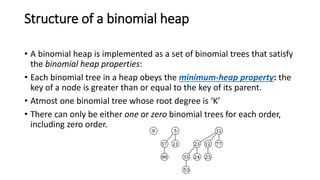
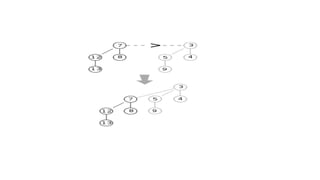
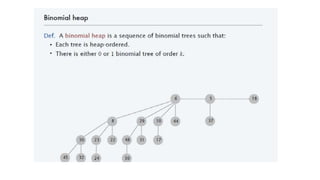
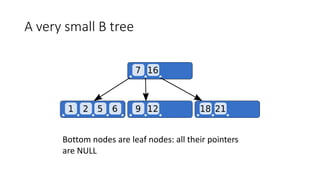
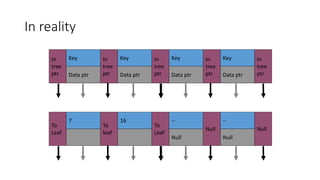
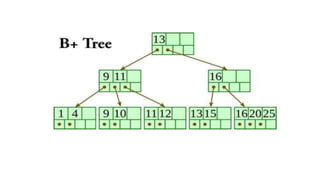
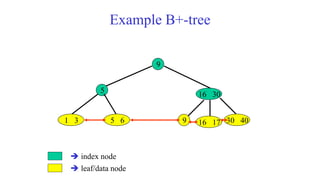
A Fibonacci heap is a data structure used to implement priority queues. It is composed of a collection of heap-ordered trees that store minimum priority elements. Each node stores a key-value and pointers to its parent and children. Operations like insertion, deletion, and decreasing key values are performed using cuts, melds, and tree rotations to maintain the heap properties. Fibonacci heaps support these operations in amortized O(1) time through techniques like lazy merging of trees and path compression. They are useful for graph algorithms like Dijkstra's and Prim's algorithms that require efficient priority queue operations.
























![• Disjoint set operations
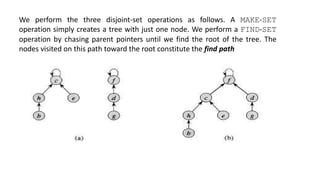
1. Make Set - c
2. FIND
3. UNION
• Detecting the Cycles
DSJ is useful for detecting the Cycle in undirected graph. Example Kruskal’s
Algorithm, If the set consist of elements in same sets, lets say cycle.
• Disjoint set using Sets
• Disjoint set using Graph representation [weighted Union, and Find
Collapsing]
• Disjoint set using Array
• Disjoint set using Rank and Path Compression](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter6-230317140932-f8f46f74/85/chapter-6-1-pptx-45-320.jpg)

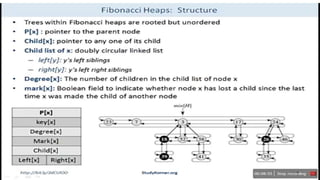
![Introduction
• Called a lazy data structure
• Delay work for as long as possible
• Collection of heap ordered Trees
• Each Tree is rooted but unordered
• It maintains pointer to minimum elements
• It set marked nodes
• Each node X has pointed p[X] to its parent and child [X] to one of its
children
• Fibonacci heaps, in fact, are loosely based on binomial heaps
• Children are linked together represents by circular, doubly linked list.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter6-230317140932-f8f46f74/85/chapter-6-1-pptx-47-320.jpg)

![Properties and Notations used in Fibonacci
heaps
1. Set of Heap ordered trees
2. Maintain pointer to minimum element Properties
3. Set of marked nodes
• n[H] = number of nodes in heap.
• degree/rank(x) = number of children of node x.
• degree/ rank(H) = max rank of any node in heap H. Notations
• trees(H) = number of trees in heap H.
• marks(H) = number of marked nodes in heap H.
• Min (H)= minimum key in heap](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter6-230317140932-f8f46f74/85/chapter-6-1-pptx-51-320.jpg)
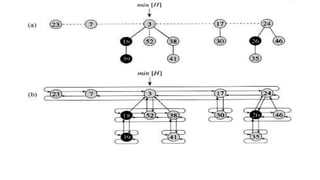


![Create Fibonacci heaps
n[H] = 0 and min[H] = NIL; there are no trees in H.
Because t (H) = 0 and m(H) = 0, the potential of the empty Fibonacci
heap is Ф(H) = 0.
The amortized cost of MAKE-FIB-HEAP is thus equal to its O(1) actual
cost.
Steps:
1. Set of heap-ordered trees.
2. Maintain pointer to minimum element.
3. Set of marked nodes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter6-230317140932-f8f46f74/85/chapter-6-1-pptx-55-320.jpg)
