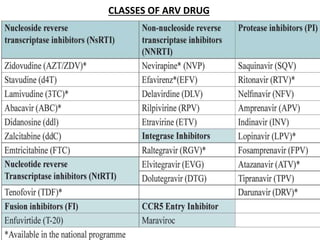
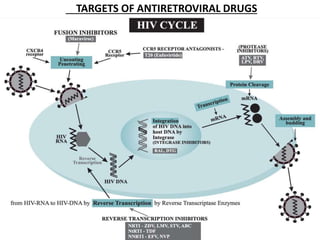
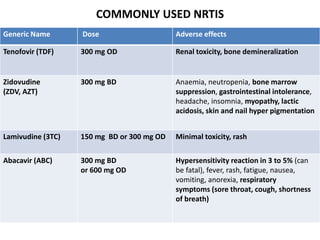
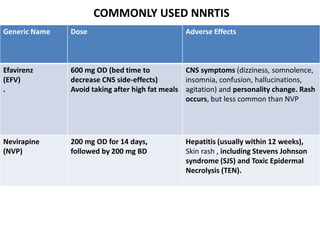
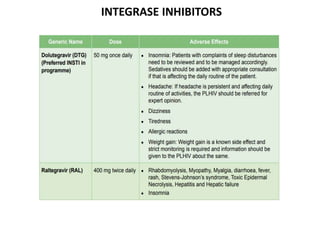
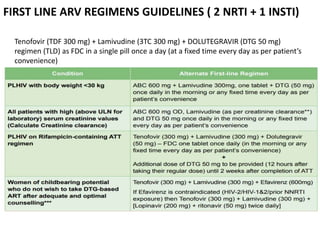
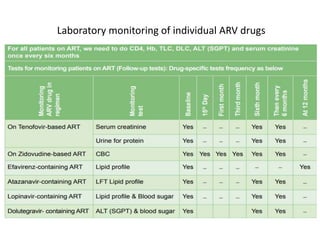
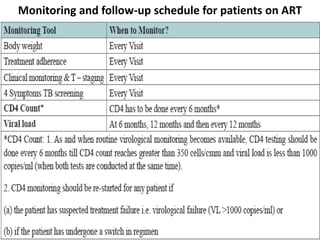
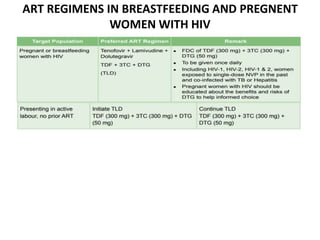
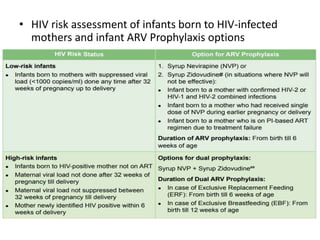
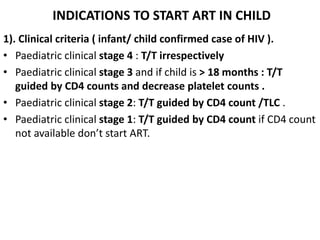
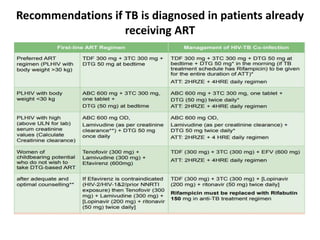
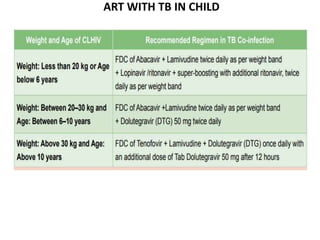
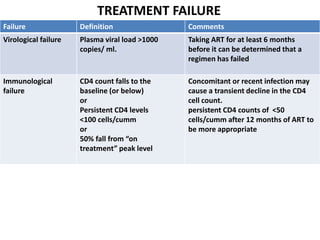
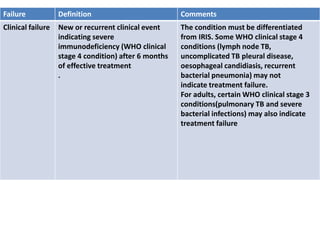
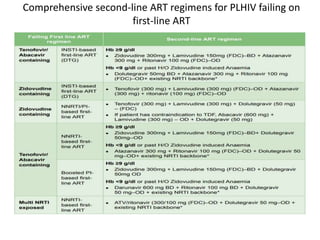
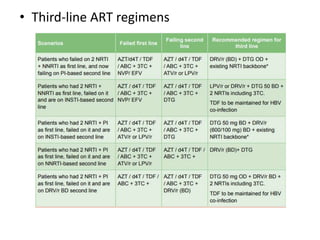
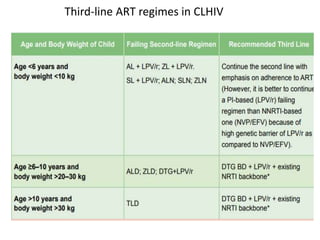
HAART, or highly active antiretroviral therapy, involves using a combination of antiretroviral drugs to treat HIV. The goals of ART include increased survival, improved quality of life, reduction of viral load, immune reconstitution, and limiting drug toxicity while maintaining treatment options and adherence. Commonly used drug classes include NRTIs, NNRTIs, integrase inhibitors, and protease inhibitors. Treatment involves monitoring viral load, CD4 count, adverse effects, and potential treatment failure or immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. Guidelines provide recommendations on treatment initiation and first, second, and third-line regimens for both adults and children.