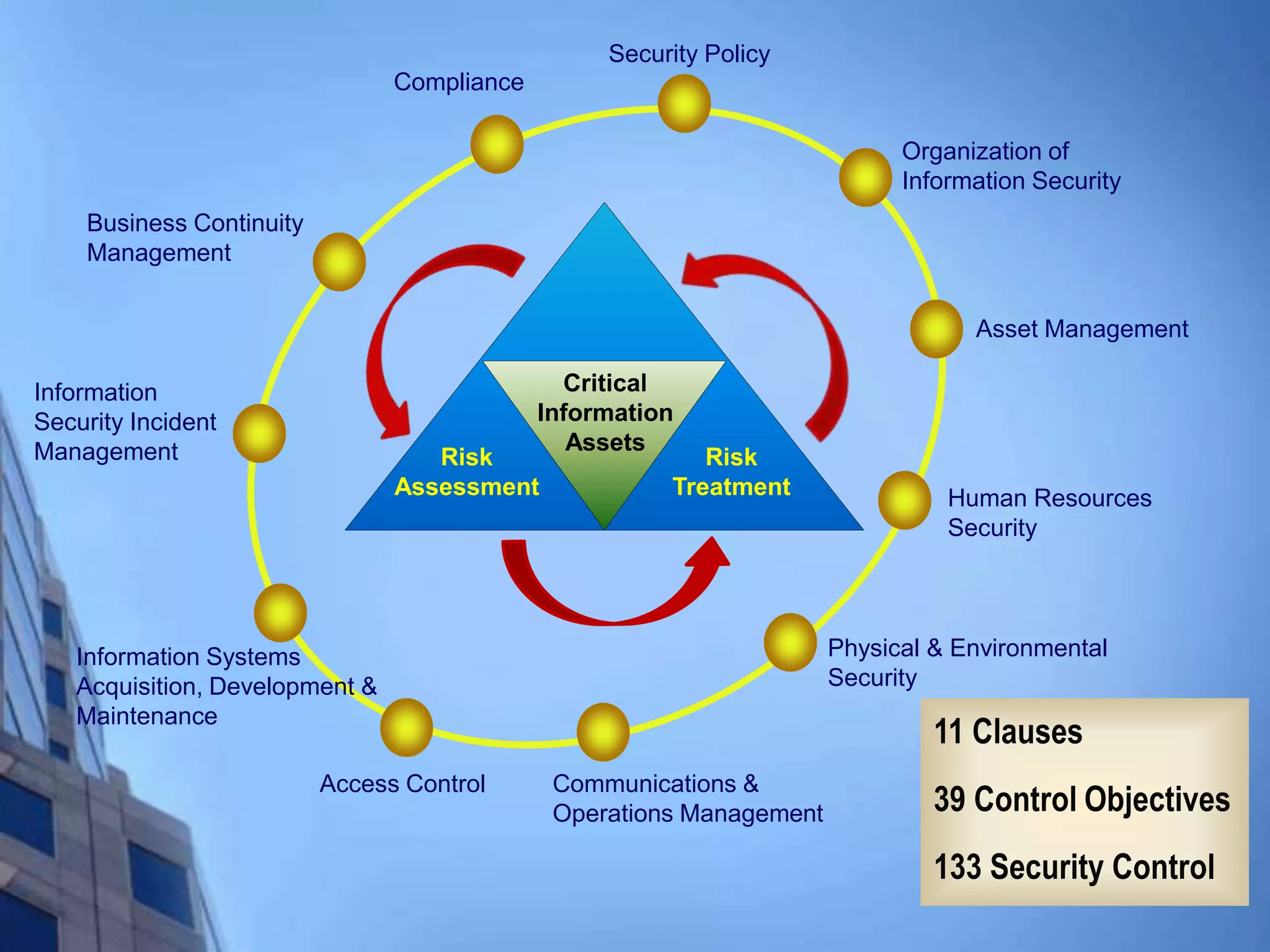
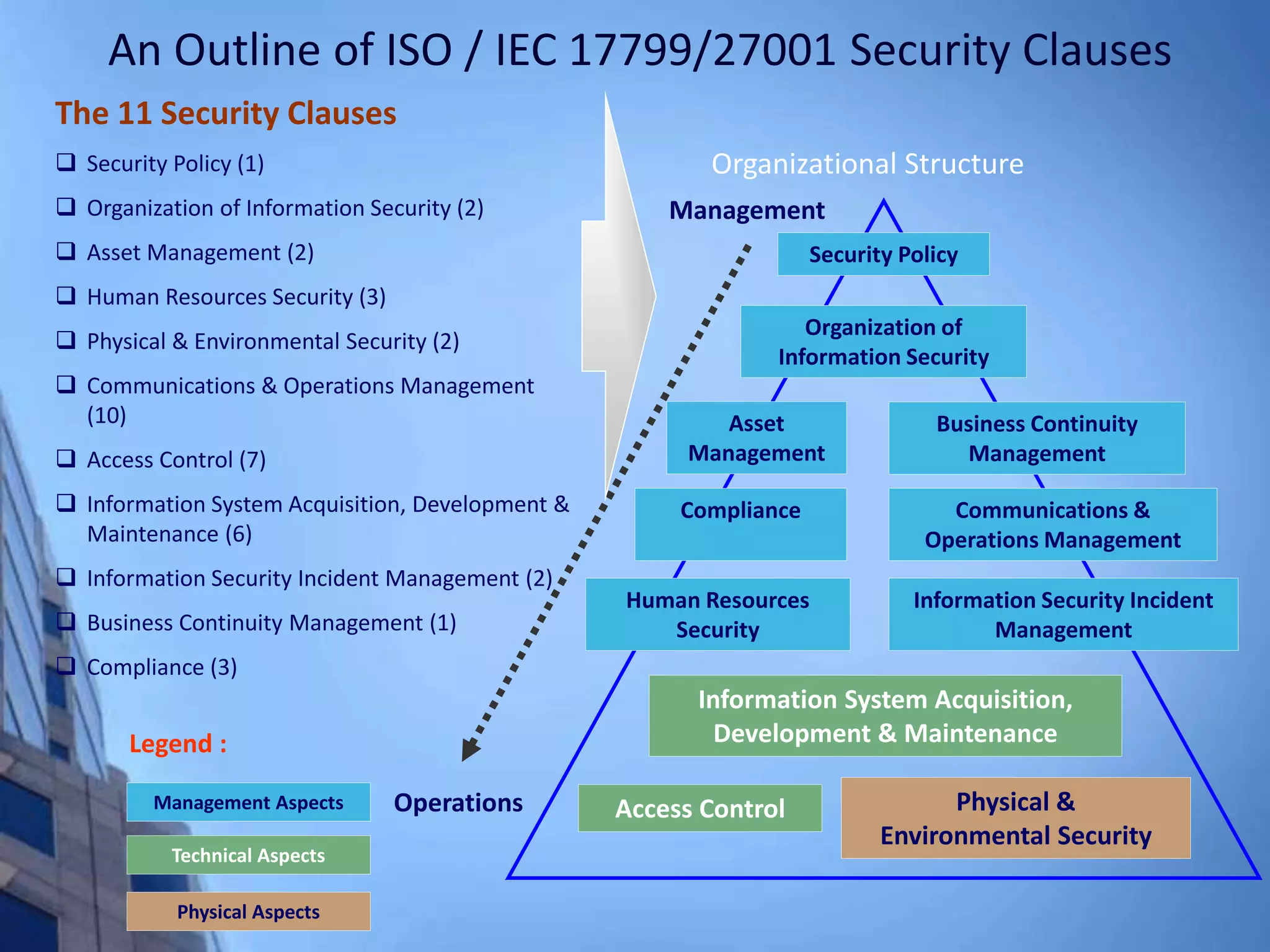
