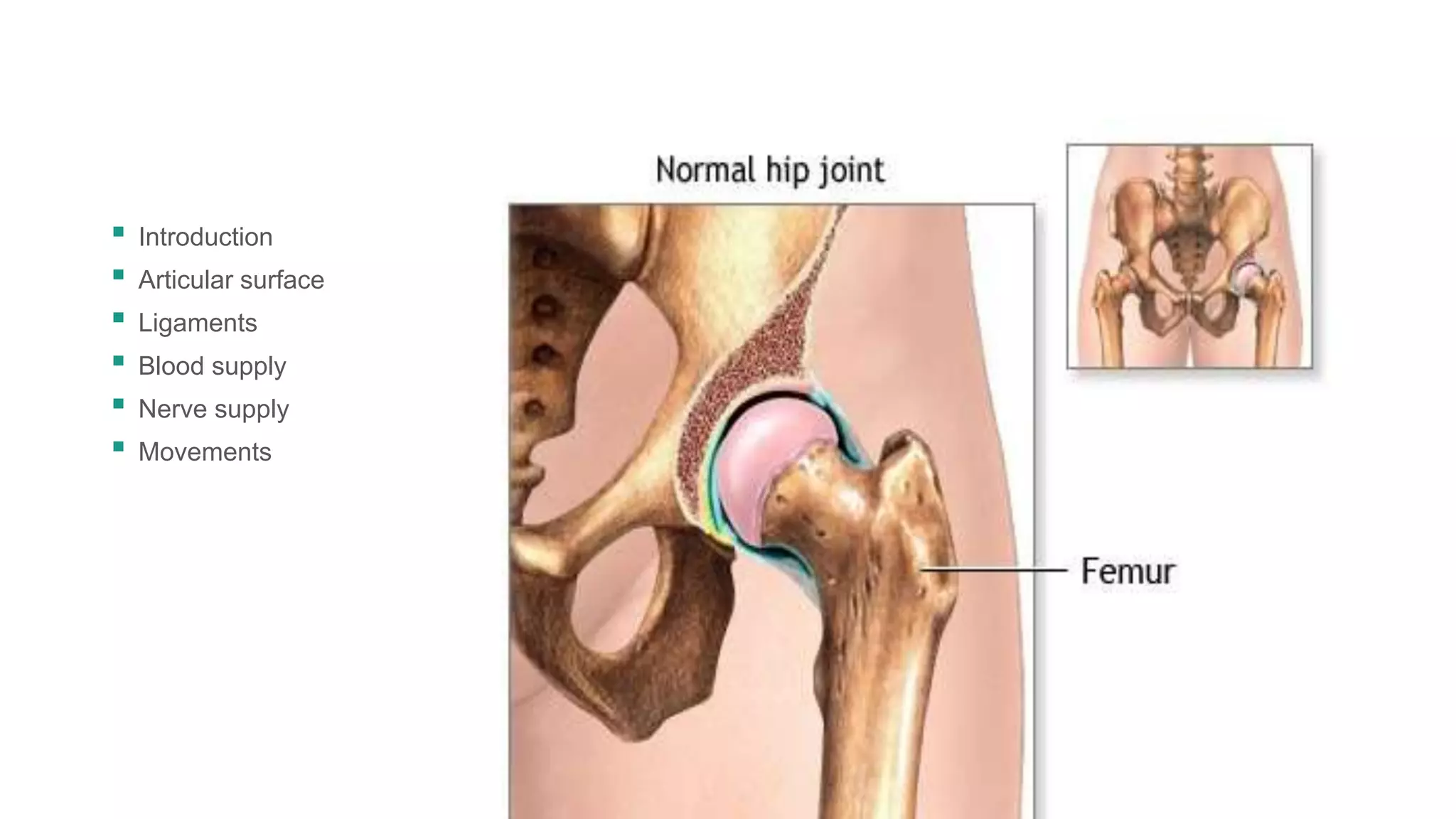
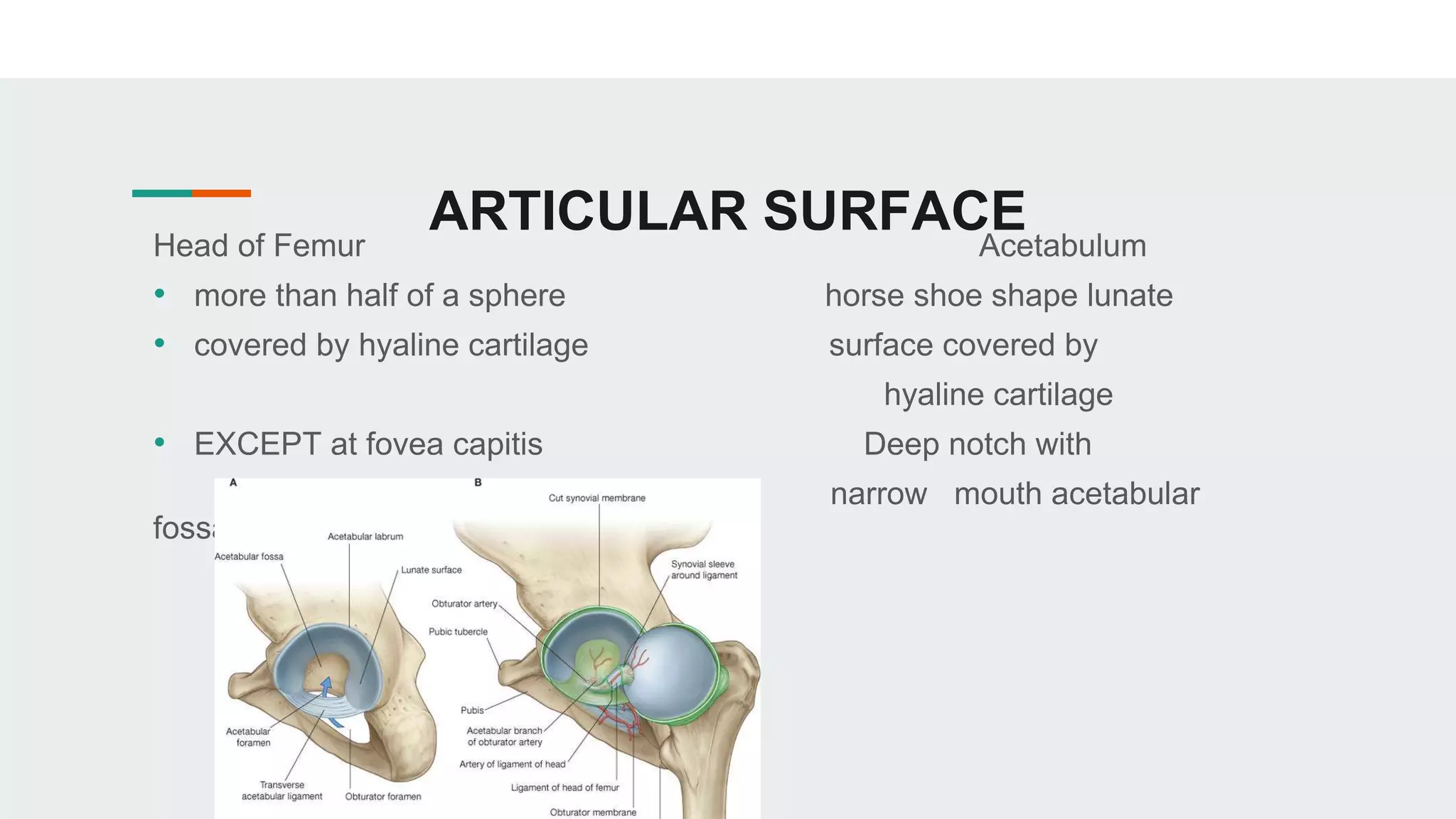
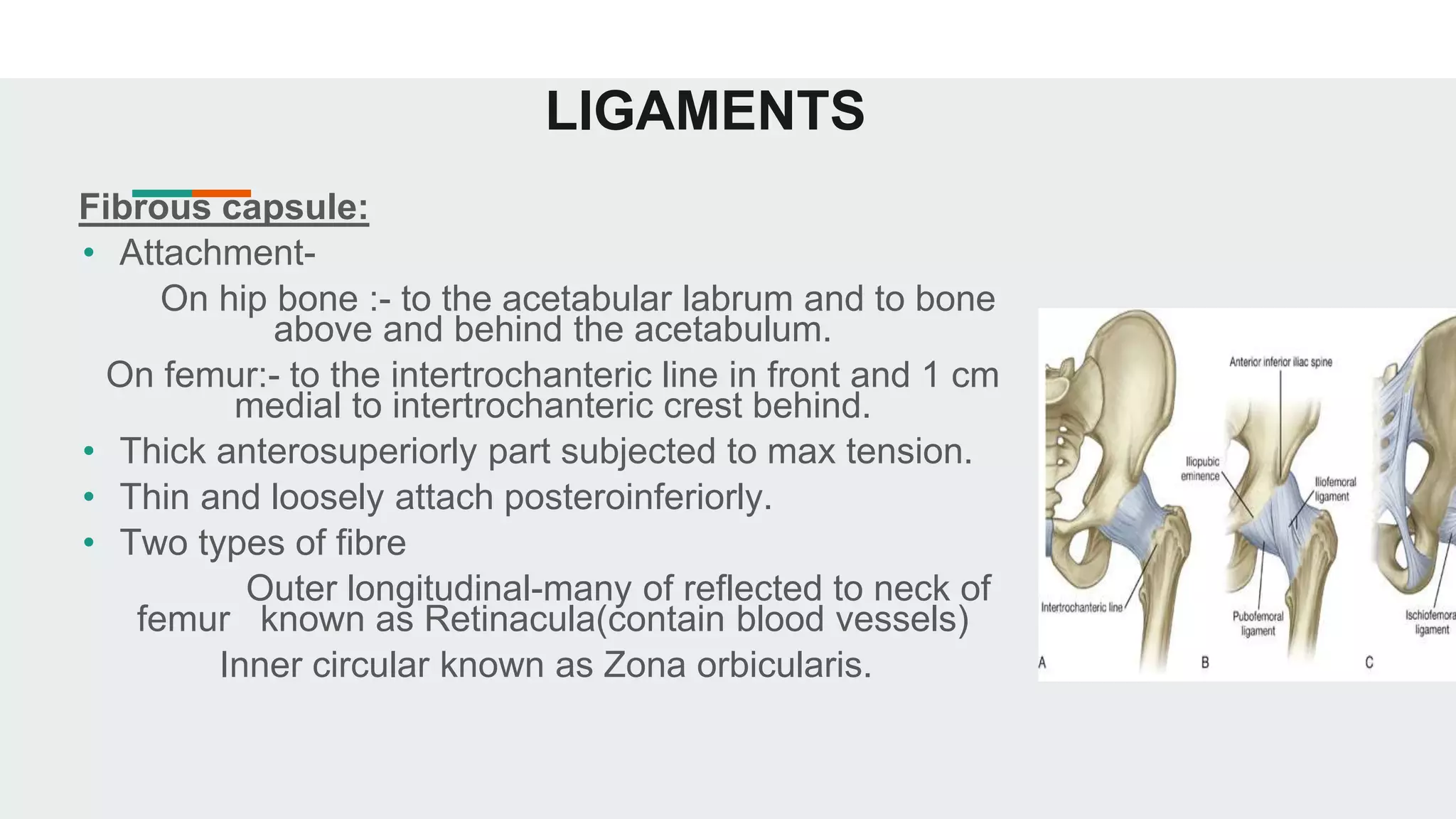
