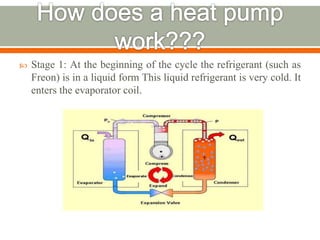
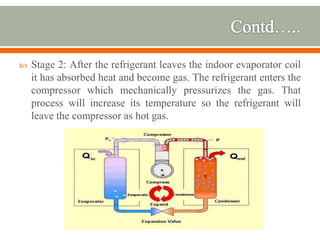
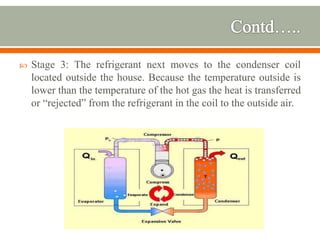
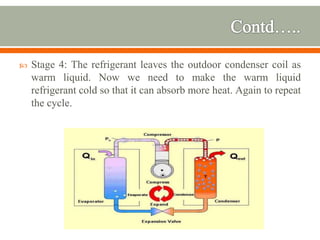
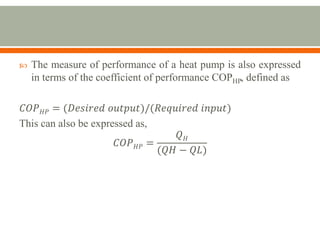
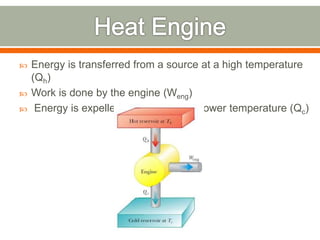
The document discusses heat pumps and heat engines. It explains that a heat pump uses mechanical energy to transfer heat from one place to another, with a coefficient of performance (COP) measuring its efficiency. A heat engine absorbs heat to do work on its surroundings, with its efficiency measured by how much work it produces relative to the heat absorbed. Common applications of heat pumps include heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems, while examples of heat engines are steam engines and internal combustion engines.