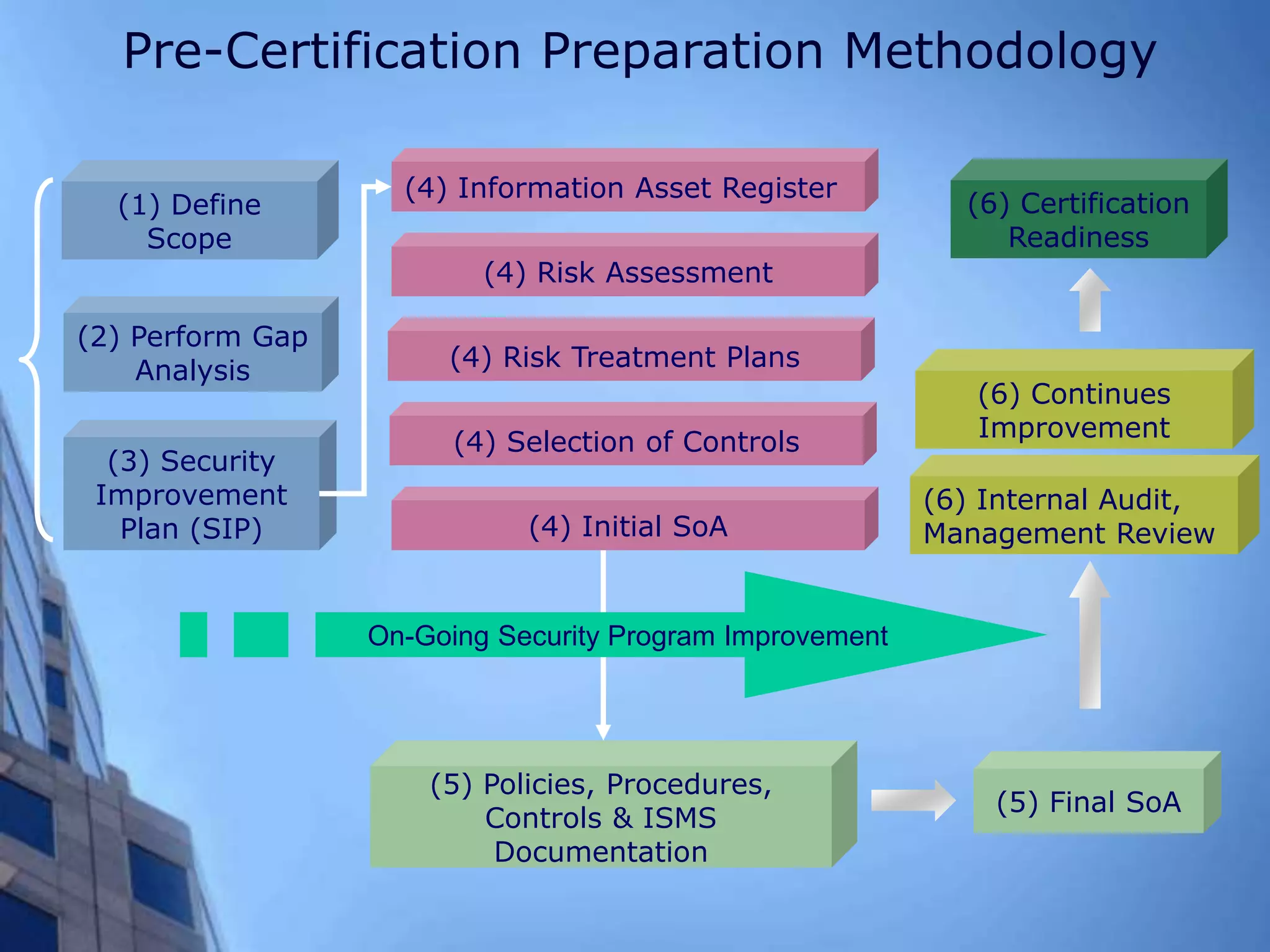
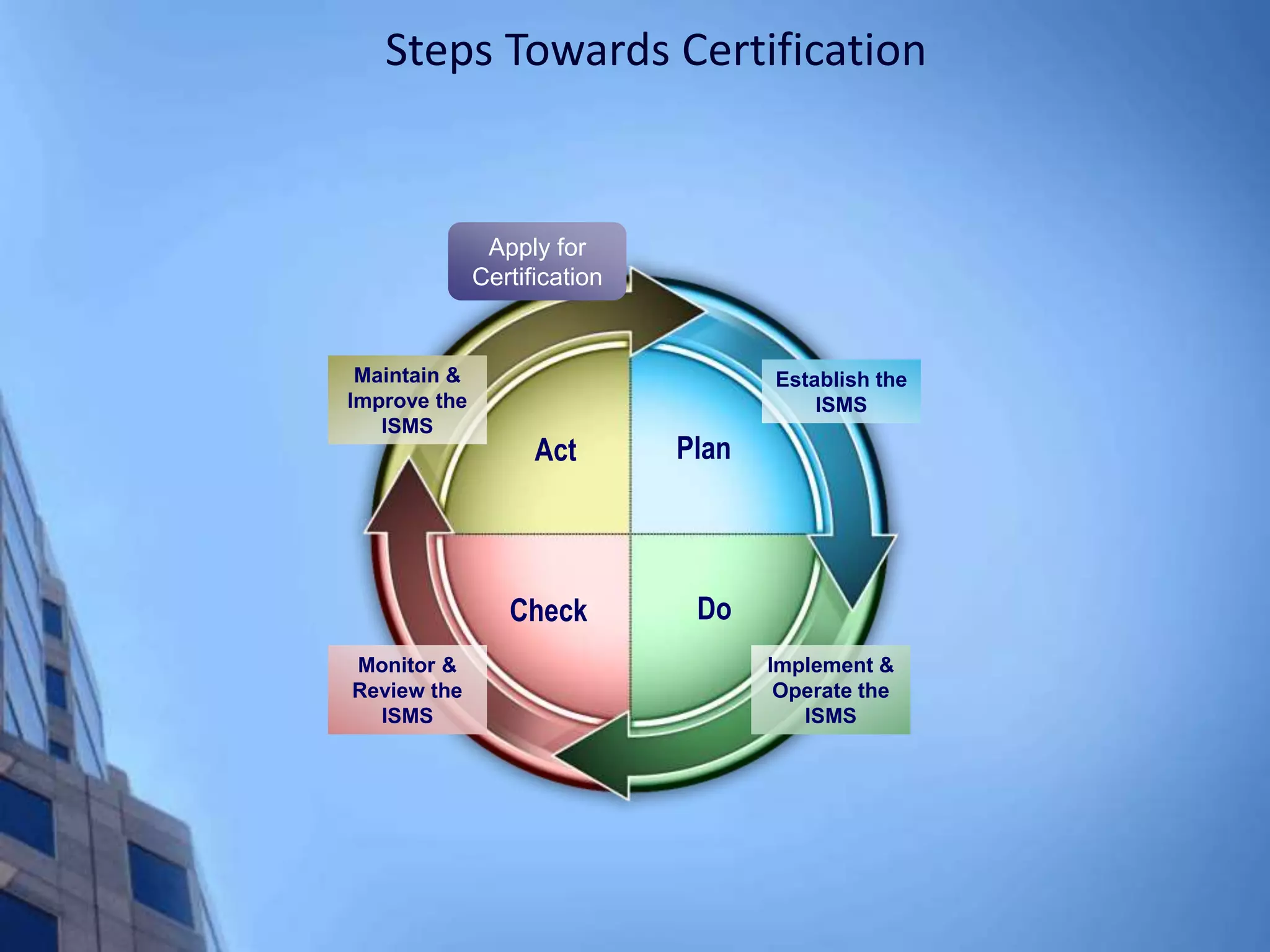
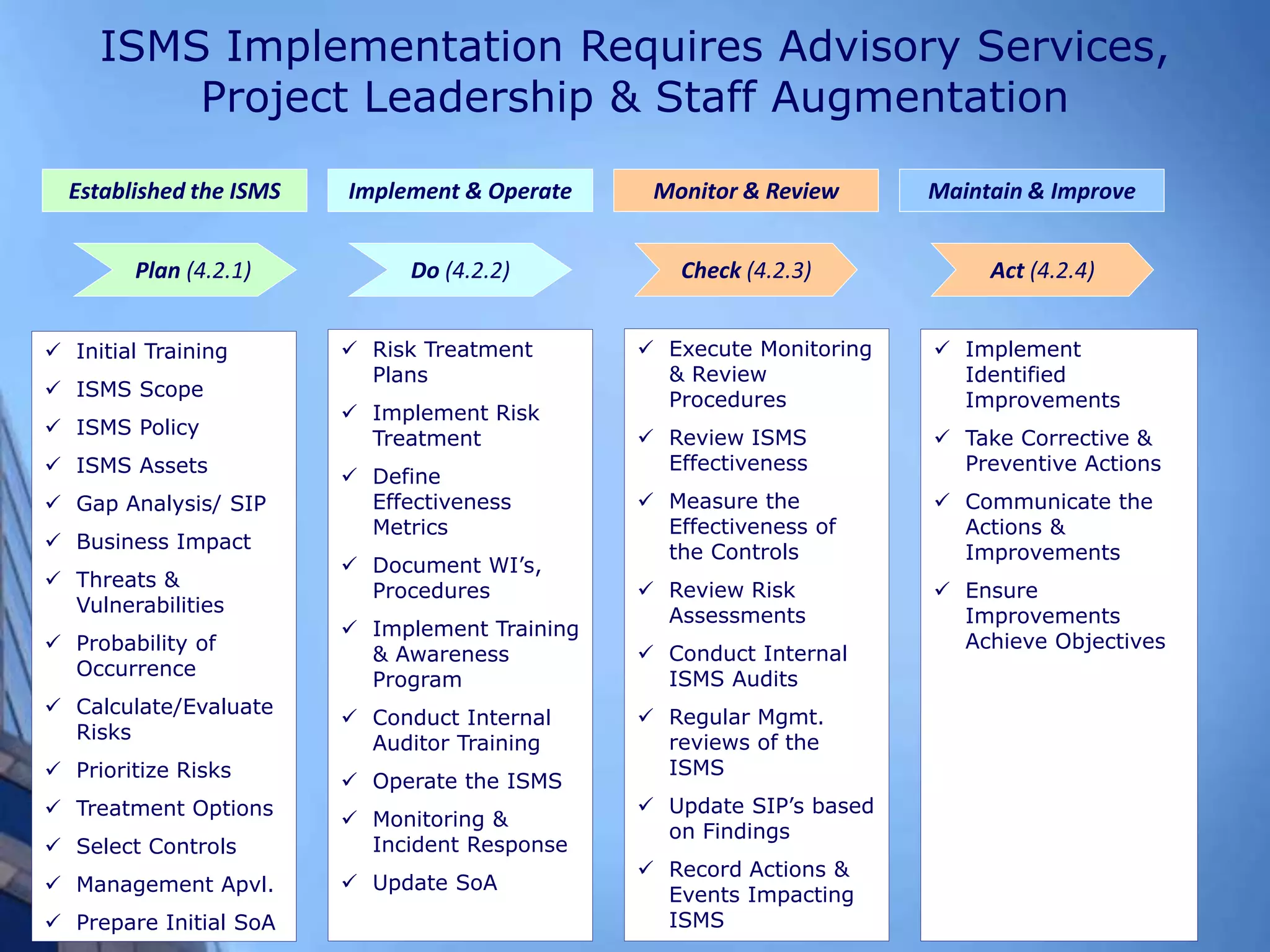
