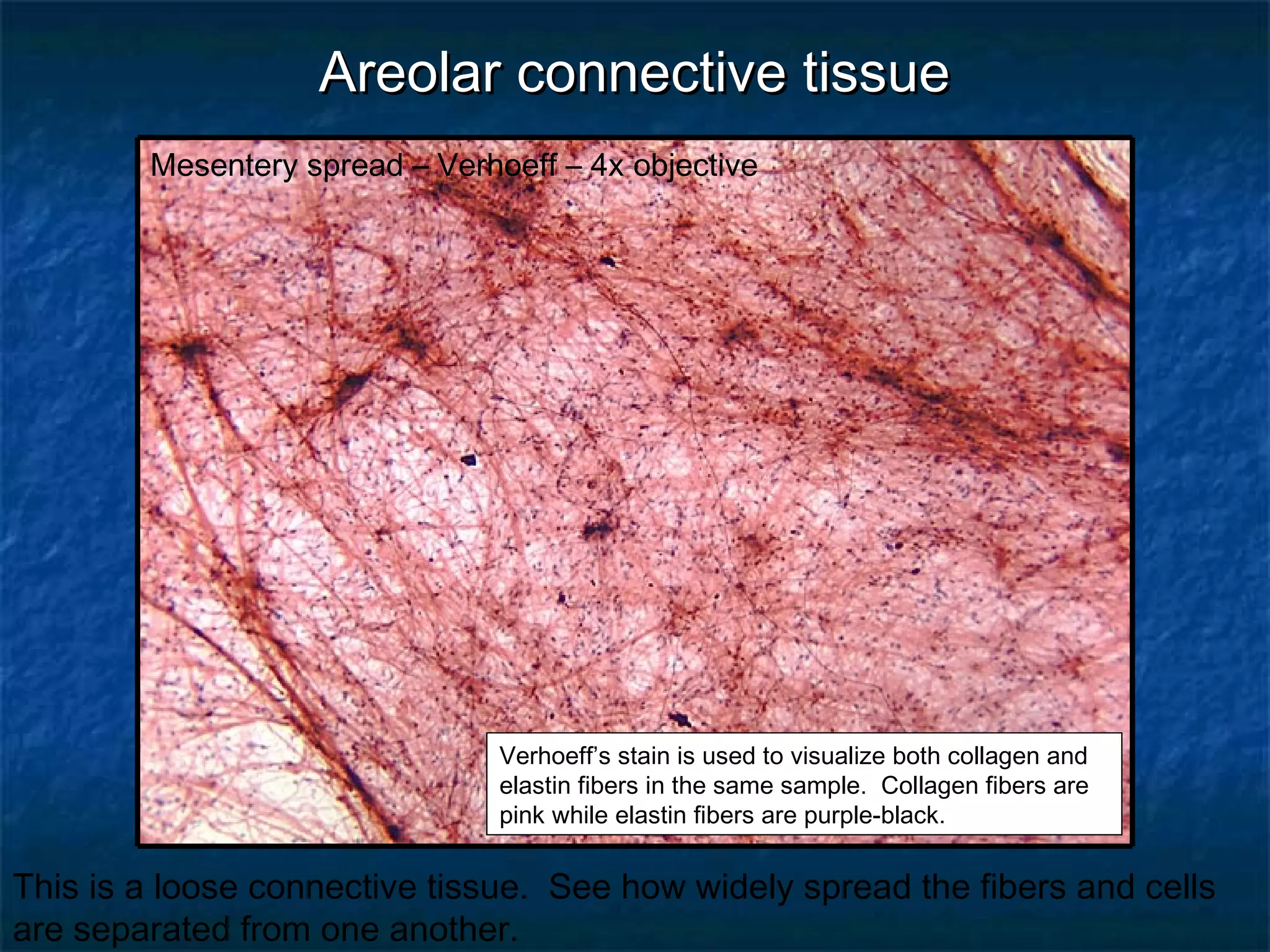
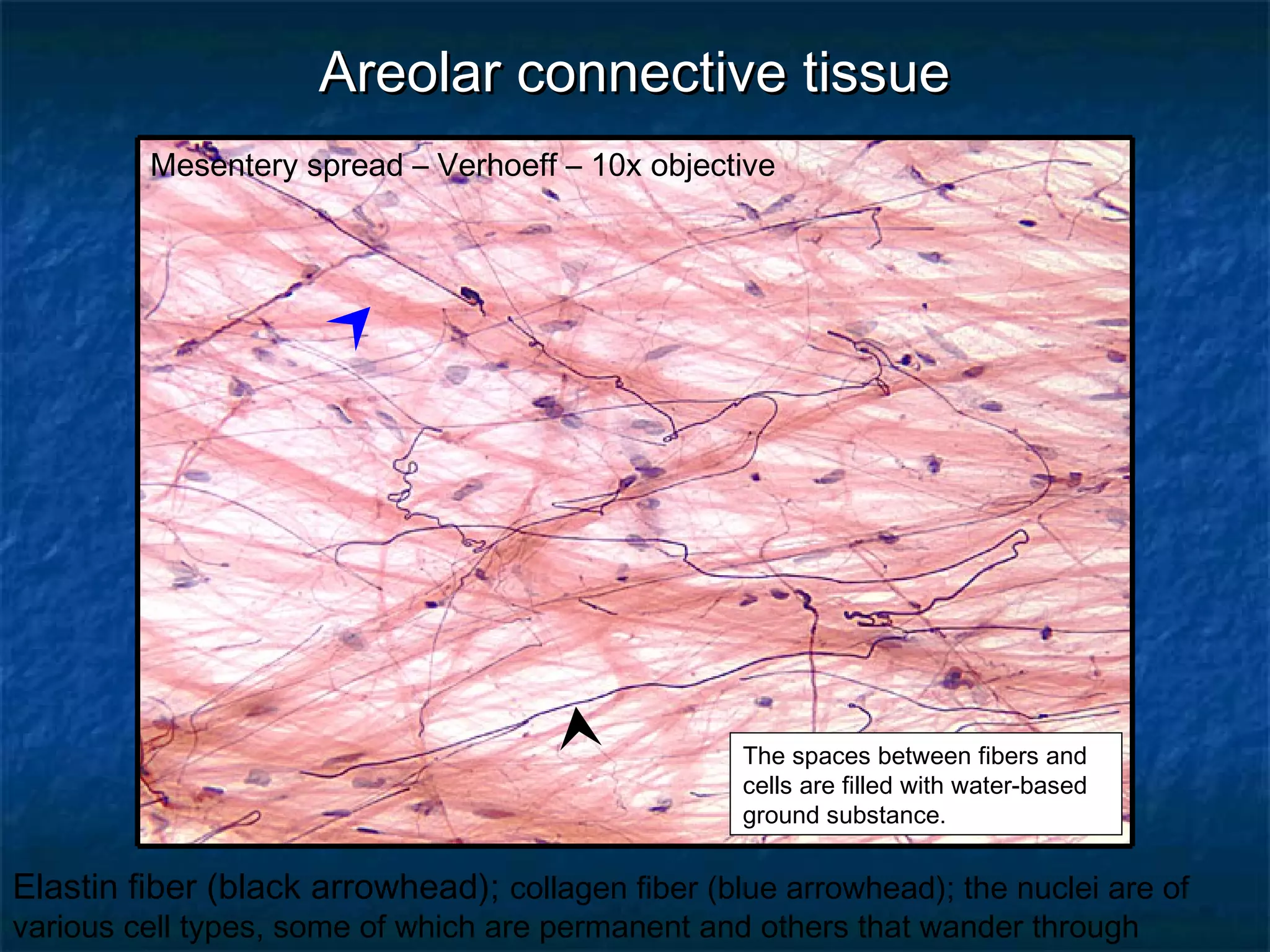
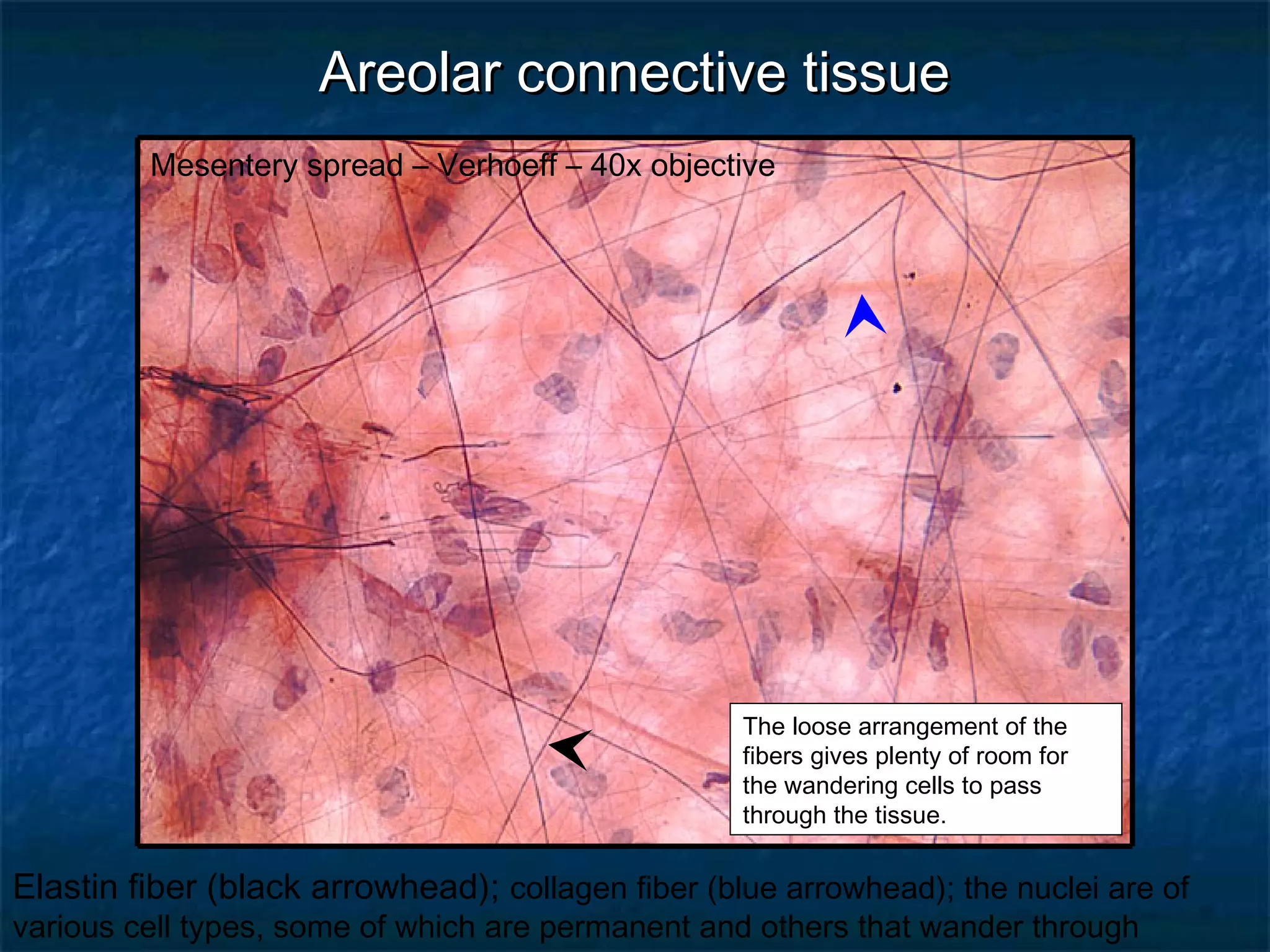
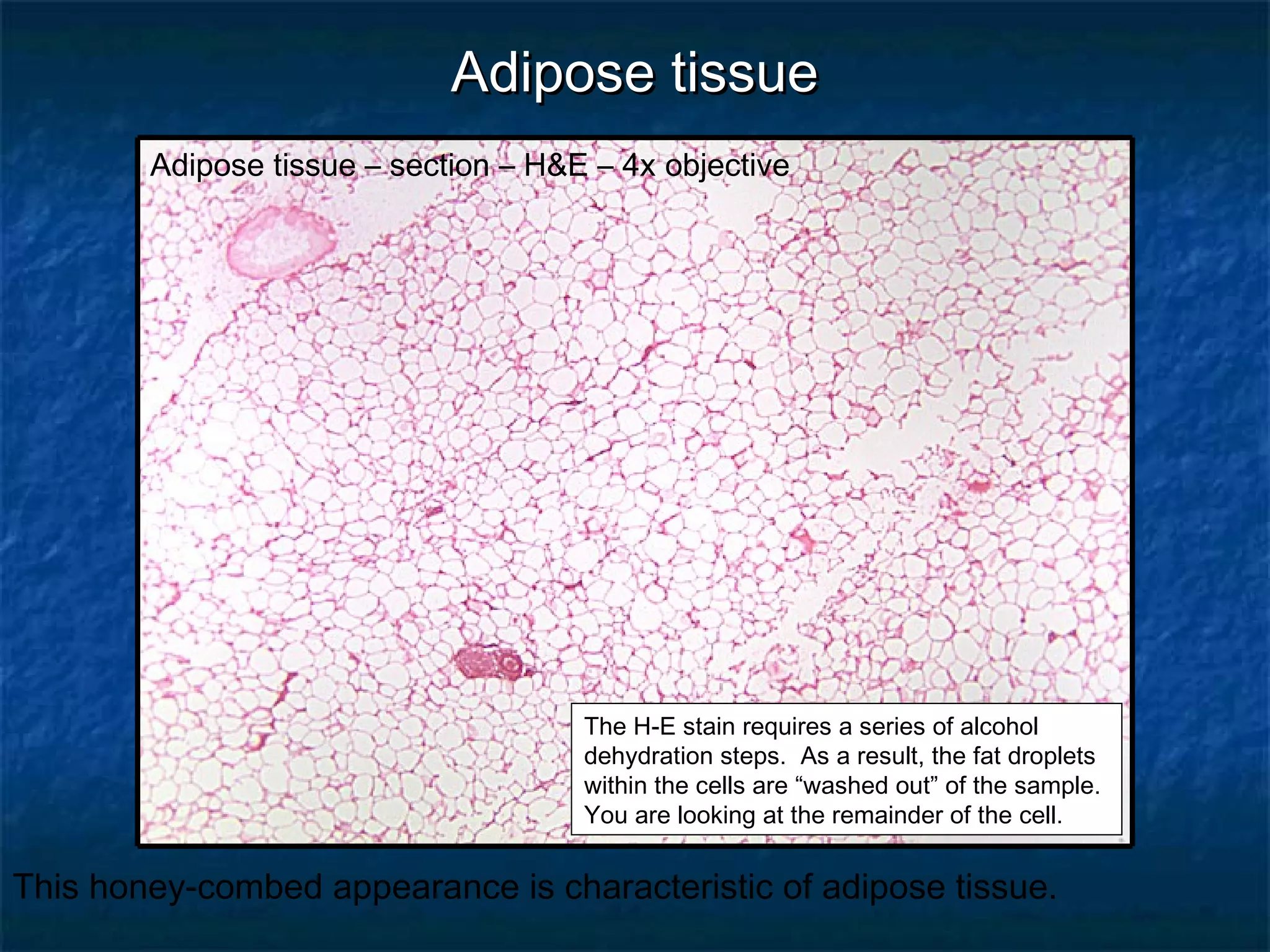
