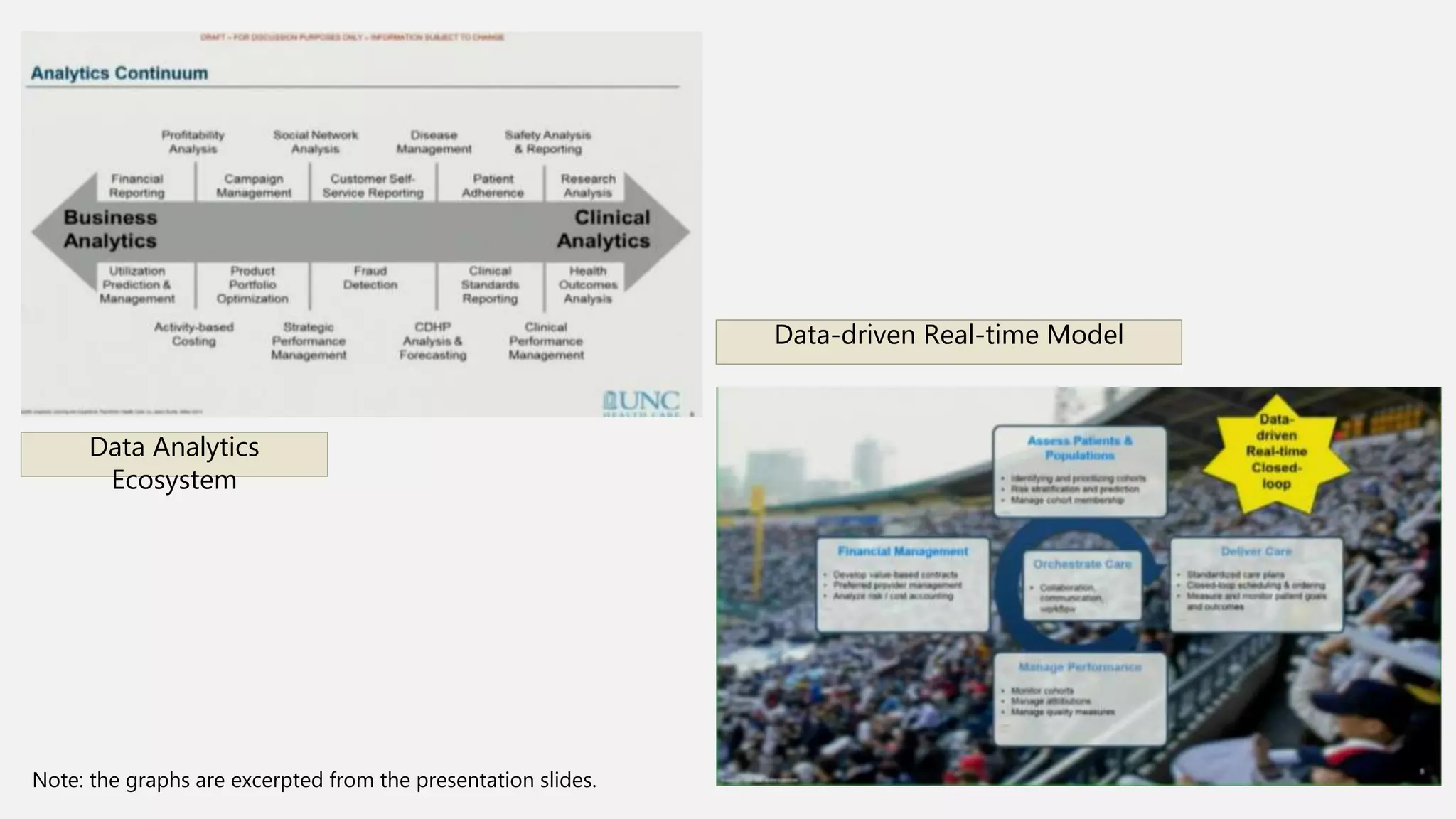
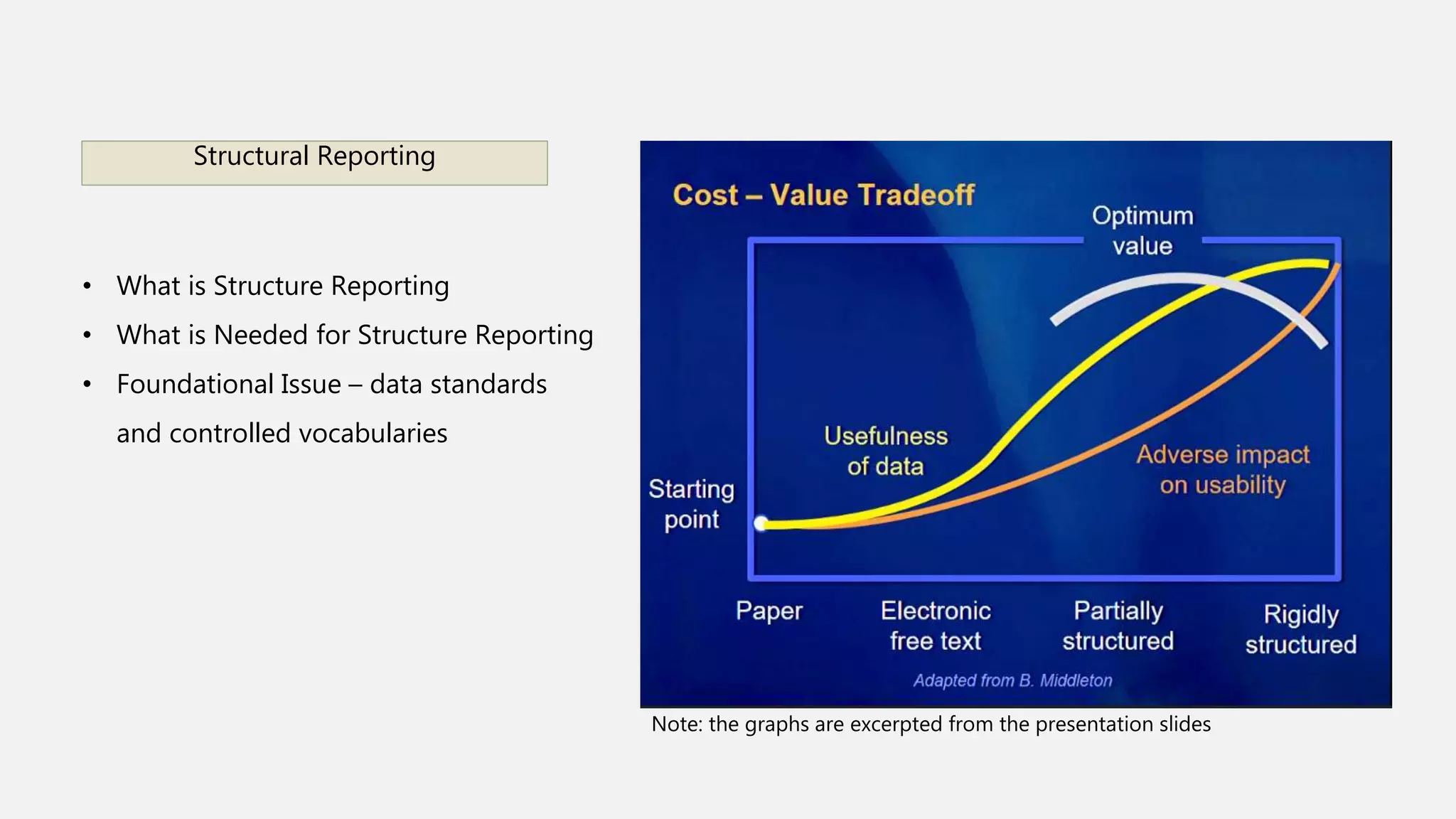
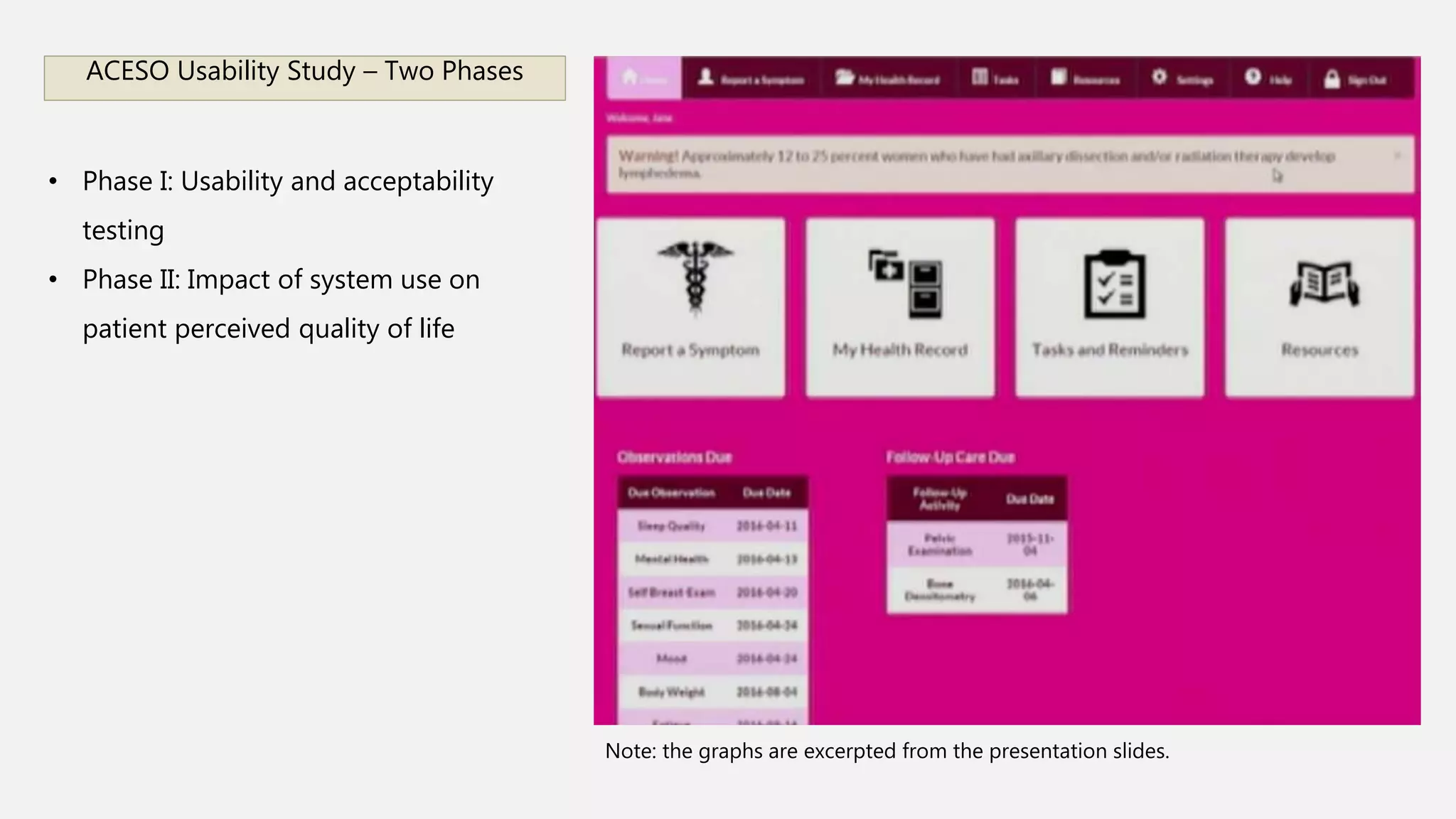
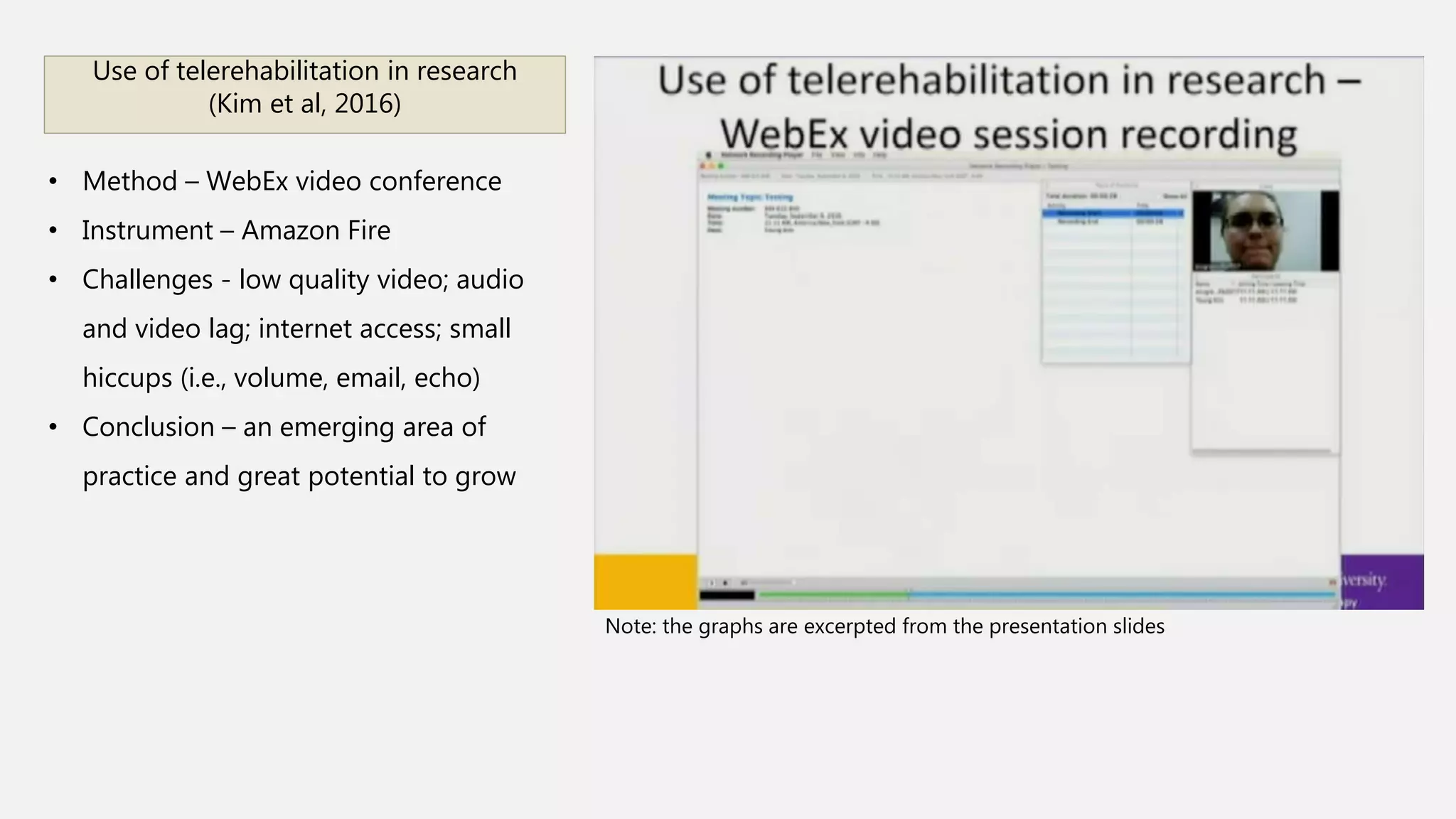
This document summarizes presentations from a health informatics seminar covering three main themes: data collection and analytics, patient-technology interaction, and clinical and translational science. It describes several presentations within each theme, including topics on sensor-based data collection, data analytics in healthcare, usability of patient portals, telerehabilitation, and using health informatics to provide healthcare solutions for those in transitional housing. The document concludes that health informatics is a growing field aimed at improving healthcare quality and reducing costs through the use of health information technology.