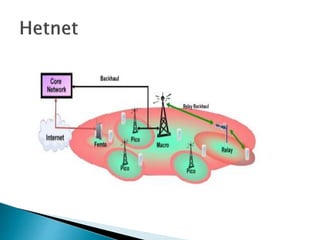
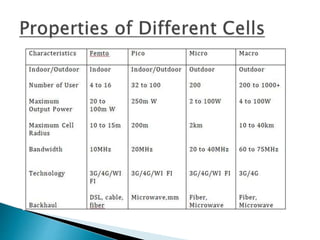
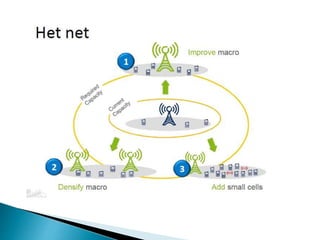
The document discusses Heterogeneous Networks (HetNets) which use a combination of different cellular technologies and base station types to increase network capacity and improve coverage. HetNets integrate macro cells, small cells like femtocells and picocells, and WiFi access points. This allows operators to boost capacity in high demand areas and extend indoor coverage. HetNets provide enriched capacity, guaranteed coverage, and help maximize the cost efficiency of building new networks.