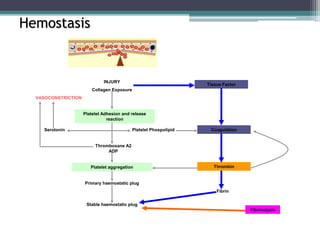
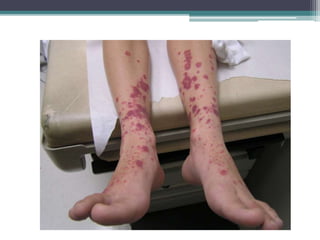
This document discusses causes and clinical features of bleeding in neonates and children. It covers etiologies such as coagulation disorders like hemophilia, platelet dysfunction including inherited conditions, thrombocytopenia due to various causes, and vascular disorders. Clinical features are described separately for neonates, which can include oozing from umbilical stump or bleeding from procedures, and for others, such as mucosal or joint bleeding, petechiae, or menorrhagia. Distinguishing features between platelet and coagulation disorders are also provided.