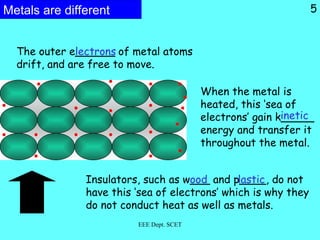
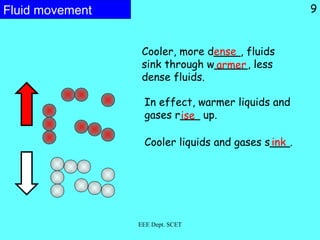
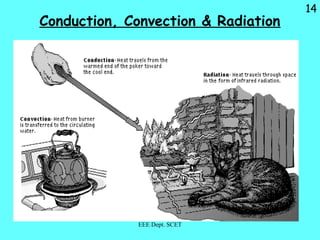
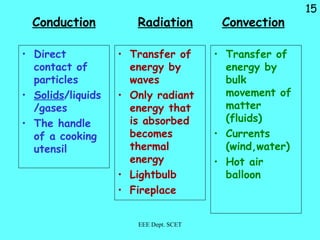
Thermal energy can be transferred through three modes: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves the direct transfer of energy between particles in direct contact, such as in solids. Convection is the transfer of energy by the bulk movement of fluids like liquids and gases. Radiation transfers energy through electromagnetic waves and does not require a medium, allowing heat transfer through a vacuum like from the sun to Earth.