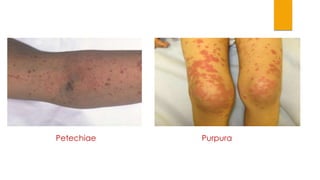
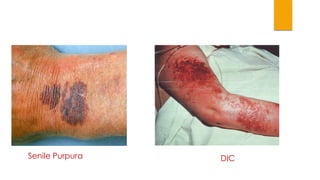
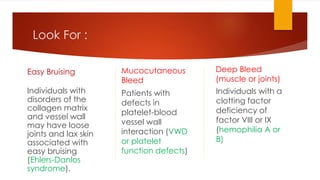
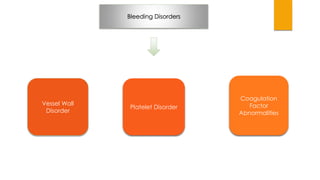
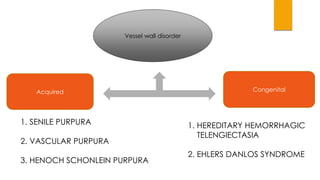
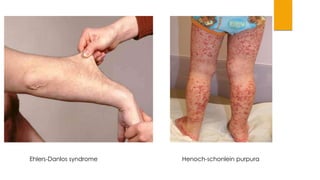
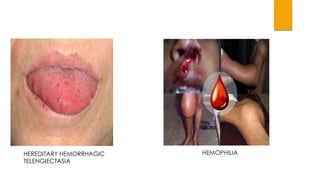
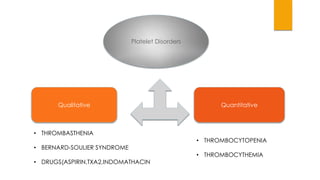
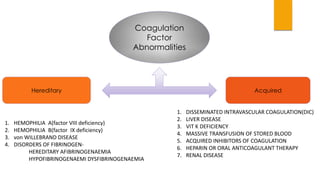
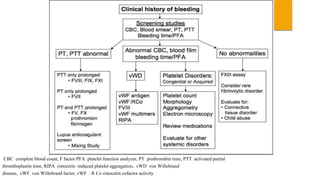
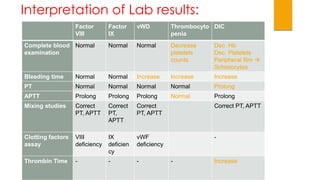
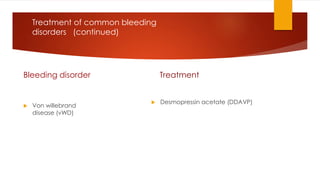
This document provides guidance on evaluating and treating children with bleeding disorders. It outlines the key steps in the clinical approach: obtaining a medical history, conducting a physical exam, and ordering laboratory tests. Common inherited disorders include hemophilia A/B and von Willebrand disease, while acquired disorders include DIC and vitamin K deficiency. Based on the history and exam findings, specific laboratory tests are interpreted to identify coagulation factor deficiencies or other causes of bleeding. Common treatments target the underlying disorder, such as intravenous immunoglobulins for ITP or DDAVP for von Willebrand disease.