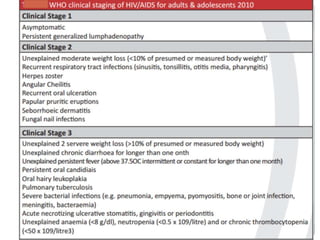
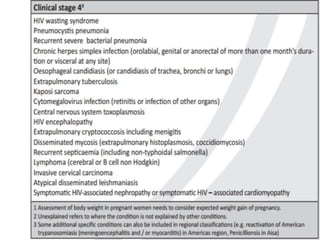
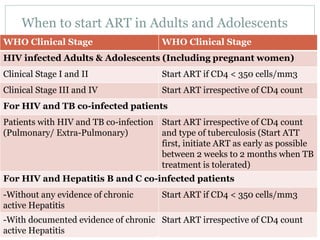
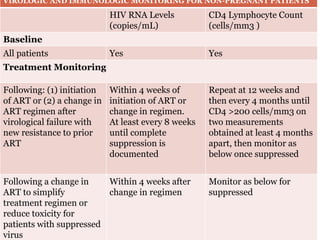
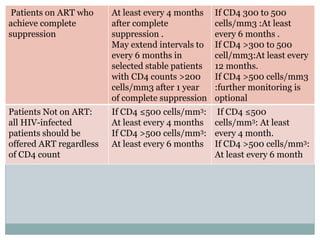
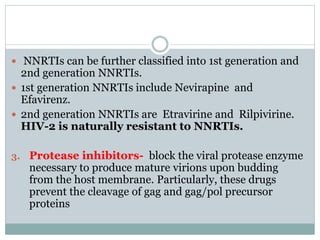
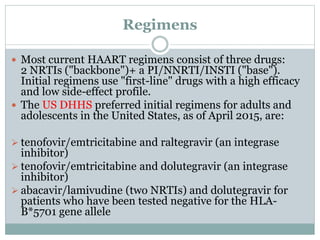
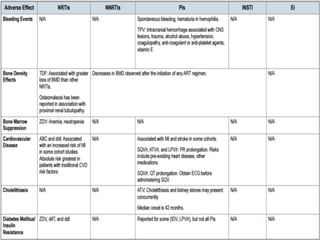
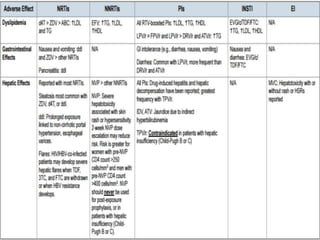
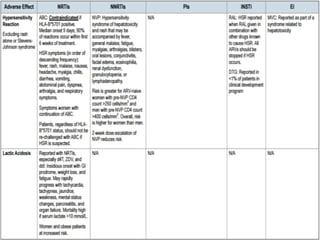
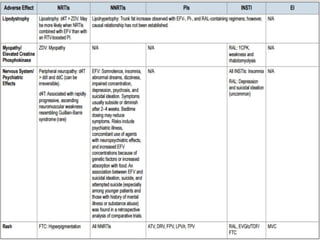
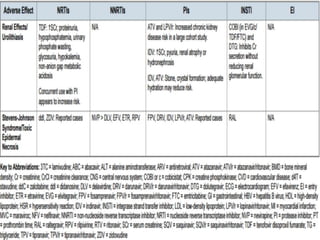
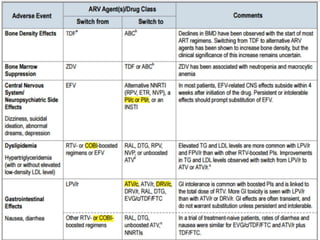
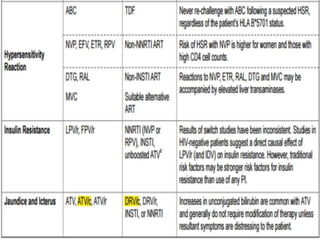
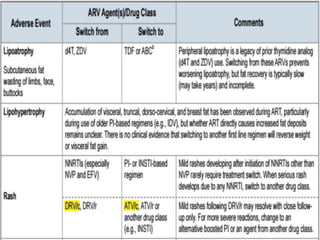
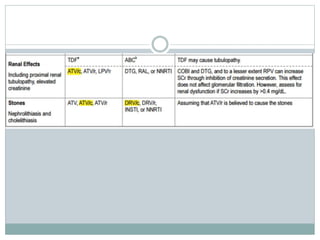
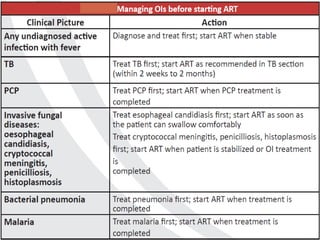
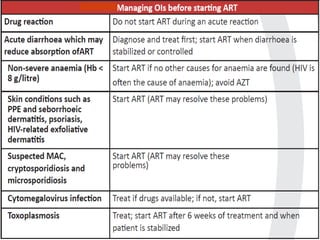
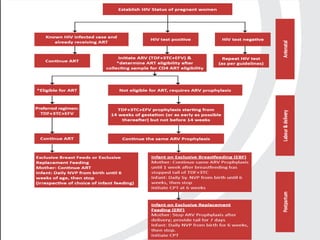
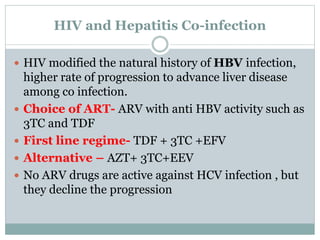
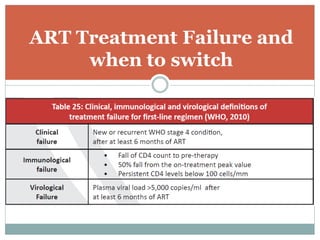
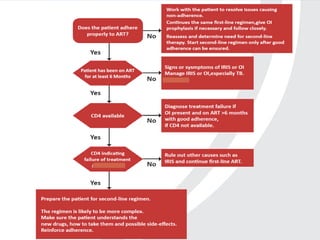
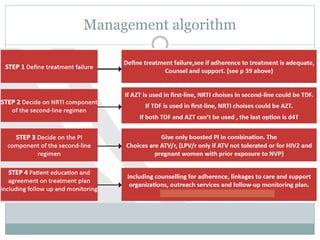