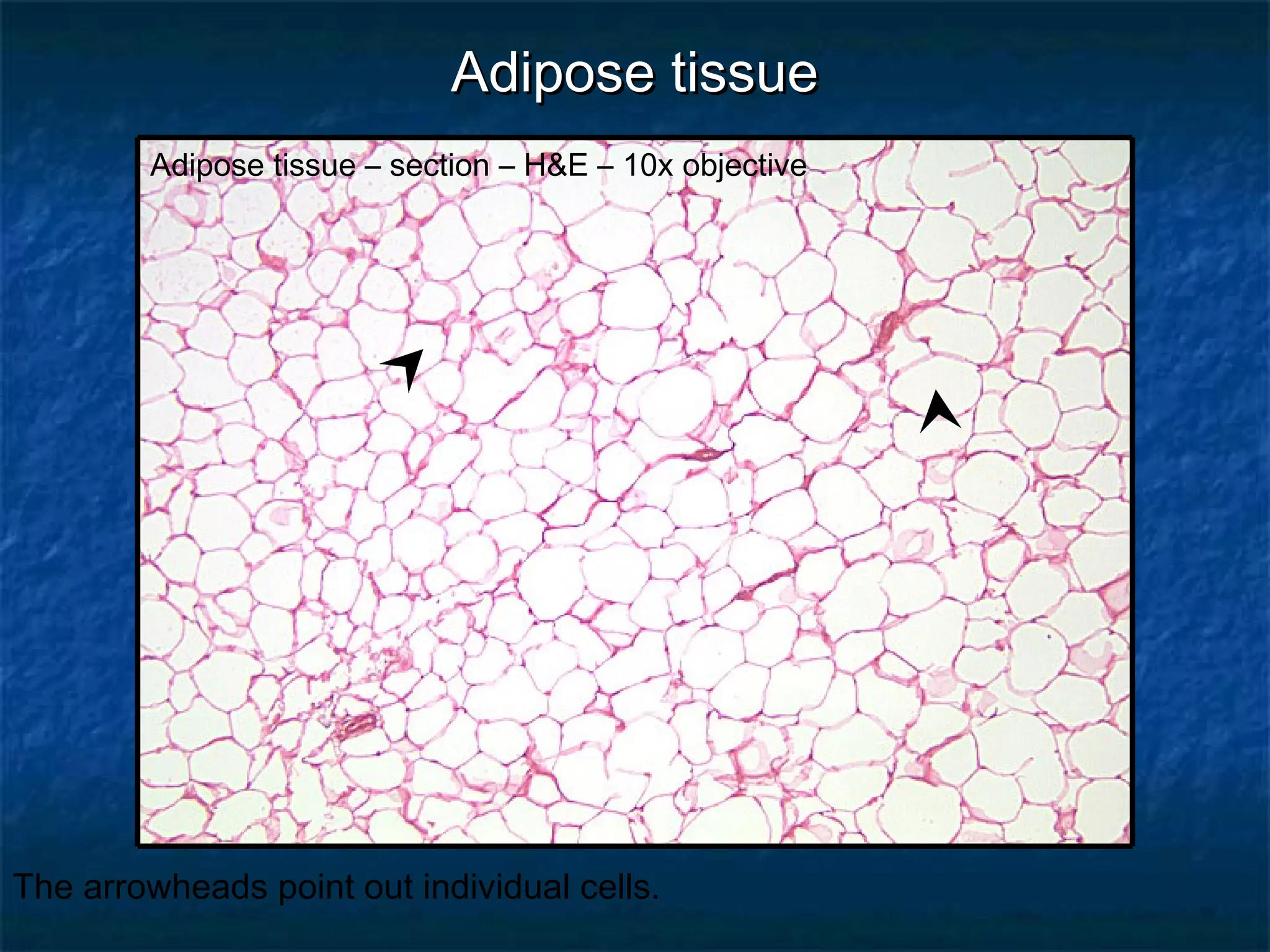
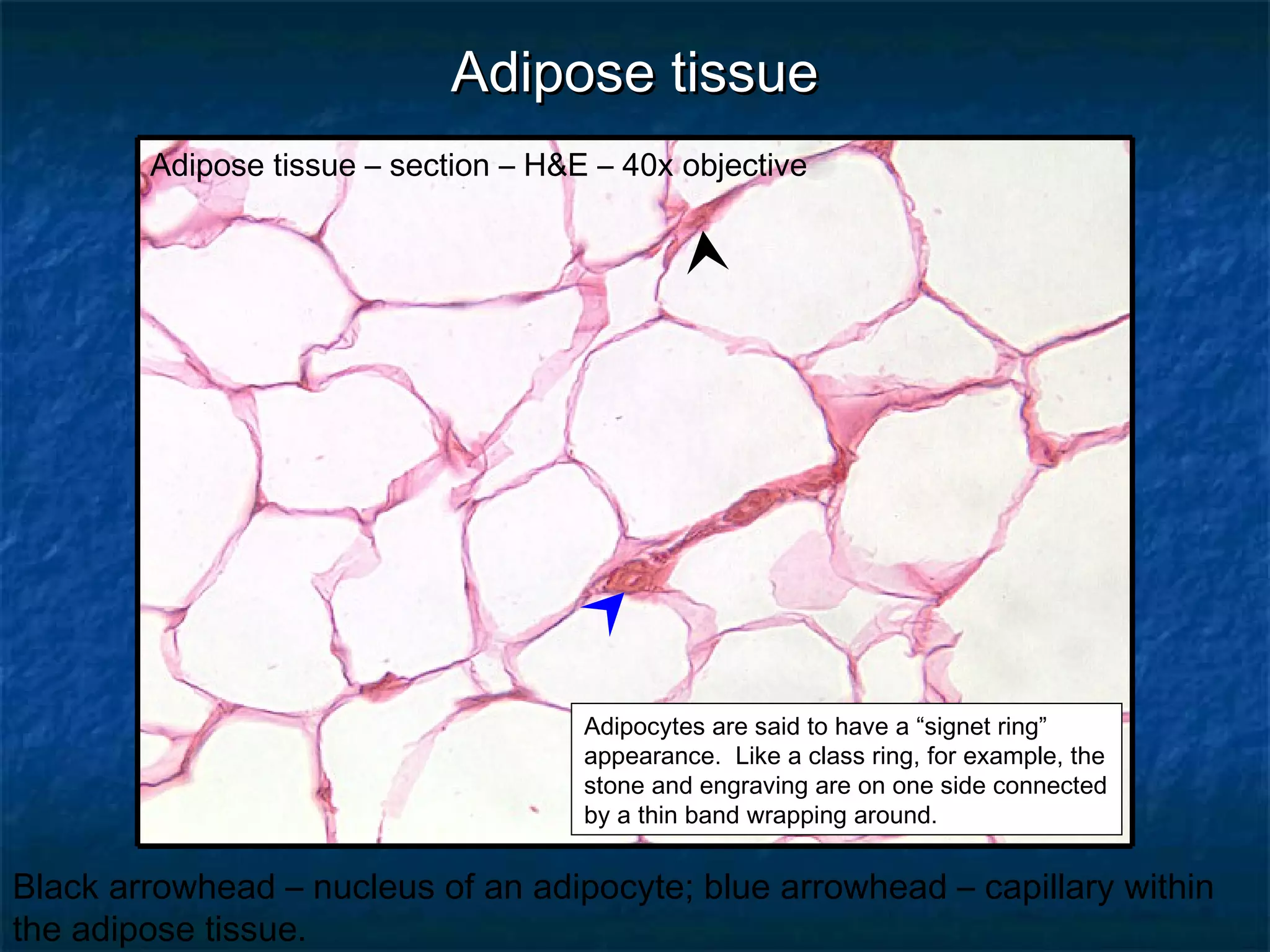
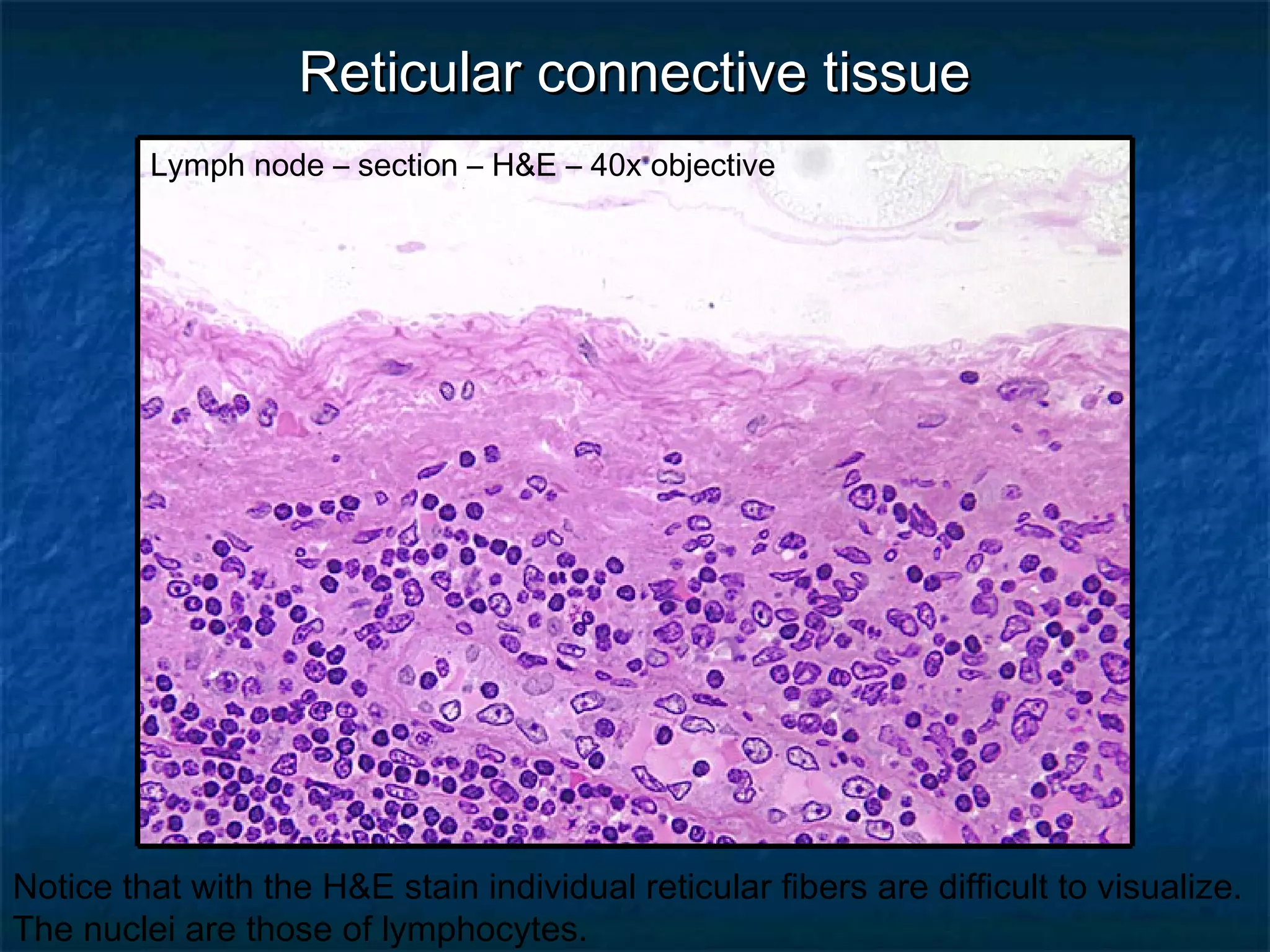
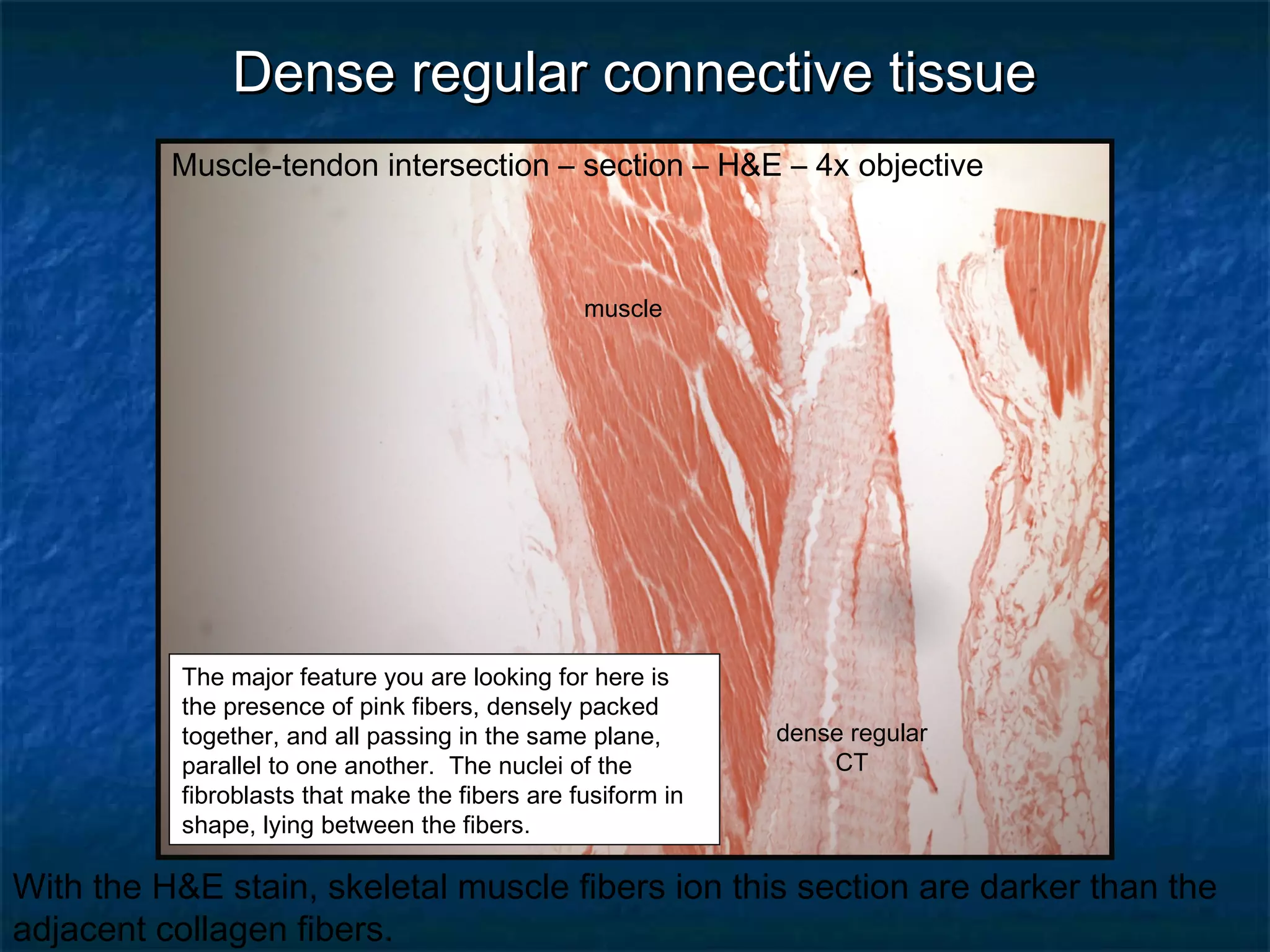
