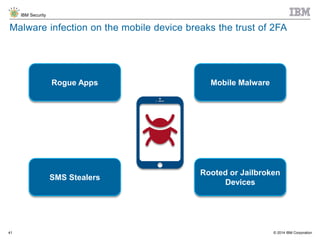
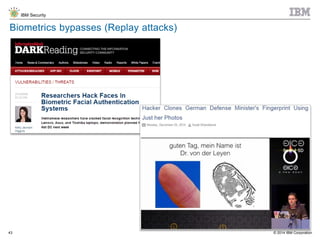
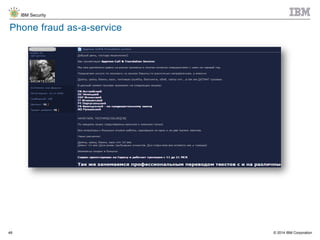
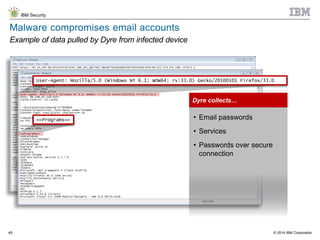
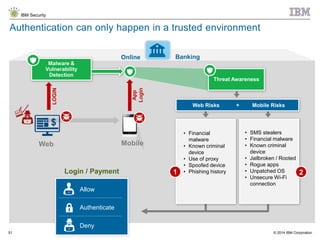
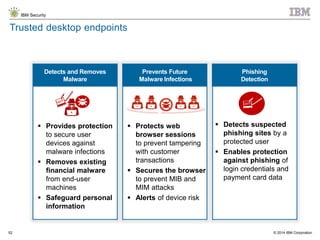
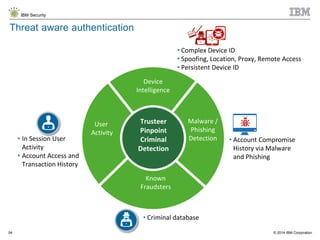
The document discusses the challenges of two-factor authentication (2FA) evasion techniques employed by cybercriminals, including various bypass methods such as social engineering, malware, and mobile vulnerabilities. It highlights the evolving threats to user trust, particularly in online banking, and emphasizes the need for robust authentication processes to combat these risks. Additionally, it addresses the limitations of current 2FA methods and the ongoing adaptation of fraud tactics in response to security measures.