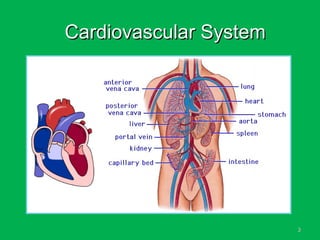
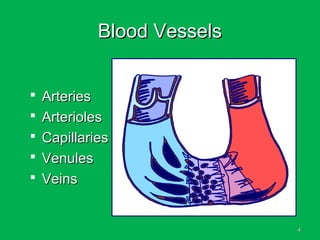
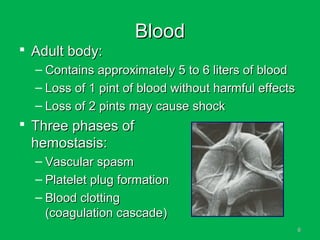
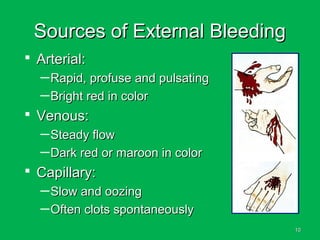
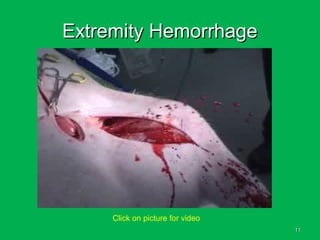
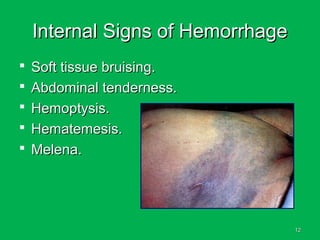
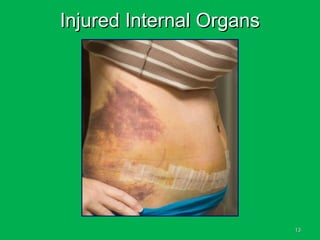
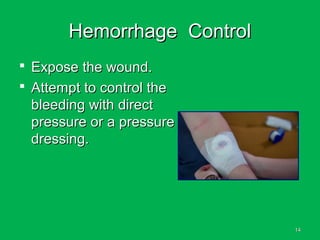
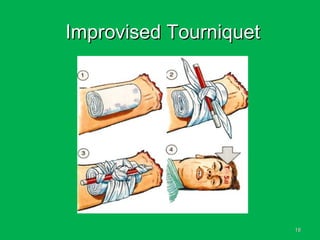
This document discusses methods of hemorrhage control in the pre-hospital setting. Hemorrhage is the leading cause of preventable death in trauma. The document outlines signs of blood loss and sources of external and internal bleeding. It describes techniques for hemorrhage control including applying direct pressure, pressure dressings, and tourniquets. The goals of pre-hospital care are continuing hemorrhage control and rapid transport to a surgical facility to prevent patients from bleeding to death.