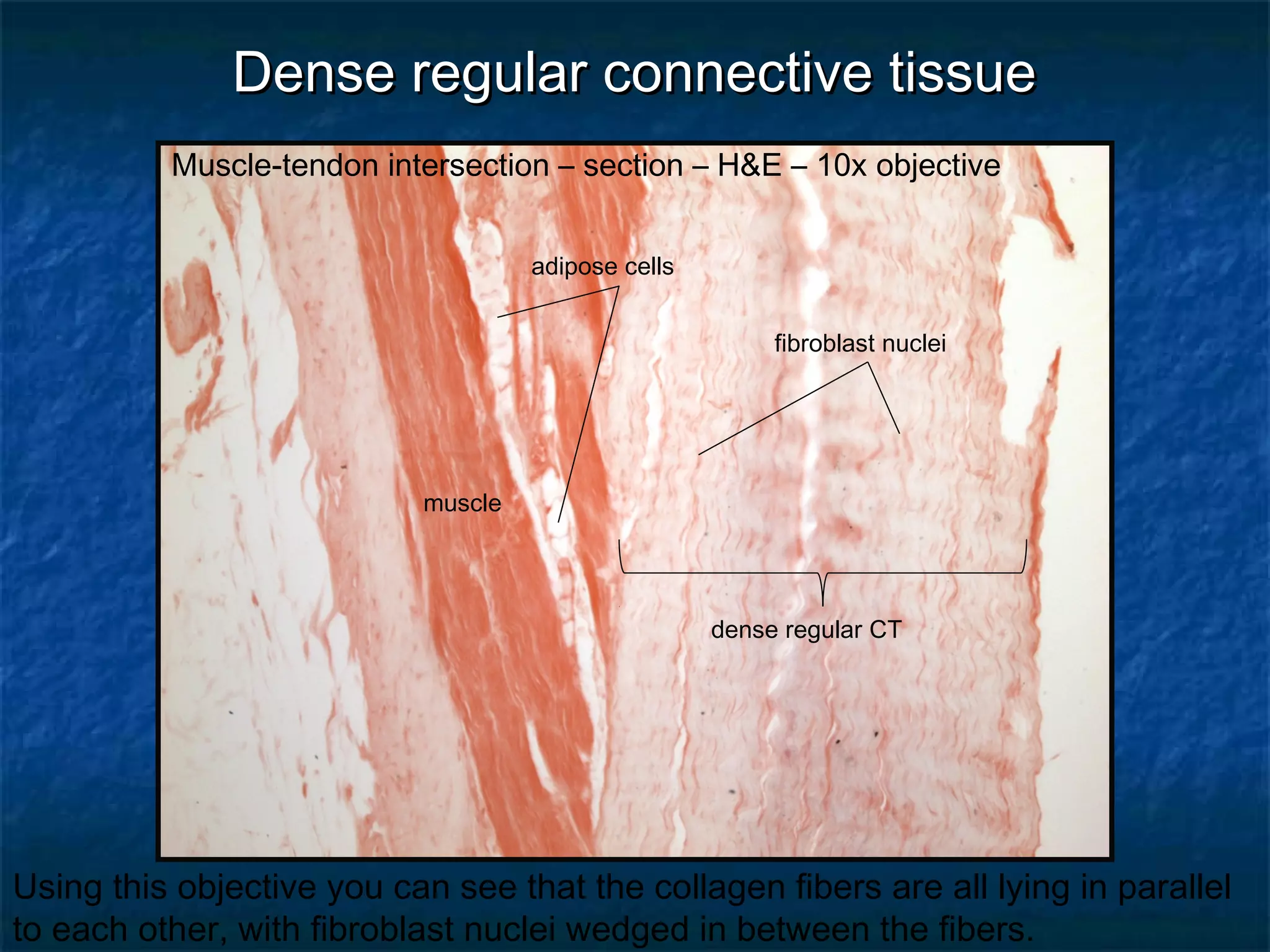
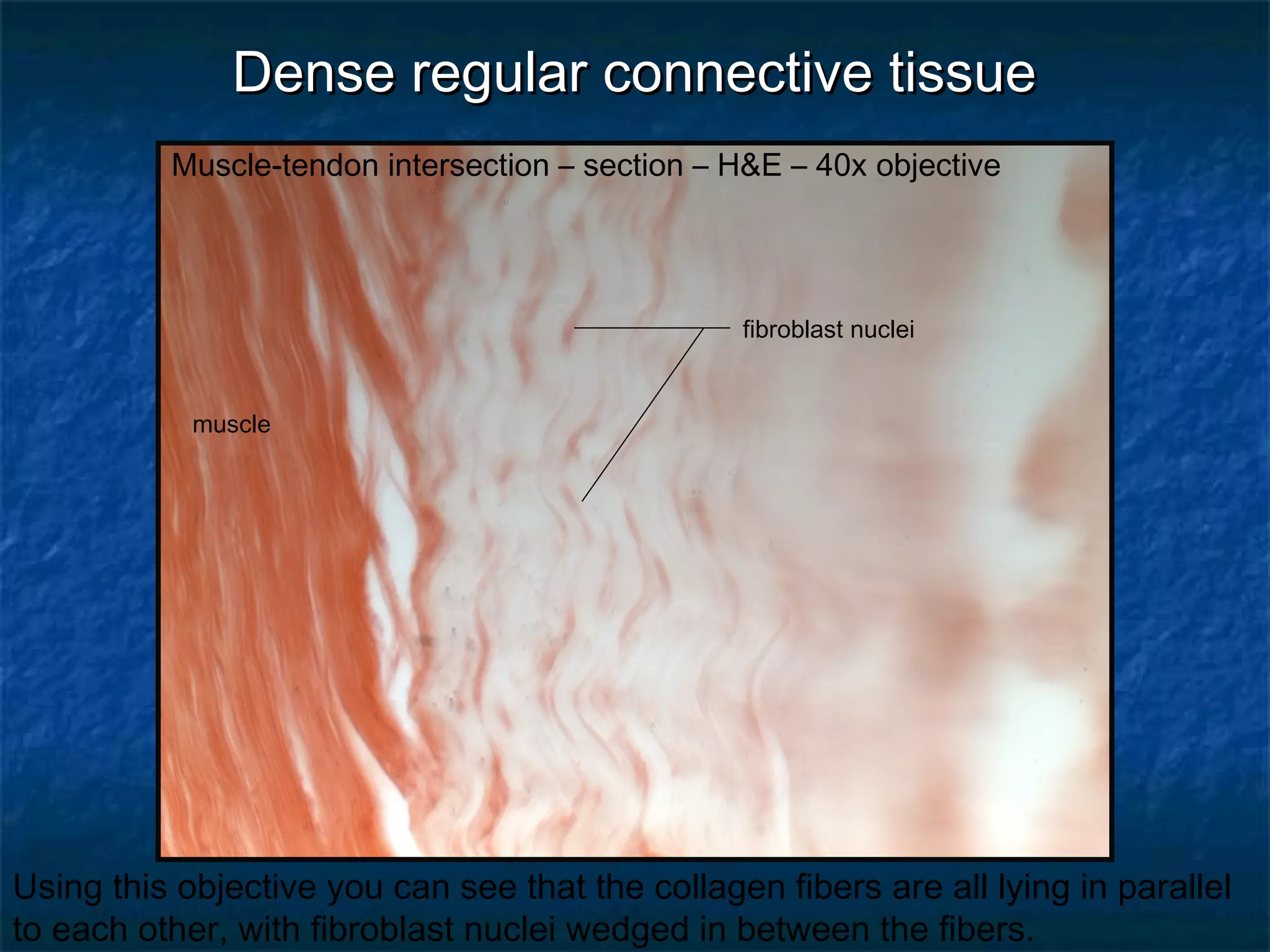
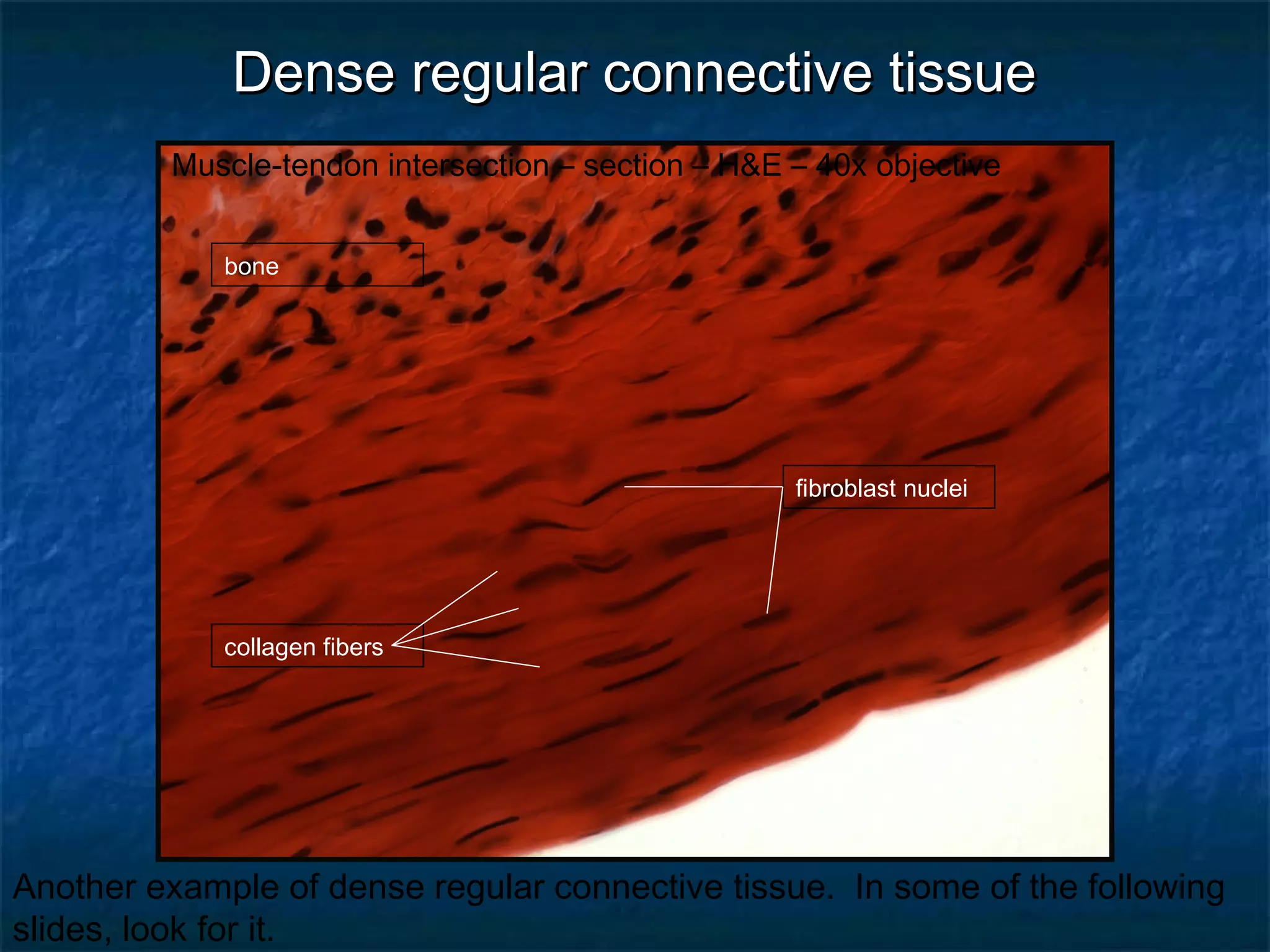
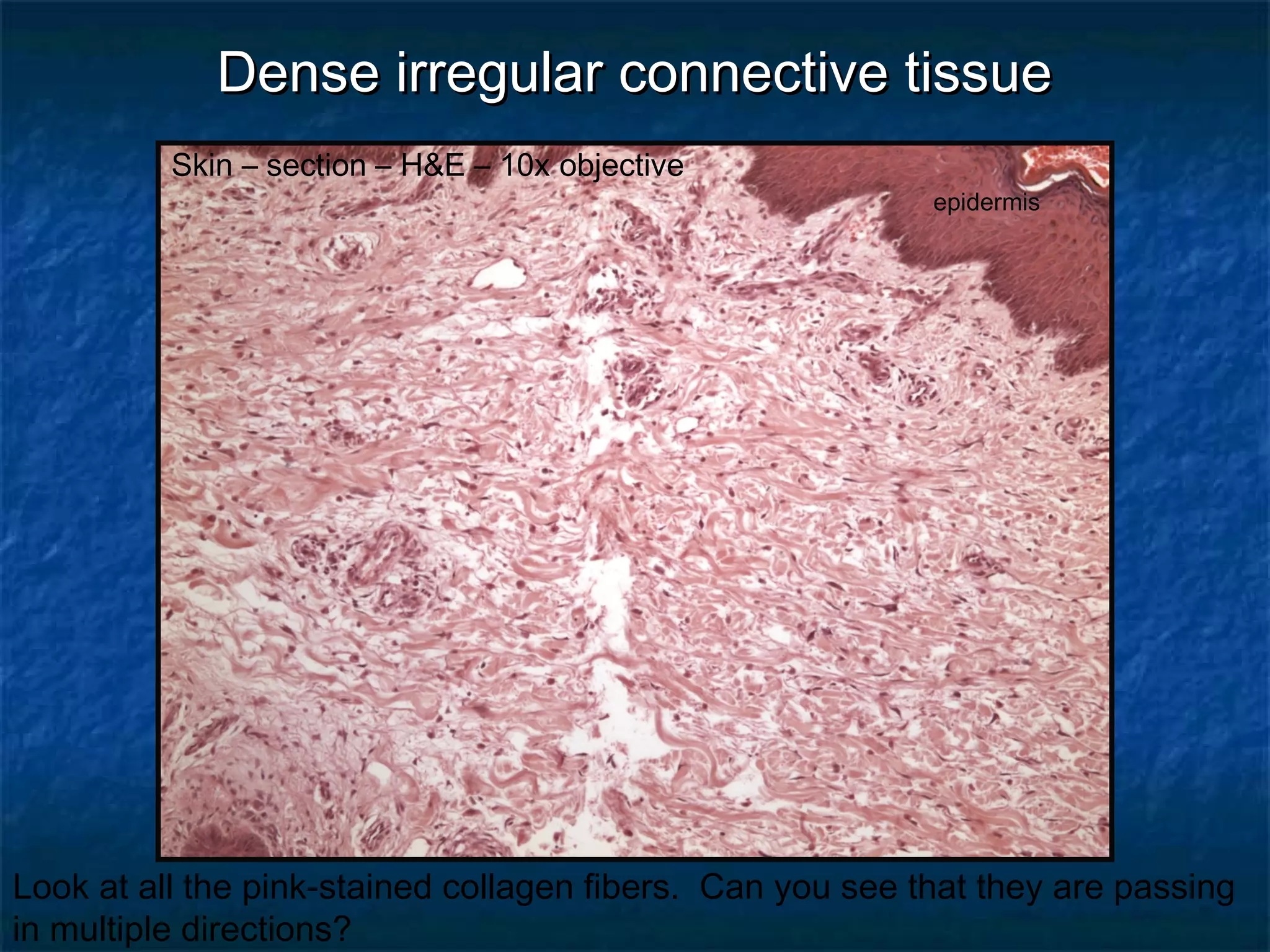