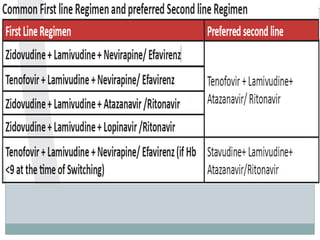
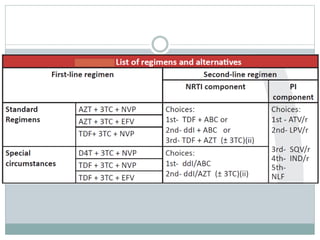
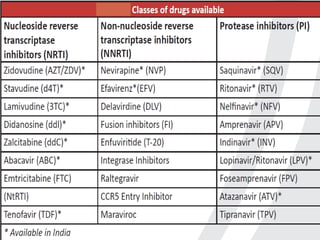
Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART) involves using a combination of at least three antiretroviral drugs to suppress the HIV virus and stop the progression of HIV disease. HAART decreases the viral load, improves immune function, and prevents opportunistic infections. The goals of HAART are to prolong life, improve quality of life, achieve maximal viral suppression, restore immune function, reduce HIV transmission, and rationally sequence drugs to limit toxicity while maintaining treatment options. Current guidelines recommend starting ART for all individuals regardless of CD4 count. Second line regimens are recommended when clinical or immunological failure occurs on first line therapy. Managing adverse events and comorbidities like hepatitis co-infection is also