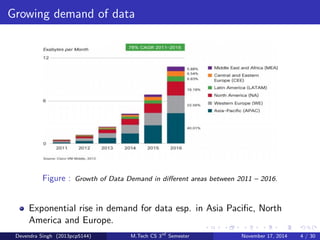
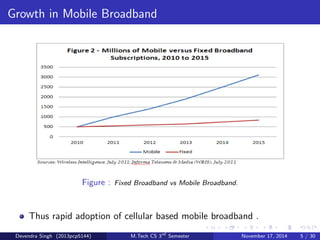
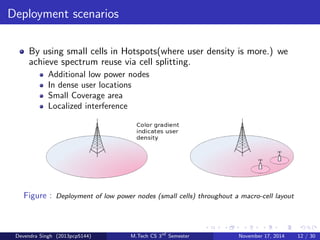
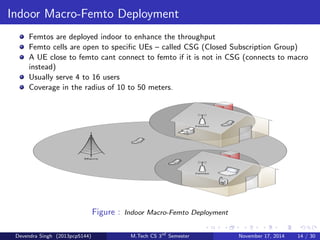
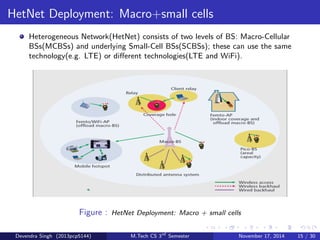
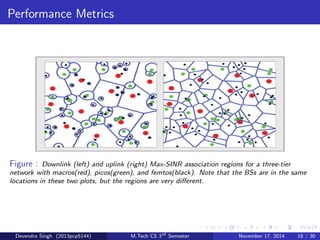
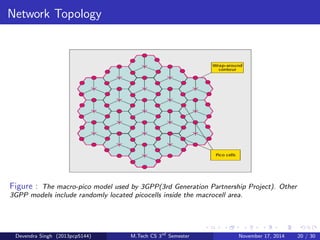
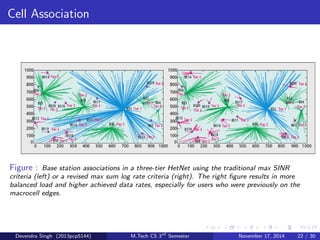
The document discusses the concept of heterogeneous networks (hetnets) as a solution to the growing demand for data in mobile broadband, caused by an increasing number of connected devices. It outlines the advantages of hetnets, such as capacity scaling, low power requirements, and the need for effective interference management and mobility optimization. The paper concludes that hetnets will be crucial for the future of mobile cellular networks, emphasizing their flexibility and efficiency in handling increasing data traffic.