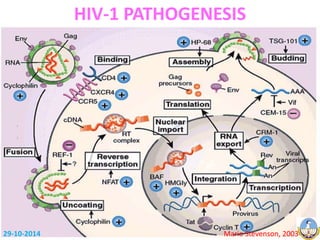
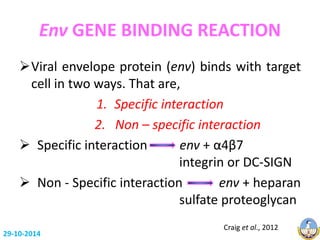
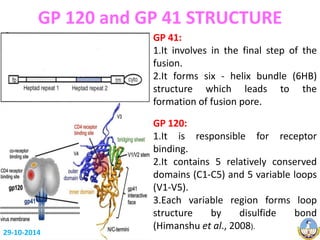
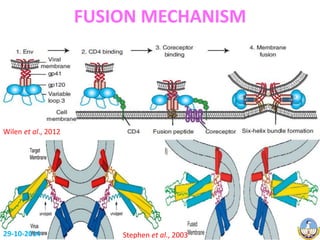
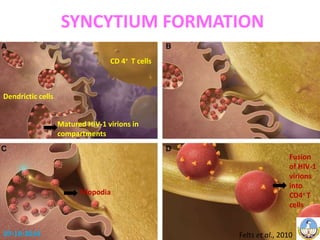
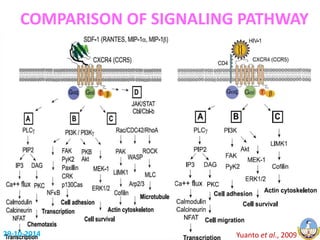
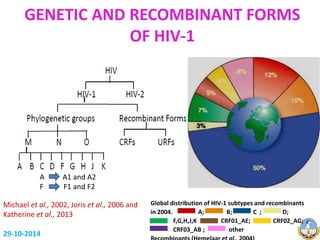
This document summarizes HIV-1 pathogenesis with a focus on genetic forms. It discusses how HIV-1 enters cells through envelope protein binding and membrane fusion. The virus infects CD4+ T cells and dendritic cells, forming syncytia. It describes the structure and roles of the envelope glycoproteins GP120 and GP41 in fusion. The document also outlines the major genetic subtypes and recombinants of HIV-1 globally. It concludes that HIV-1's high genetic variability poses challenges for vaccine and drug development.