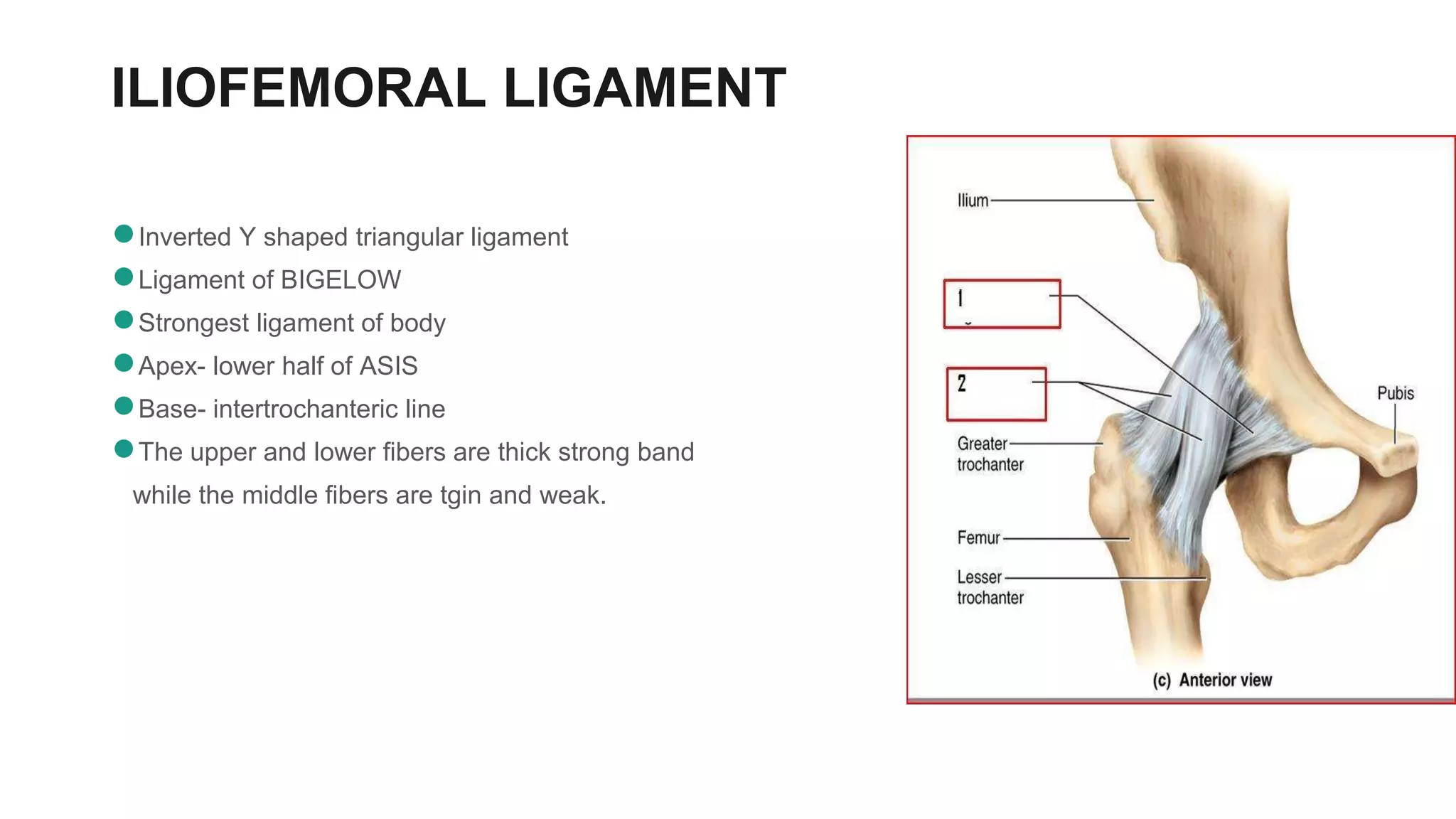
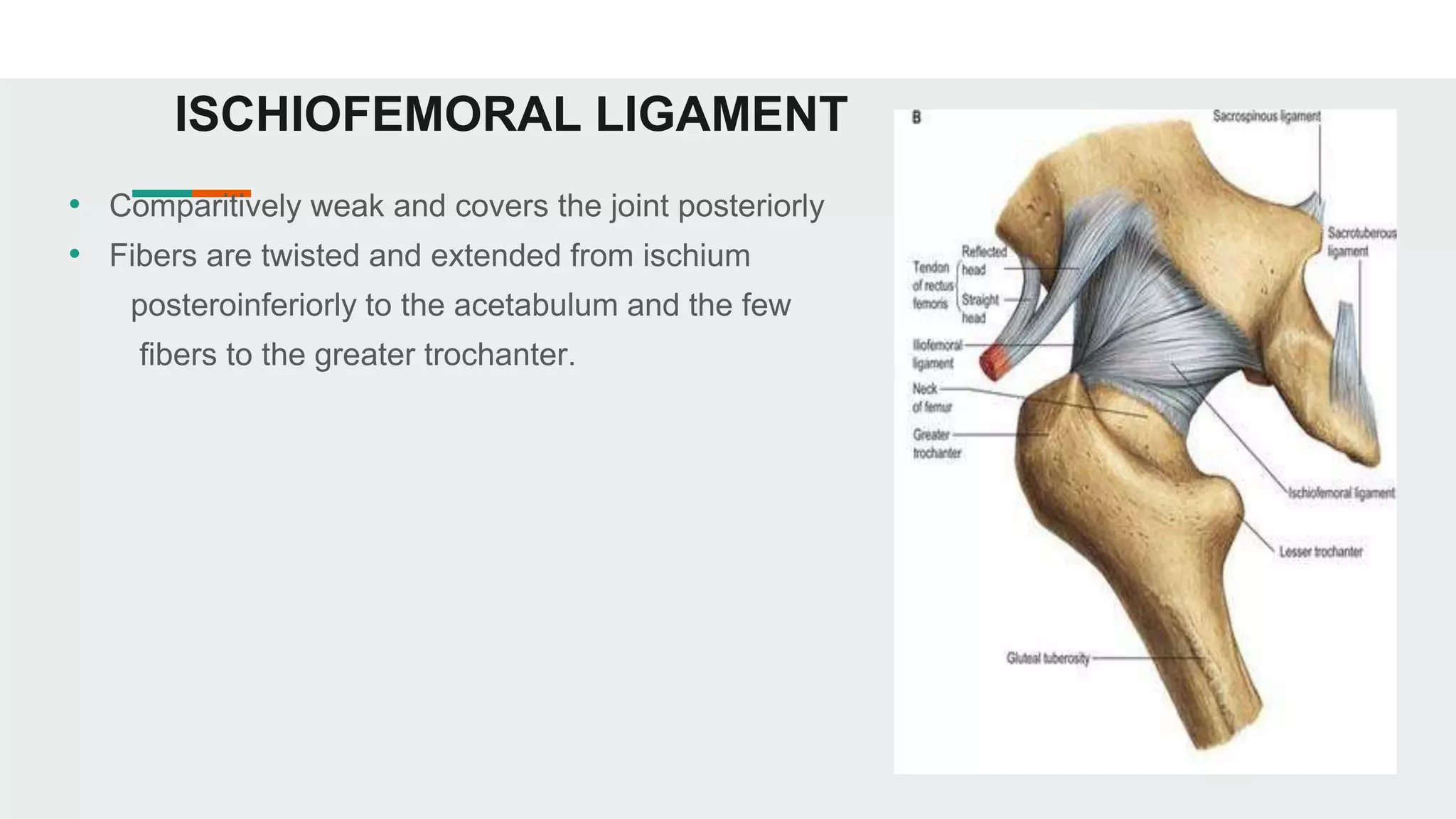
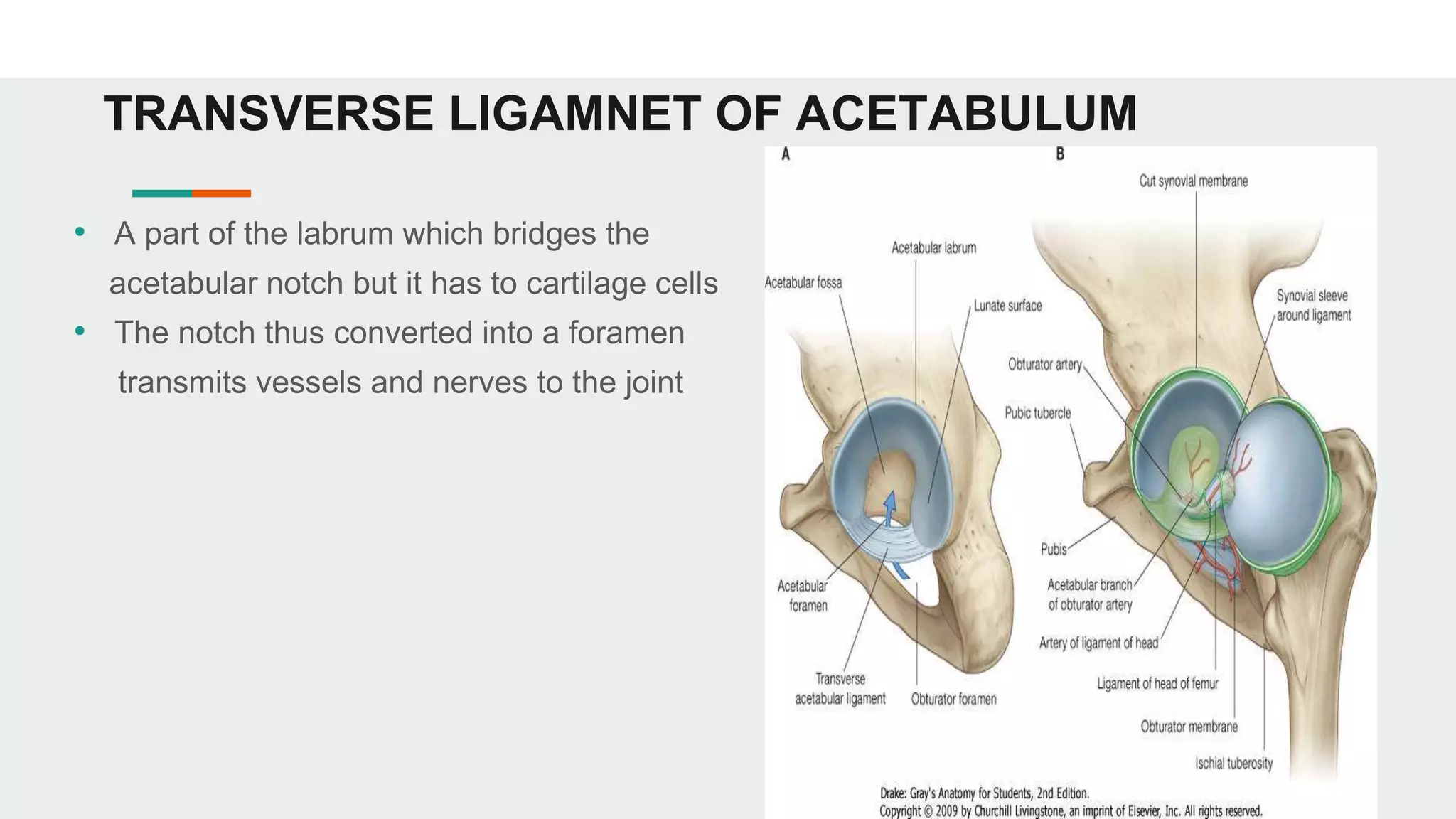