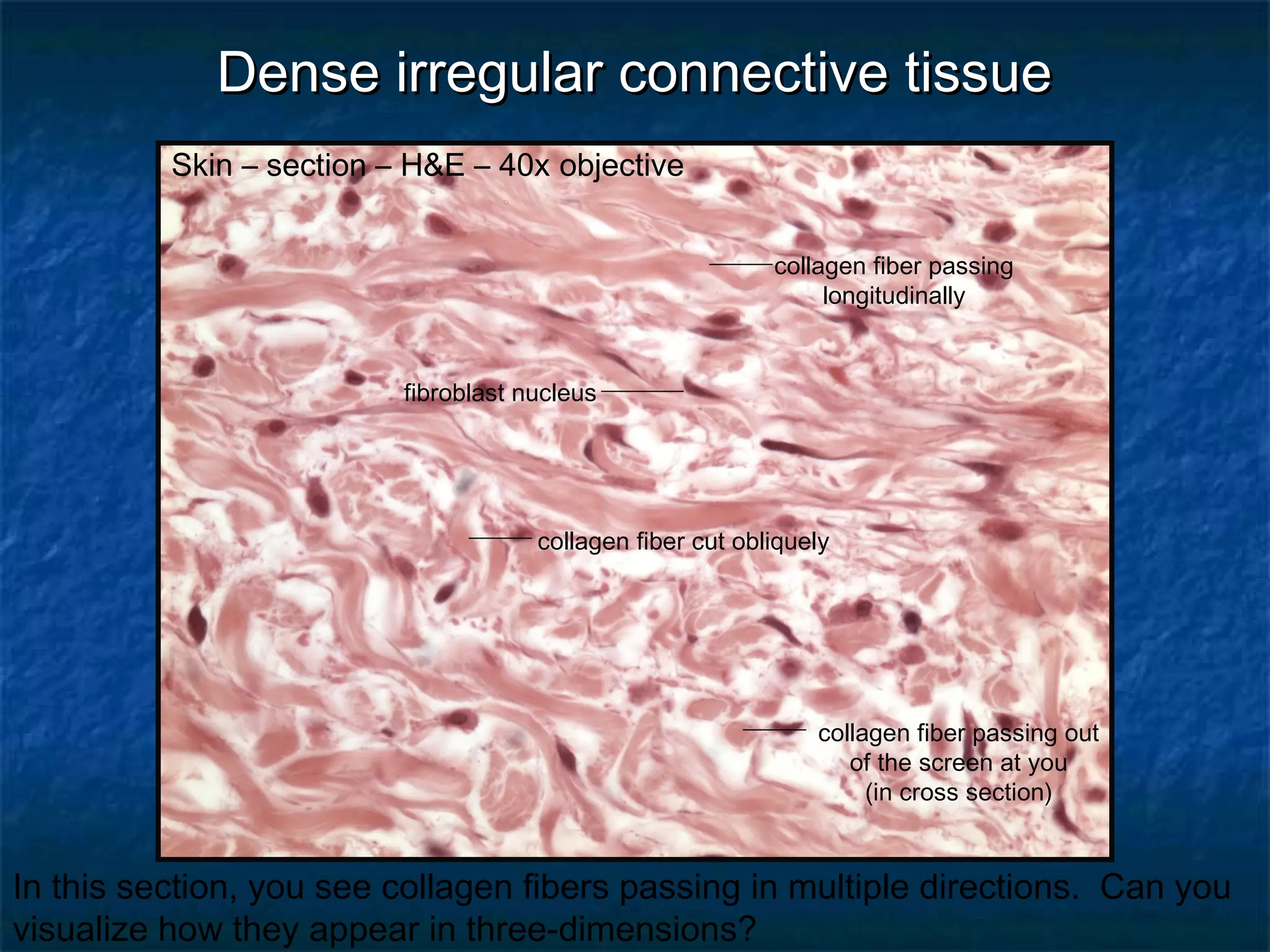
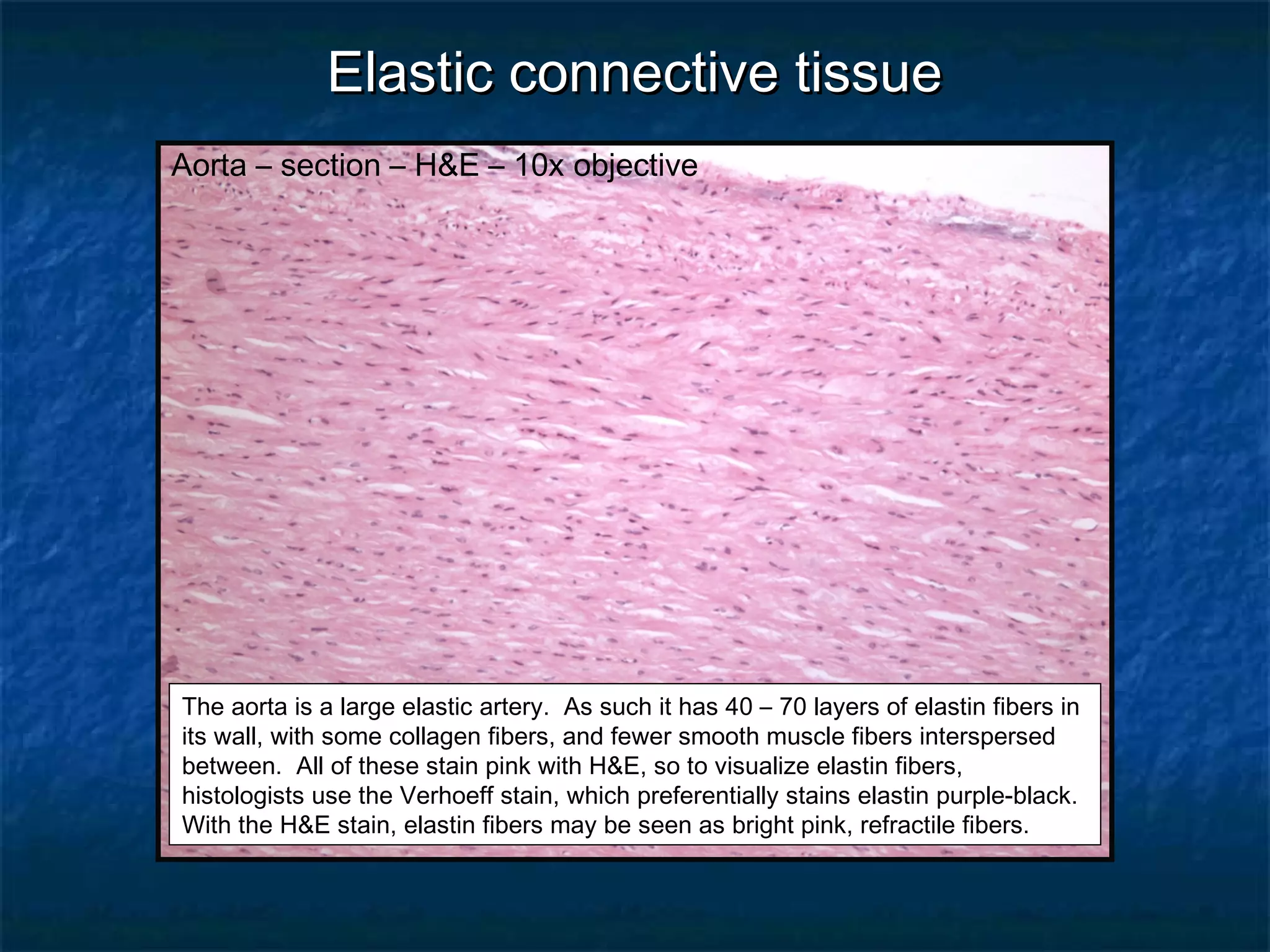
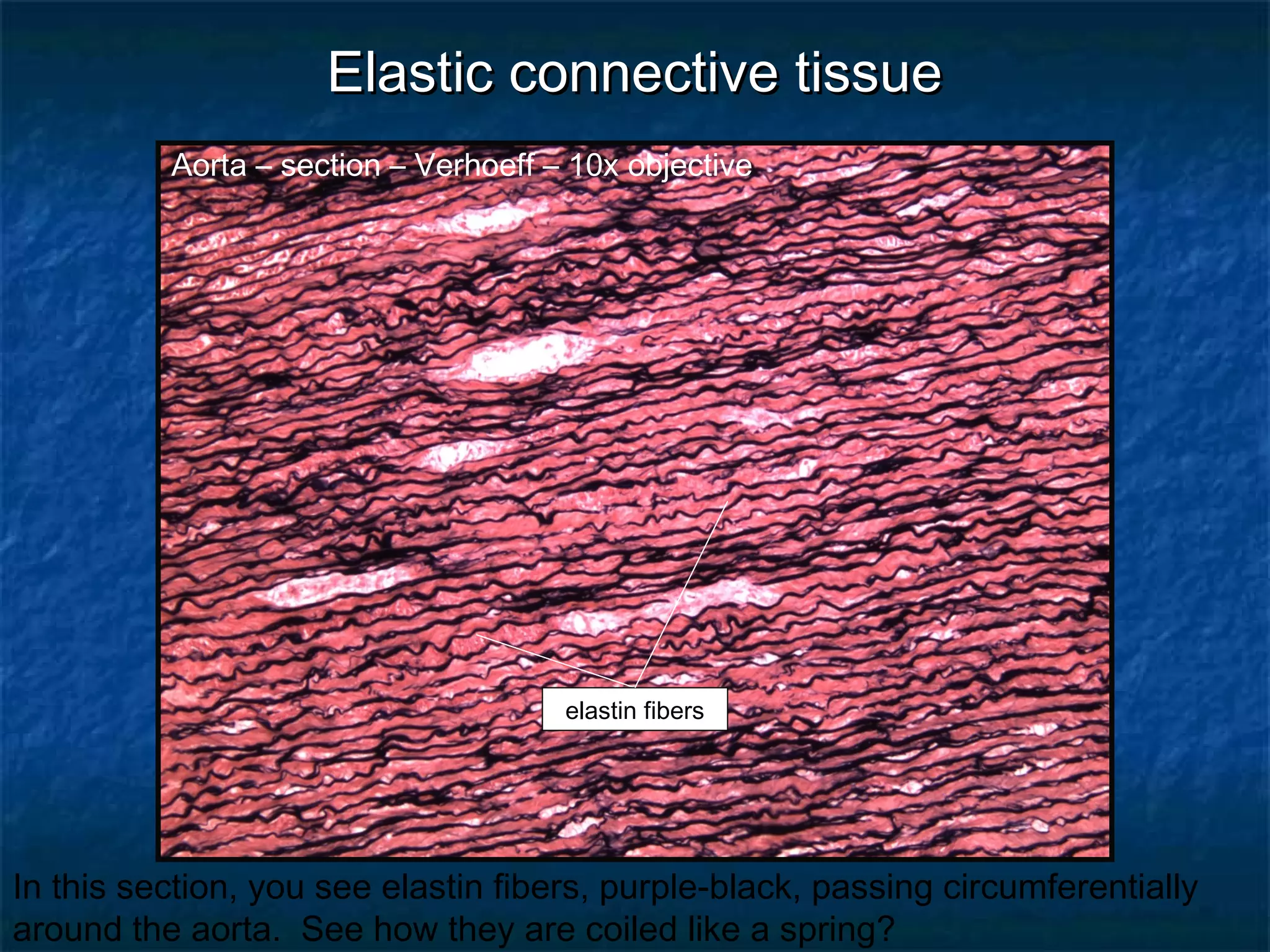
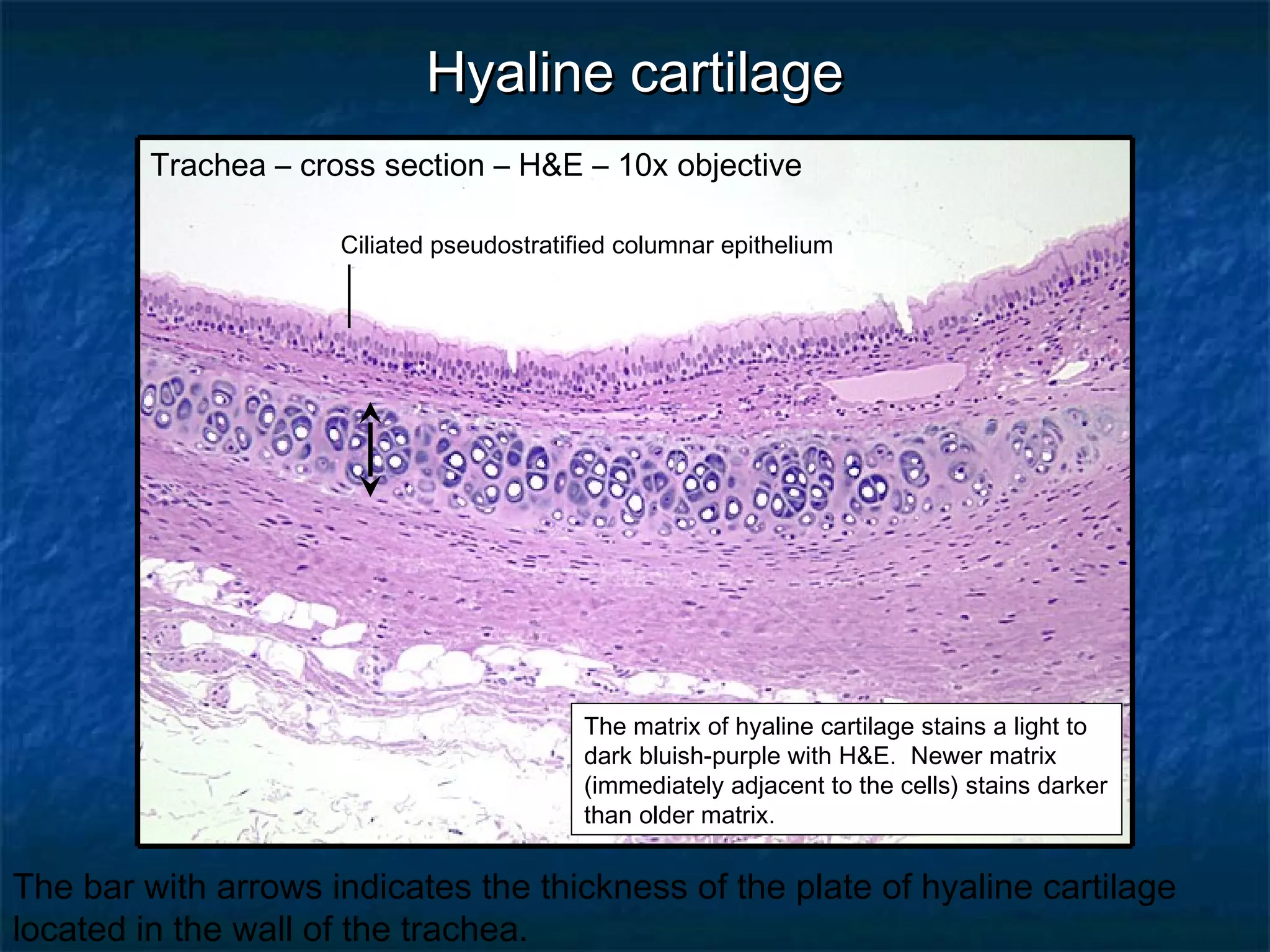
