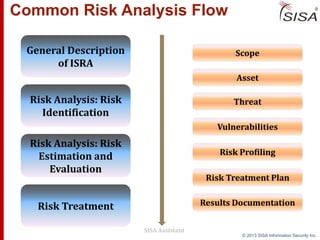
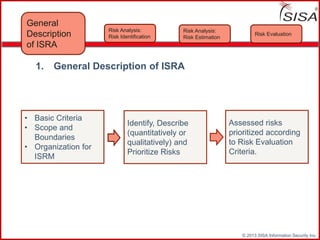
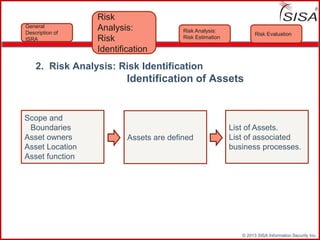
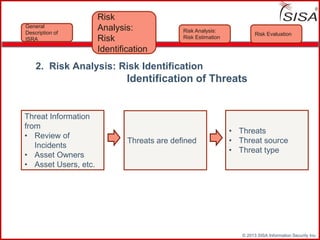
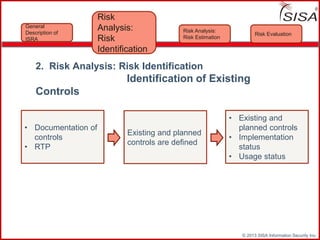
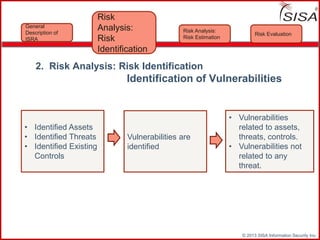
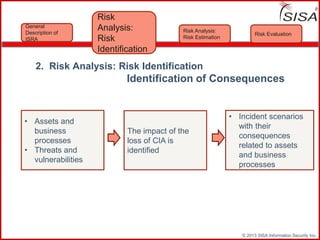
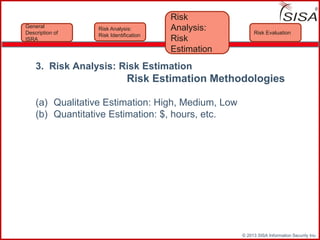
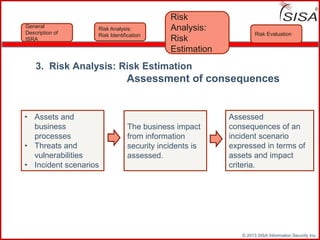
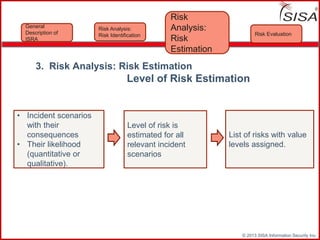
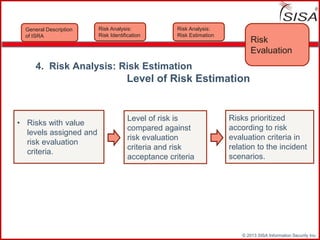
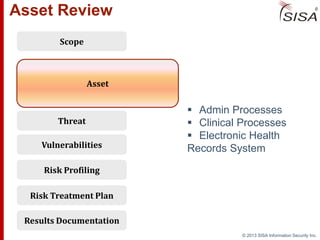
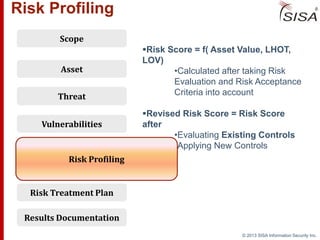
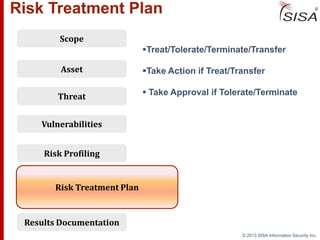
Sisa Information Security Inc., founded in 2003, specializes in risk analysis with a focus on HIPAA compliance, leveraging its widely-used tool, Sisa Assistant. The document highlights the importance of formal risk assessment in protecting organizational information security, addressing misconceptions, and outlining processes for risk identification, estimation, and treatment. It emphasizes that effective risk management is vital for safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring ongoing compliance across various sectors, including healthcare and finance.