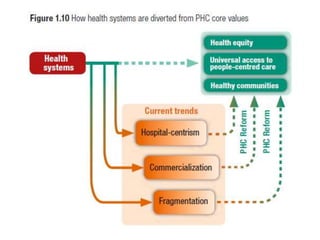
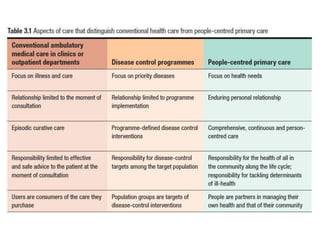
The document discusses several key aspects of health systems, including:
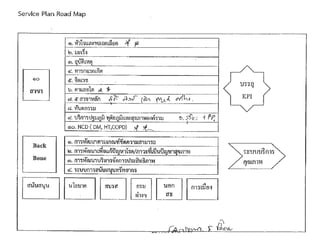
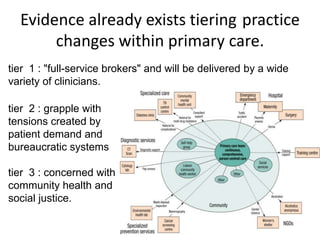
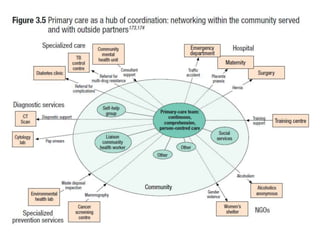
1) It outlines three tiers of primary care and examines tensions between patient demand and bureaucratic systems.
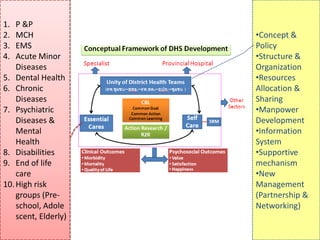
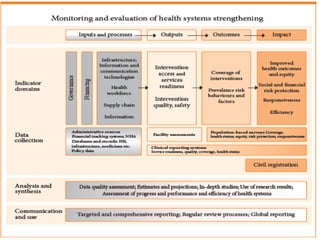
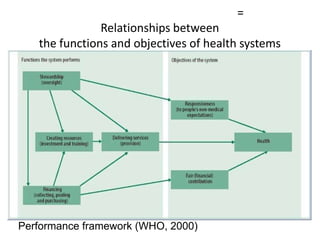
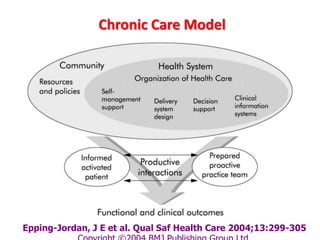
2) It explores the six building blocks of health systems according to the WHO - service delivery, health workforce, information, medical products/vaccines, financing, and leadership/governance - and how strengthening these can improve health outcomes.
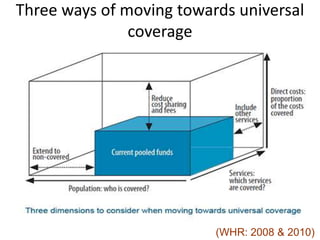
3) It presents three approaches to moving towards universal health coverage according to the World Health Report 2008: expanding health insurance, expanding public provision of personal health services, and expanding community-based health workers.


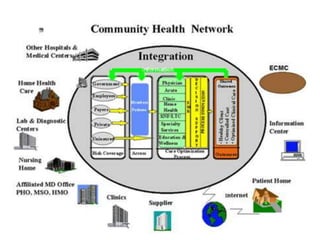
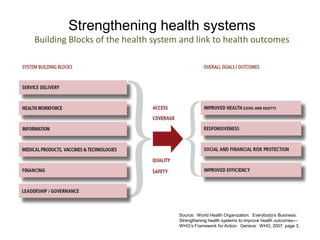

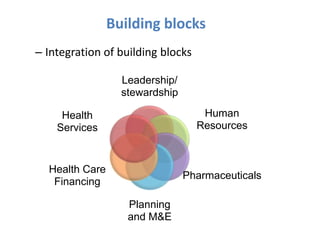


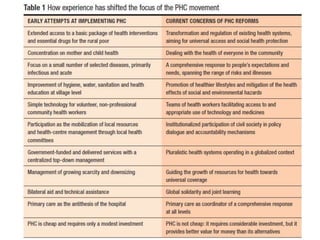



![2557-
2557
[ ]
1,056.96 1,056.96
1,018.35 1,027.94
3 281.02 271.33
4 383.61 383.61
5 14.95 14.95
6 8.19 8.19
7 128.69 128.69
8 3.32 3.32
9 - 0.10
2,895.09 2,895.09](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/healthsystemmntdevelopment-130709221243-phpapp01/85/Health-systemmn-tdevelopment-28-320.jpg)