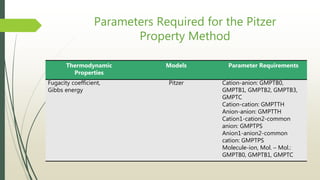
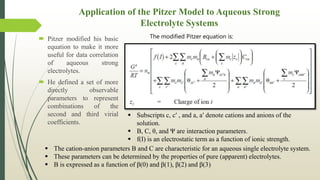
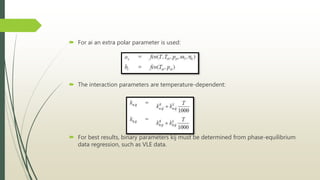
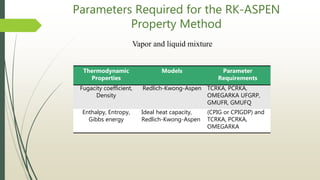
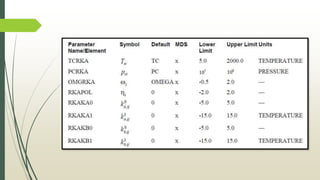
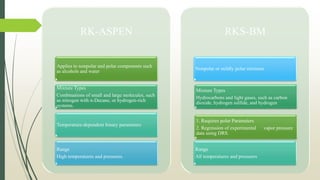
The document discusses the Pitzer and RK-ASPEN property methods in ASPEN Plus. The Pitzer method is based on an aqueous electrolyte activity coefficient model that can accurately calculate behavior of aqueous electrolyte solutions up to 6 molal ionic strength. The RK-ASPEN method uses the Redlich-Kwong-Soave equation of state with temperature-dependent binary parameters, allowing it to model mixtures of nonpolar and slightly polar compounds like alcohols and water at high temperatures and pressures. Both methods require regressed interaction parameters from experimental data to model various thermodynamic properties.