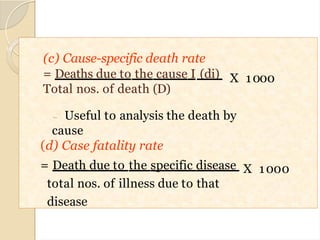
This document provides information on health statistics and vital statistics. It defines key terms like statistics, biostatistics, health statistics, and vital statistics. It discusses the importance and uses of health statistics in measuring health status, quantifying health problems, and planning health services. It describes methods of data collection from experiments, surveys, and records. It also covers data presentation methods like tabulation and diagrams. Sources of health information are also listed. The document then focuses on vital statistics and its uses. It defines vital statistics and describes sources of data for vital statistics like the civil registration system, national sample surveys, and sample registration system. It concludes by covering tools and terms used to measure mortality and fertility rates.