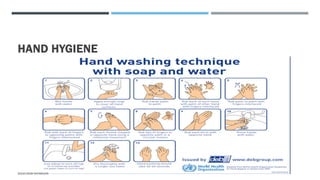
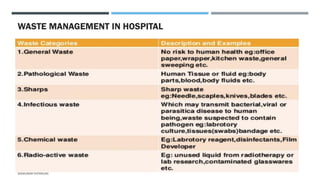
A hospital porter plays a crucial role in patient care and the operations of a hospital by transporting patients, handling medical equipment, and maintaining cleanliness. Essential skills include good interpersonal communication, physical fitness, and emotional resilience, while duties encompass moving medical supplies, assisting healthcare professionals, and managing waste disposal. Proper hygiene and safety protocols, especially regarding hazardous waste, are paramount in their responsibilities.