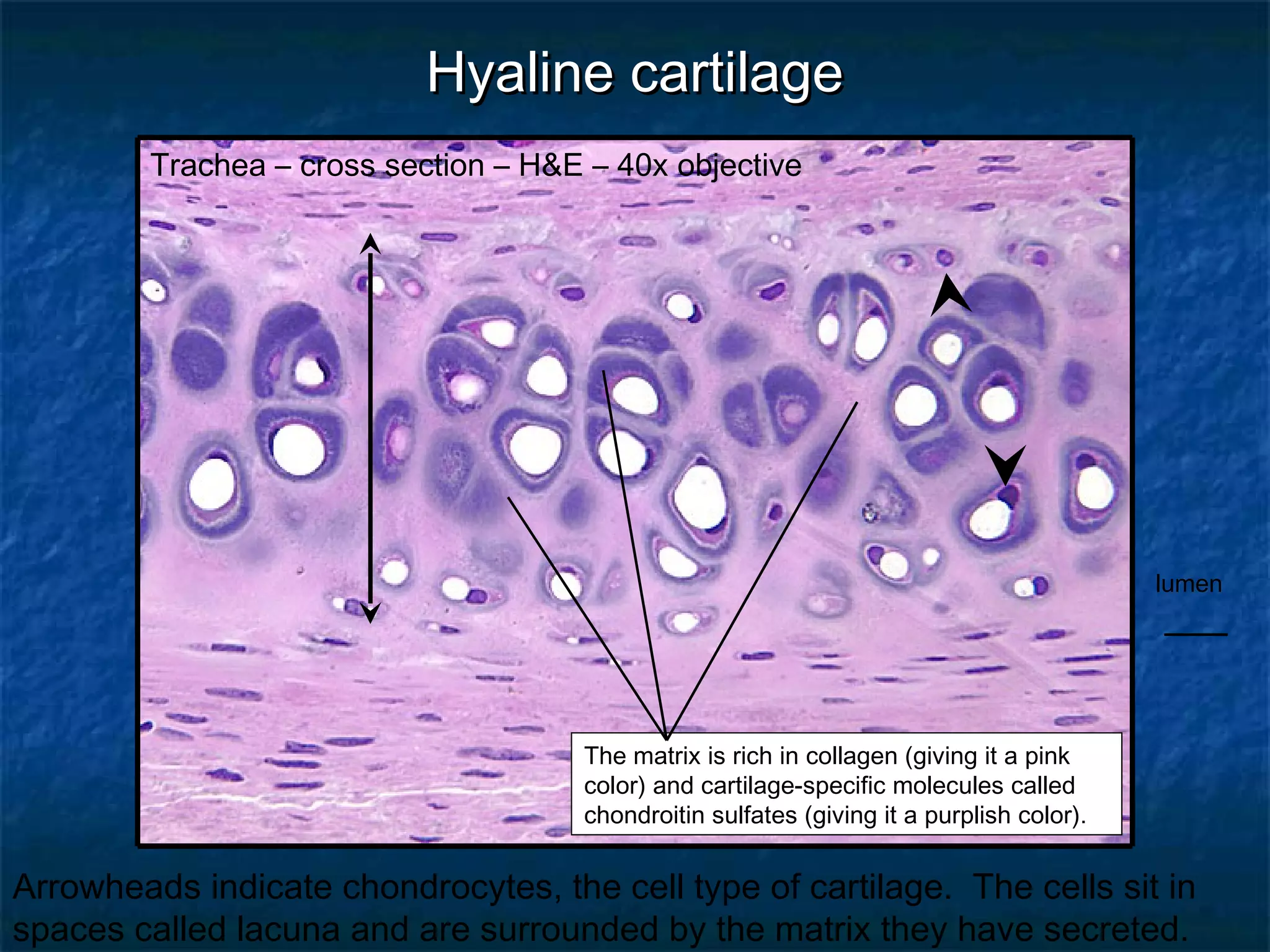
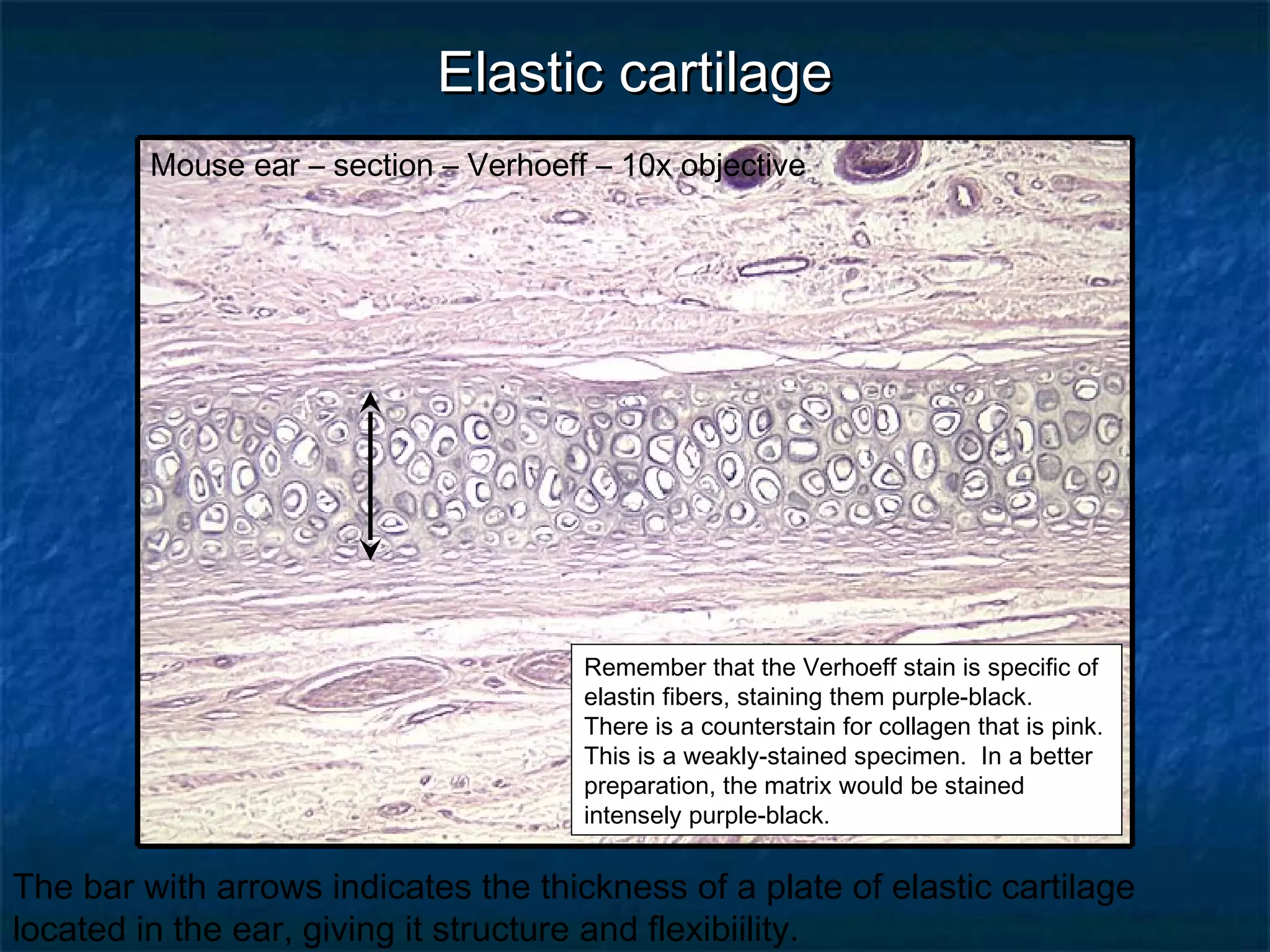
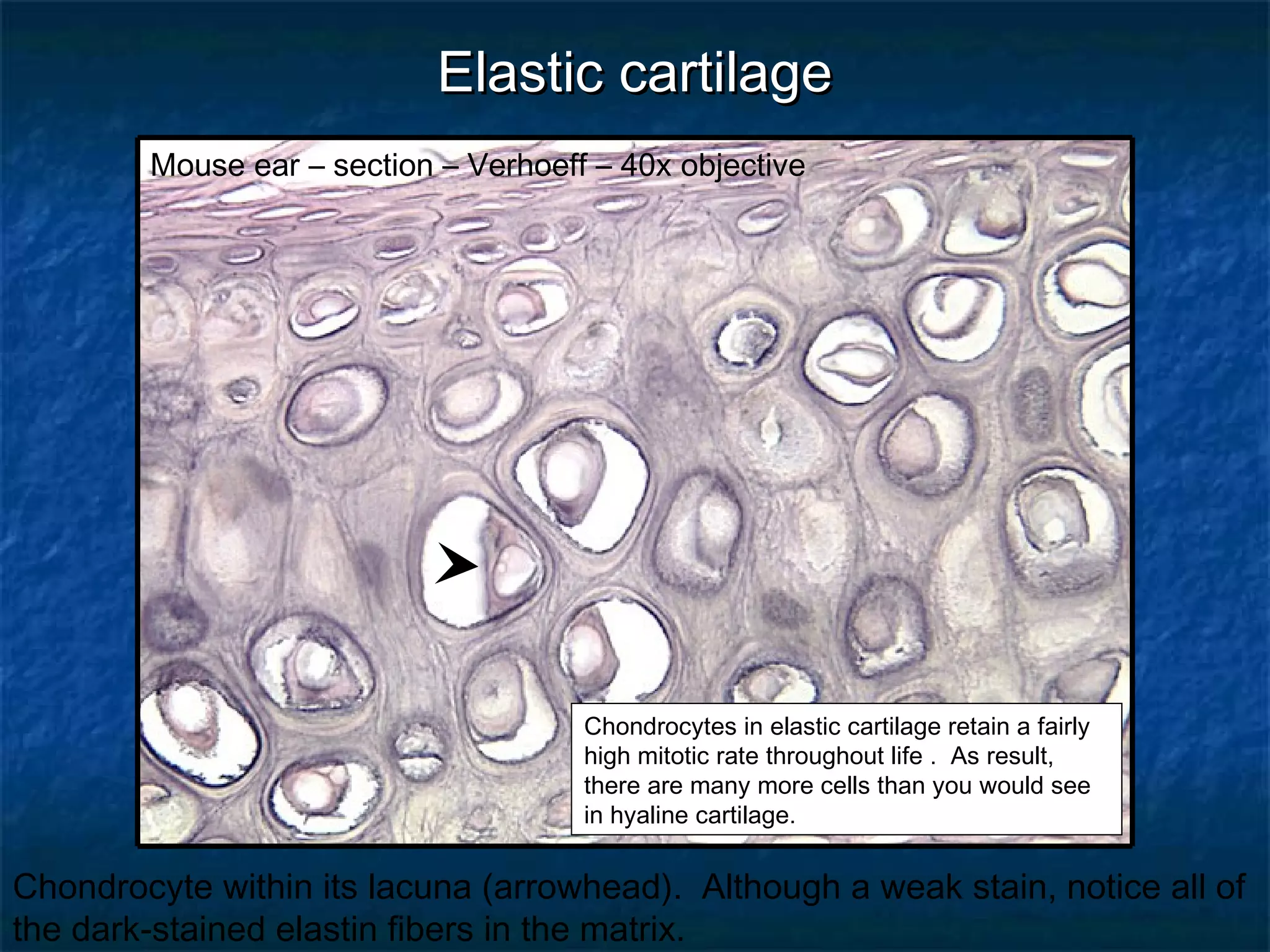
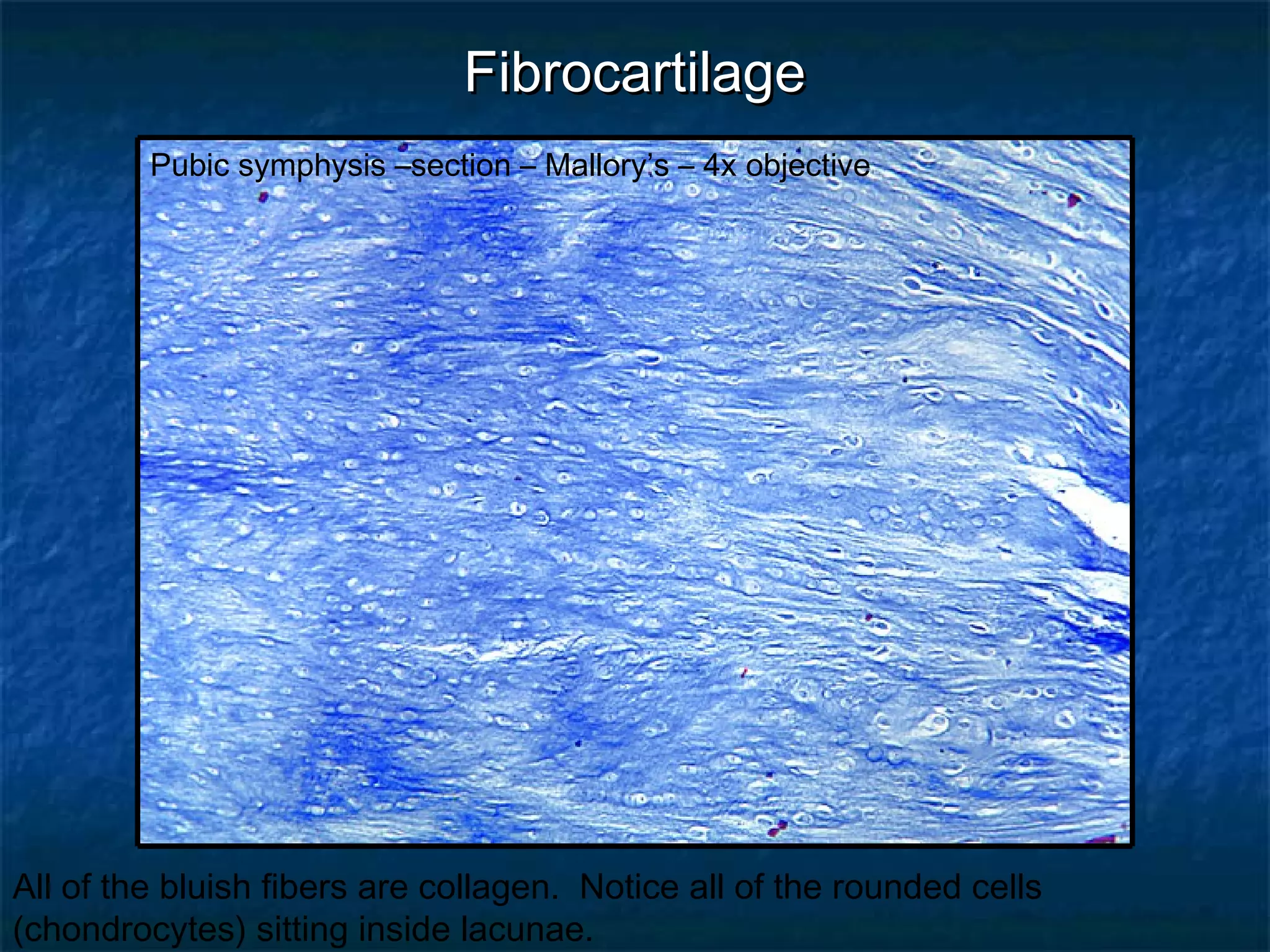