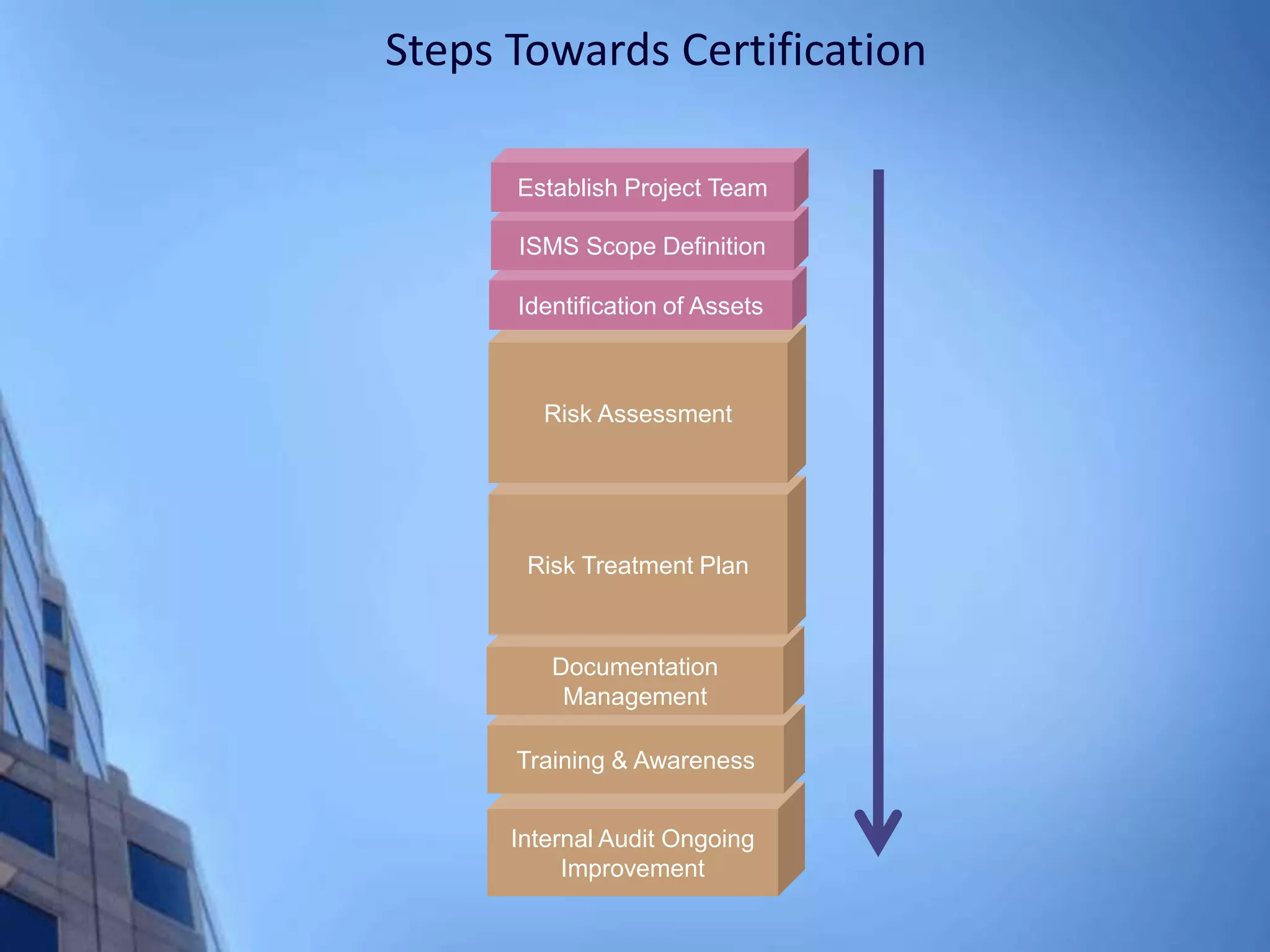
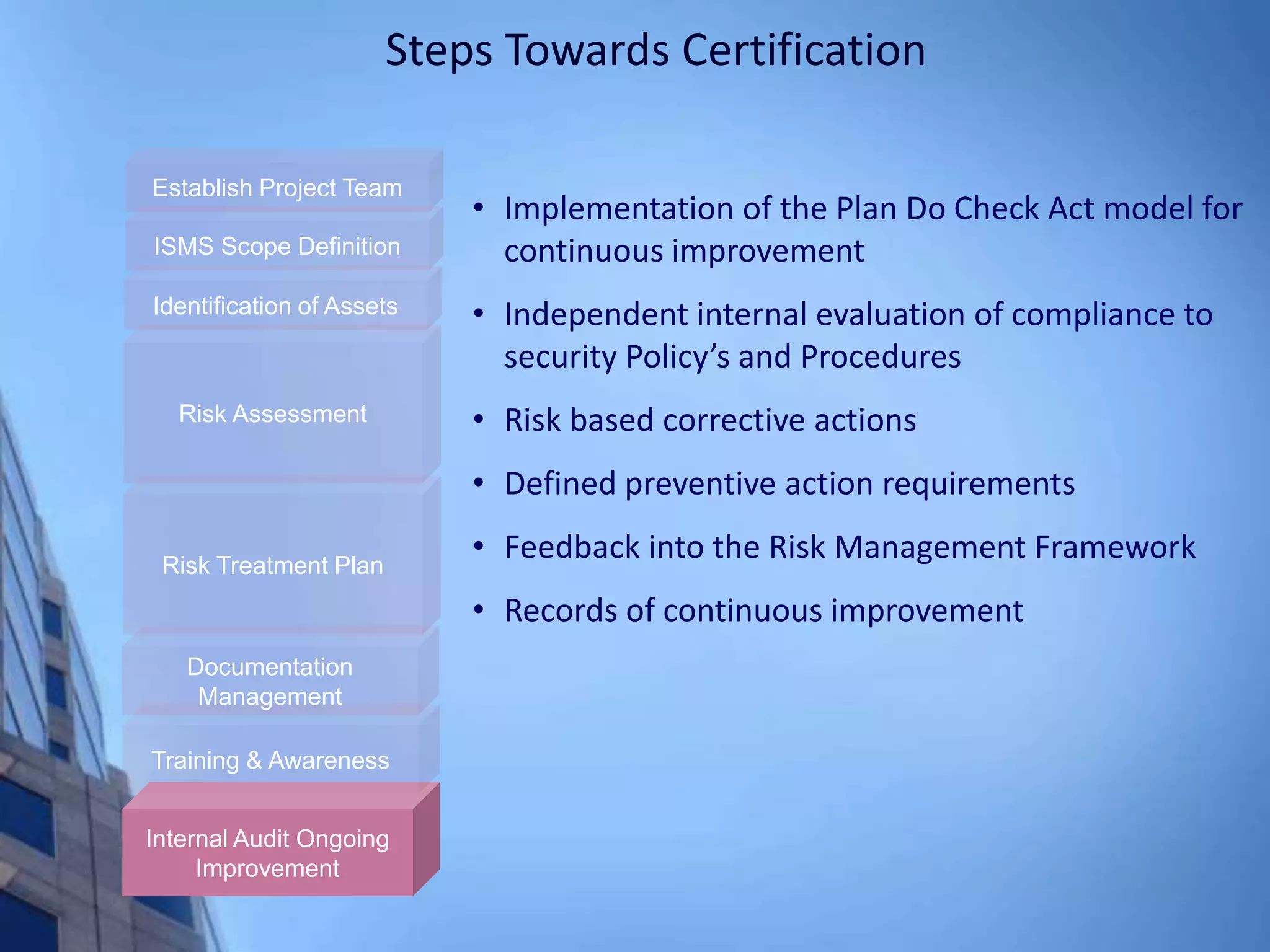
