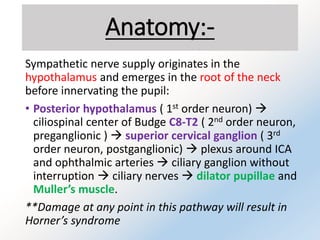
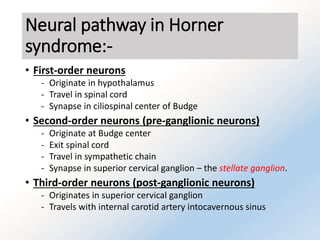
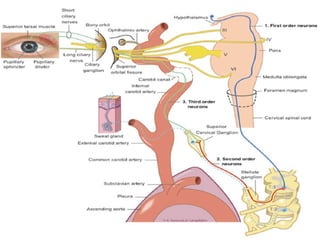
Horner syndrome results from disruption of the sympathetic nerve supply to the eye. It is characterized by three key signs: ptosis, miosis, and anhidrosis. The syndrome can be classified based on where along the sympathetic pathway the disruption occurs. Testing involves confirming the diagnosis with apraclonidine, which causes reversal of miosis and ptosis in denervated eyes. Investigations depend on classification and may include imaging of the brain, cervical spine, chest, or neck vessels to identify underlying causes.