The document discusses heap trees, including their definition, representation, operations, and applications. It defines a heap tree as a complete binary tree where the value of each parent node is greater than or equal to its children (for max heaps) or less than or equal (for min heaps). Heap trees can be represented using an array. Common operations are insertion, deletion, and merging. Key applications include sorting algorithms like heapsort and implementing priority queues.





![7
Max heap tree
╸ The value of the parent node
should be greater than or equal to
either of its children.
╸ Or
╸ In other words, the max heap can
be defined as for every node I; the
value of node I is less than or
equal to its parent value except
the root node. Mathematically, it
can be defined as:
A[Parent(i)] >= A[i]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heaptree-211108065112/85/Heap-tree-7-320.jpg)

![9
Min heap tree
╸ The value of the parent node
should be less than or equal to
either of its children.
╸ Or
╸ In other words, the min-heap can
be defined as, for every node I, the
value of node I is greater than or
equal to its parent value except
the root node. Mathematically, it
can be defined as
A[Parent(i)] <= A[i]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heaptree-211108065112/85/Heap-tree-9-320.jpg)

![Representative of a heap tree
11
╸ A binary heap is typically represented as array. The
representation is done as:
The root element will be at A[0].
Below table shows indexes of other nodes for the ith node,
i.e., A[i]:
A[(i-1)/2] Returns the parent node
A[(2*i)+1] Returns the left child node
A[(2*i)+2] Returns the right child node
The traversal method use to achieve Array representation is
Level Order](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heaptree-211108065112/85/Heap-tree-11-320.jpg)



![Algorithm InsertMaxHeap
Input: ITEM, the data to be interested; the strength of node
Output:ITEM,is inserted into the heap tree.
Data structure: Array A[1……SIZE] storage the heap tree;N being t
the tree.
Steps:
1. If(N≥SIZE)then
2. Print”Heap tree is saturated: Insertion is void”
3. Exit
4. Else
5. N=N+1
6. A[N]=ITEM
7. i=N
8. p=I div 2.
9. While (p>0)and(A[p]<A[I]) do
10. temp=A[I] 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heaptree-211108065112/85/Heap-tree-15-320.jpg)
![11. A[I]=A[p]
12. A[p]=temp
13. I=p
14. p=p div 2
15. EndWhile
16.EndIf
17.Stop
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heaptree-211108065112/85/Heap-tree-16-320.jpg)

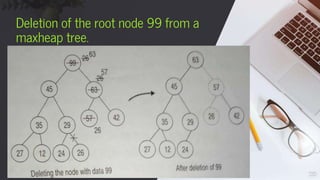
![Algorithm DeleteMaxHeap
Input: A heap tree with elements.
Output:ITEM,is being the data deleted and the remaining tree after de
Data structure: Array A[1……SIZE] storage the heap tree;N is the numb
Steps:
1. If(N=0)then
2. Print”Heap tree is exhausted:Deletion is not possible”
3. Exit
4. Endif
5. ITEM=A[1]
6. A[1]=A[N]
7. N=N-1
8. Flag=FALSE,I=1
9. While (flag=FALSE)and(i<N) do
10. lchild=2*I,rchild=2*I+1
11. . If(lchild≤N)then
12. x=A[lchilld]
13. Else
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heaptree-211108065112/85/Heap-tree-18-320.jpg)
![Algorithm DeleteMaxHeap
16. If(rchild≤N)then
17. x=A[rchilld]
18. Else
19. x=-∞
20. EndIf
21. If(A[I]>x) and (A[I]>y) then
22.. Flag=TRUE
23.. Else
24. If(x>y)and (A[i]>x)
25. Swap(A[I],A[lchild])
26. I=lchild
27.. Else
. If(y>x)and (A[i]>y)
Swap(A[I],A[rchild])
I=rchild
28.. EndIf
29.. EndIf
30.. EndIf
31.. EndWhile
32.Stop
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heaptree-211108065112/85/Heap-tree-19-320.jpg)



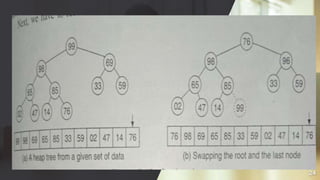
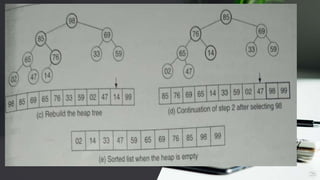
![Algorithm HeapSort
Input: A set of N input data.
Output: sorted data in ascending order.
Data structure: An Array A where the data will be stored.
Steps:
1. BuildMaxHeap(A)
2. I=N
3. While (I>1) do
4. swap(A[1],A[I])
5. i=i-1
6. j=1
7. While (j<I)do
8. lchild=2*j
9. rchilld=2*j+1
10. If(A[j]<A[lchild]) and (A[lchild]>A[rchilld]) then
11. Swap(A[j],A[lchild])
12. j=lchild
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heaptree-211108065112/85/Heap-tree-26-320.jpg)
![Algorithm HeapSort
13.. Else
14. If(A[j]<A[rchild]) and (A[rchild]>A[lchilld]) th
15. Swap(A[j],A[rchild])
j=rchild
16.. Else
17. Break ();
18. EndIf
19. EndIf
20. EndWhile
21.EndWhile
22.Stop
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heaptree-211108065112/85/Heap-tree-27-320.jpg)

