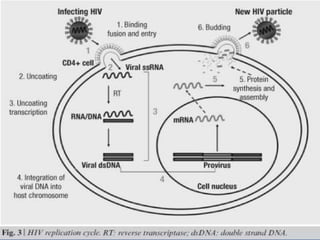
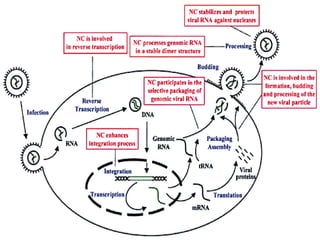
The document outlines national guidelines for antiretroviral therapy (ART) in India. It notes that India has the third highest number of people living with HIV globally. The goals of ART are to improve quality of life, reduce HIV-related illness and mortality, and suppress viral load. People are recommended to start ART if their CD4 count is below 350 or if they have WHO Stage 3 or 4 disease. First-line ART regimens typically include two nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors and one non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor. Patients are monitored regularly after starting ART to assess clinical status, adherence, and CD4 count. Treatment is changed if adverse effects occur, if treatment fails to suppress viral load