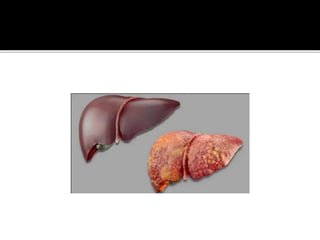
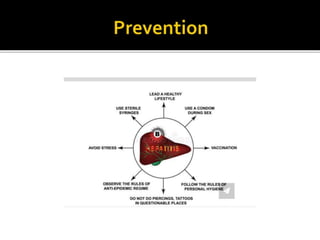
The document is a submission by Binuka Dahal on Hepatitis B virus, detailing its structure, epidemiology, transmission, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. Hepatitis B is a viral liver infection affecting millions worldwide, characterized by acute and chronic phases, with various modes of transmission and several treatment options including antiviral medications and liver transplant. The document also highlights the importance of vaccination and post-exposure prophylaxis with HBIG.