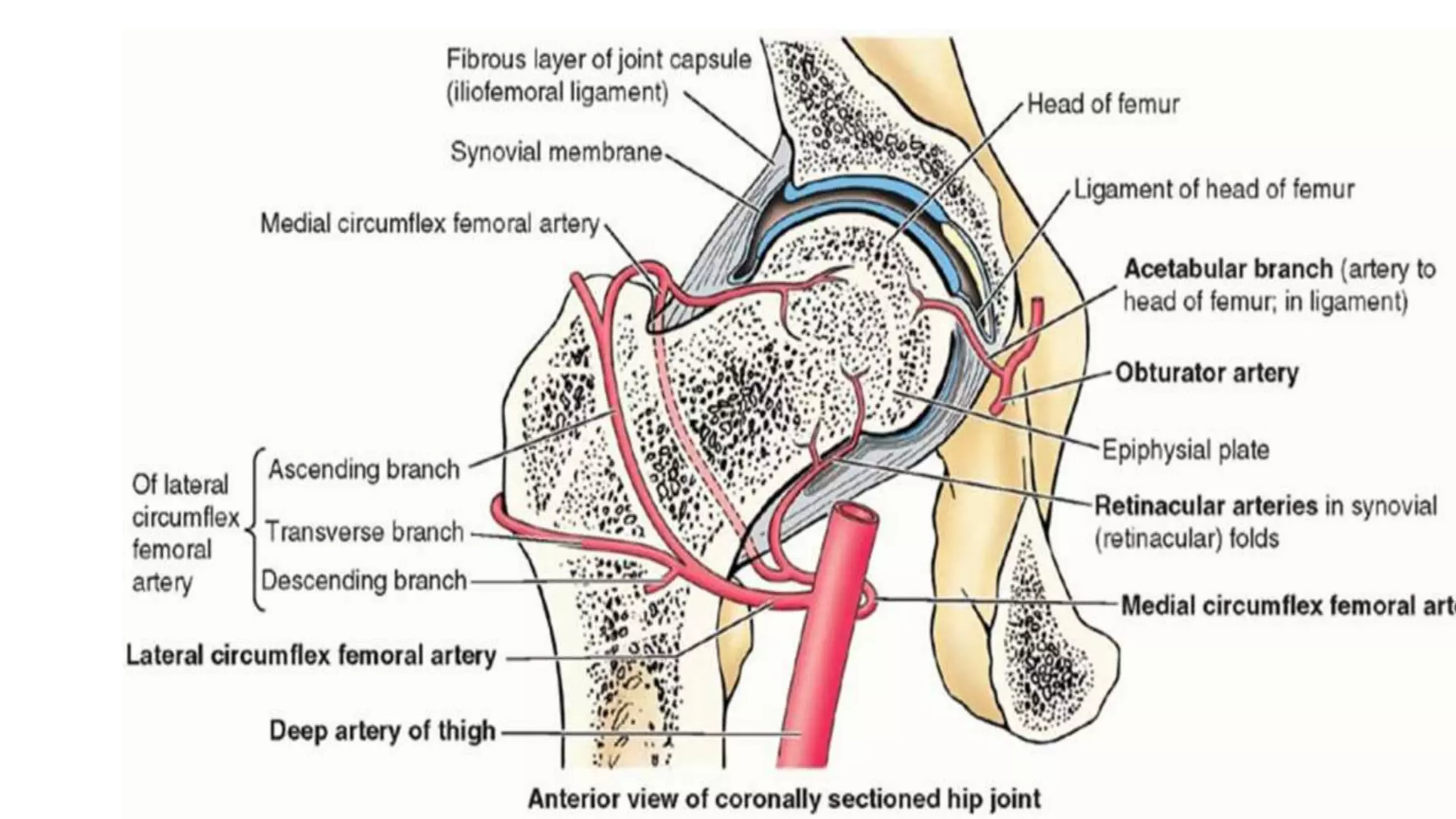
The hip joint is a ball and socket synovial joint that allows for multiaxial movement. It has a spherical femoral head that fits into the acetabulum of the pelvis. Strong ligaments like the iliofemoral ligament provide stability, while a fibrous capsule and labrum surround and deepen the socket. Blood is supplied by arteries around the joint and nerves are provided by branches of the femoral, obturator, and superior gluteal nerves. Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation allow for a wide range of motion.