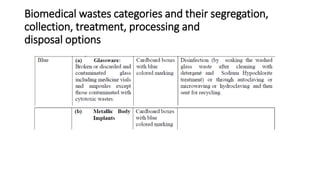
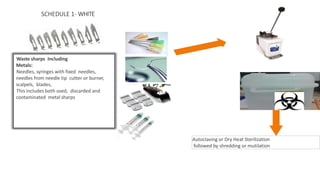
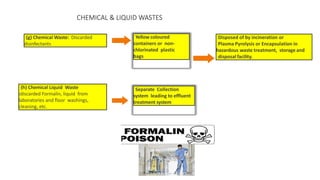
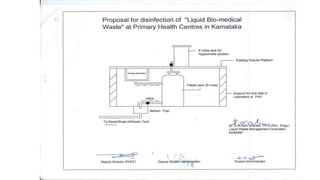
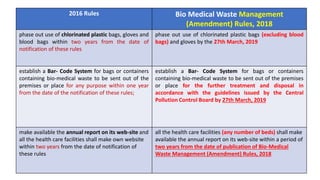
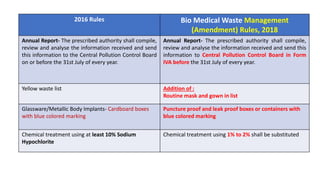
The document summarizes the key aspects of the Biomedical Waste Management Rules 2016 and its 2018 amendment in India. It defines biomedical waste and explains the importance of proper management. It outlines the classification of waste into 4 color-coded categories and their treatment and disposal options. It describes the steps of waste segregation, collection, transportation, and disposal. It highlights some major changes introduced in the 2018 amendment like phasing out of chlorinated plastic and establishing a barcode system.