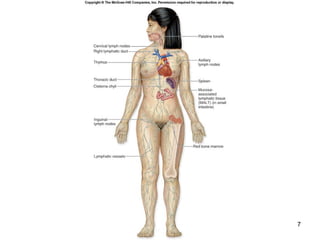
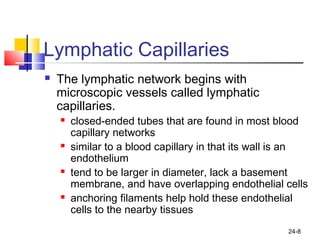
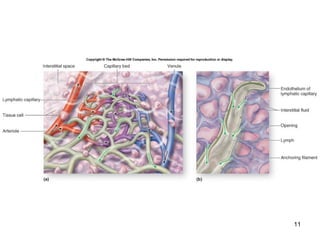
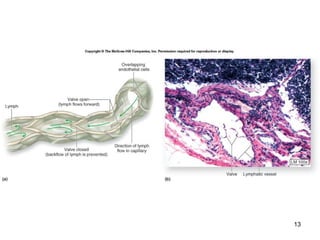
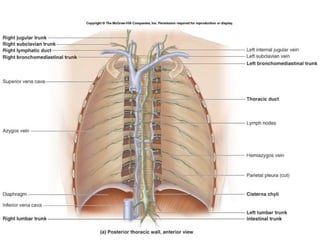
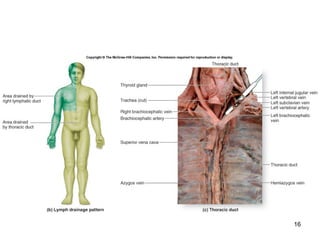
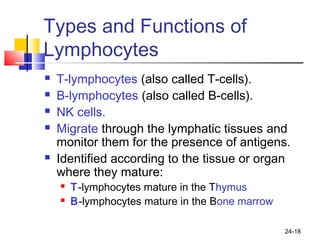
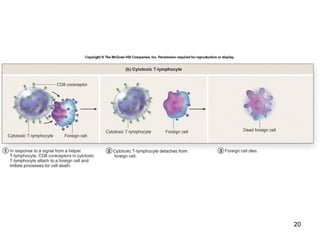
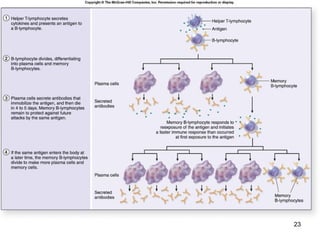
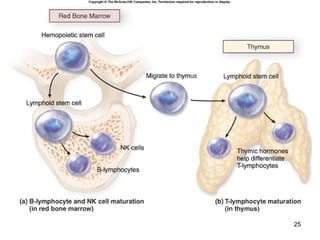
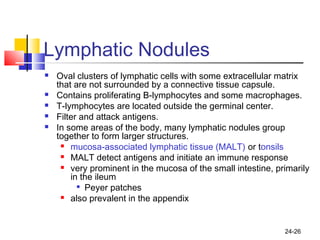
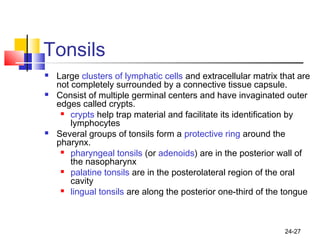
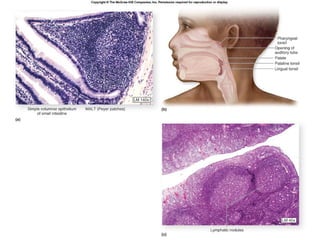
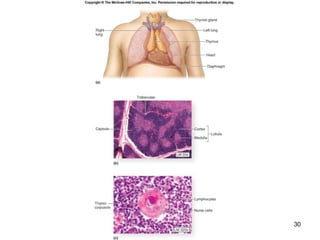
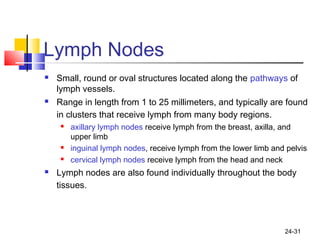
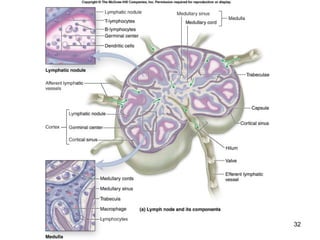
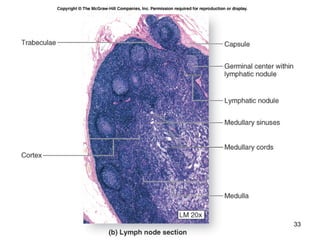
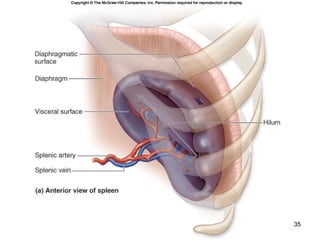
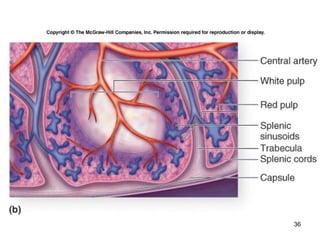
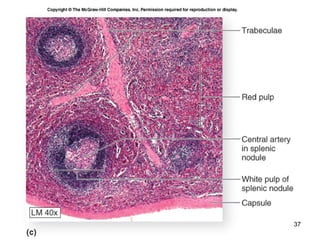
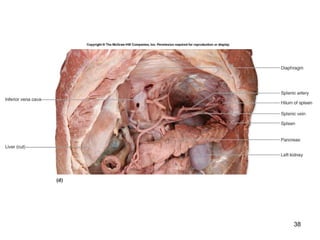
The lymphatic system transports lymph fluid and assists the immune system. It is composed of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, the spleen, thymus, and lymphatic cells. Lymph fluid is collected from tissues by lymphatic capillaries and transported through a series of vessels, nodes, and ducts where it is filtered for pathogens. The system's immune cells help fight infection and disease. As the body ages, the thymus and immune response decline, making elderly people more susceptible to illness.