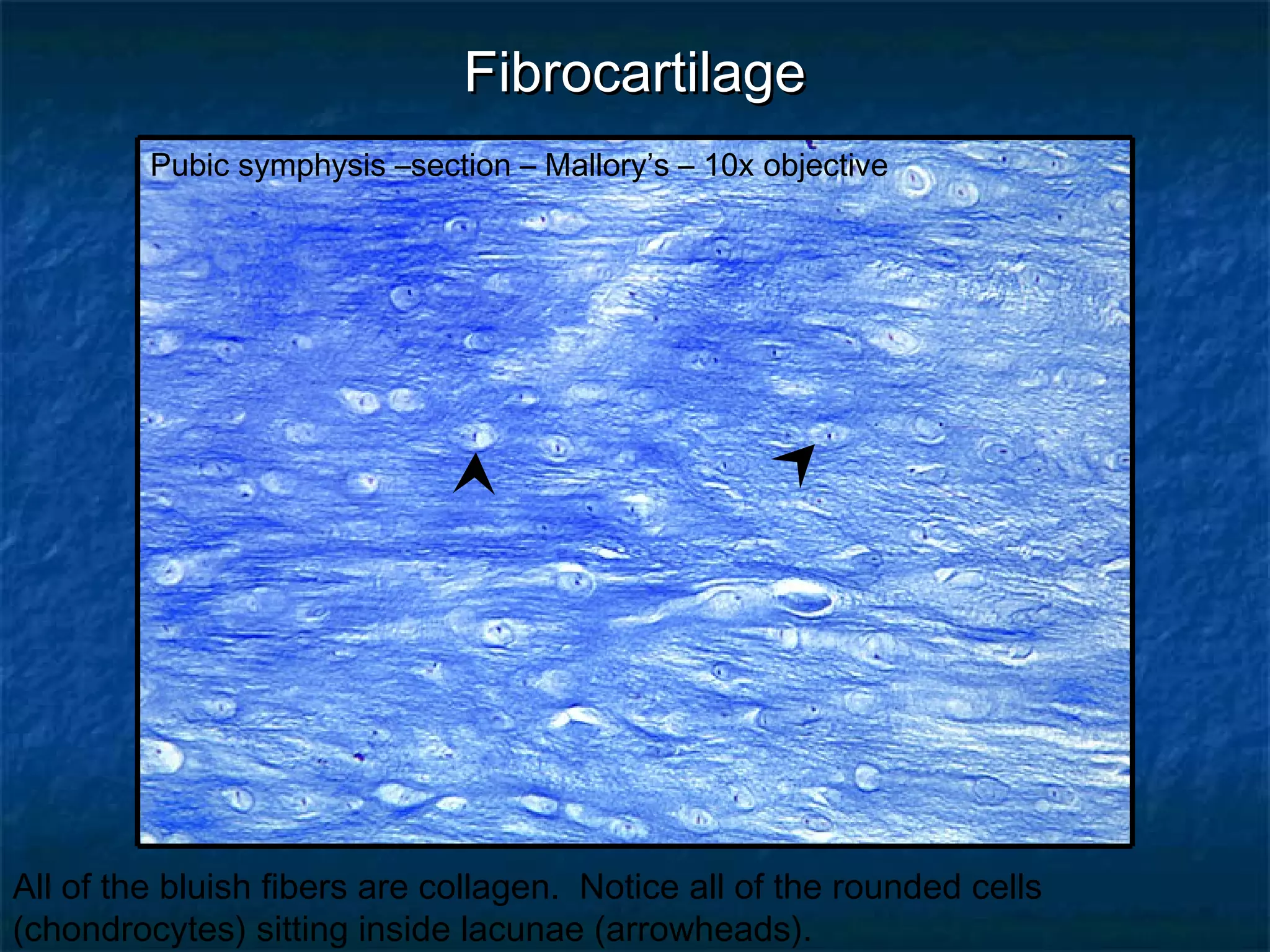
The document discusses various types of connective tissues, their characteristics, and visualizations through different staining techniques. It highlights specific examples such as areolar connective tissue, adipose tissue, reticular connective tissue, and elastin fibers in the aorta, detailing their structure and function. Additionally, it covers histological methods used to observe these tissues, including H&E and Verhoeff stains.