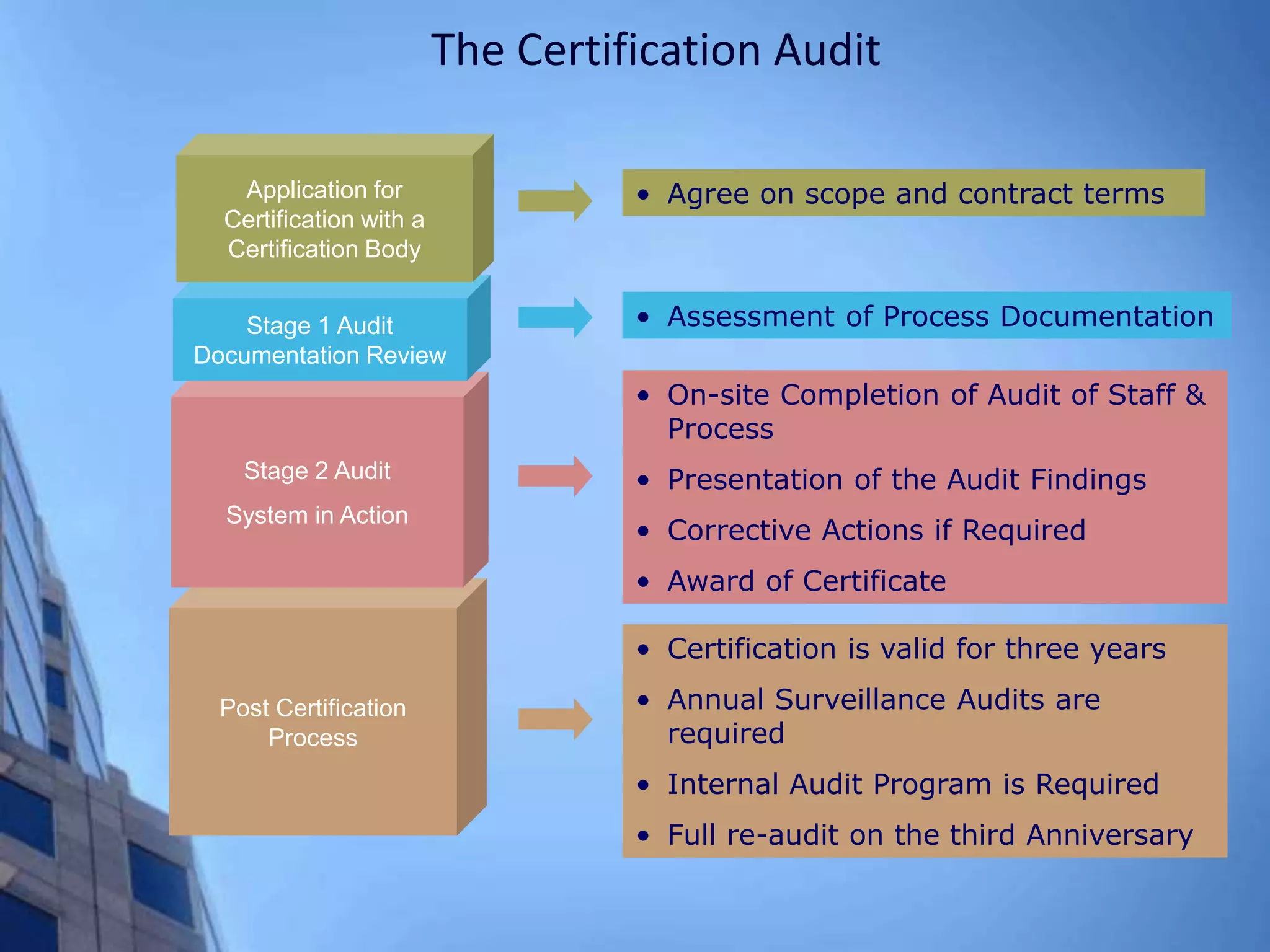
This document provides an overview of information security management systems (ISMS) and the ISO/IEC 27001 standard. It discusses how ISMS establishes a top-down, risk-based approach to securely managing an organization's information assets. Key points covered include the business drivers for ISMS, the components of an effective ISMS based on ISO 27001, and the steps involved in implementing, certifying and maintaining an ISMS over time.