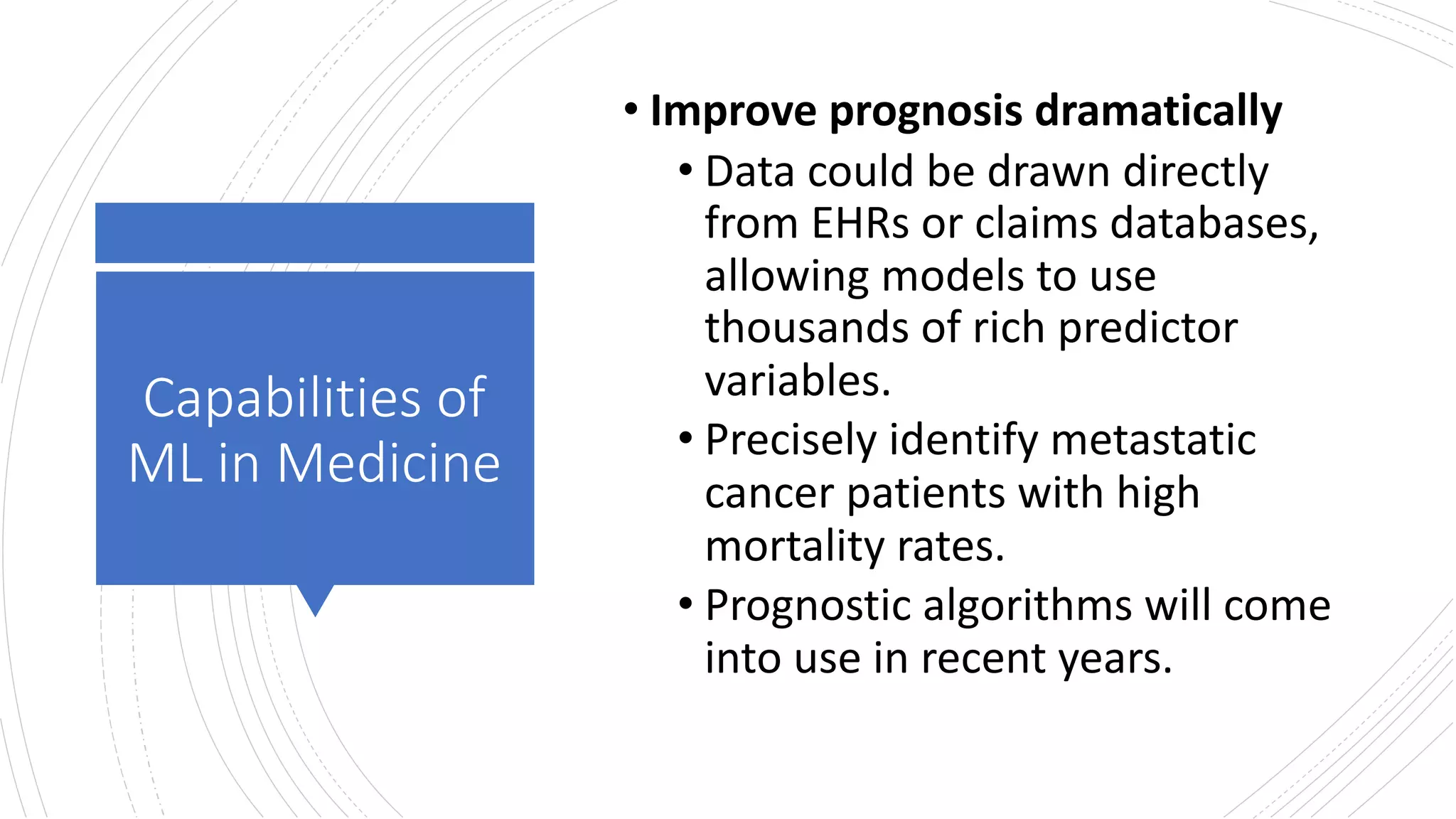
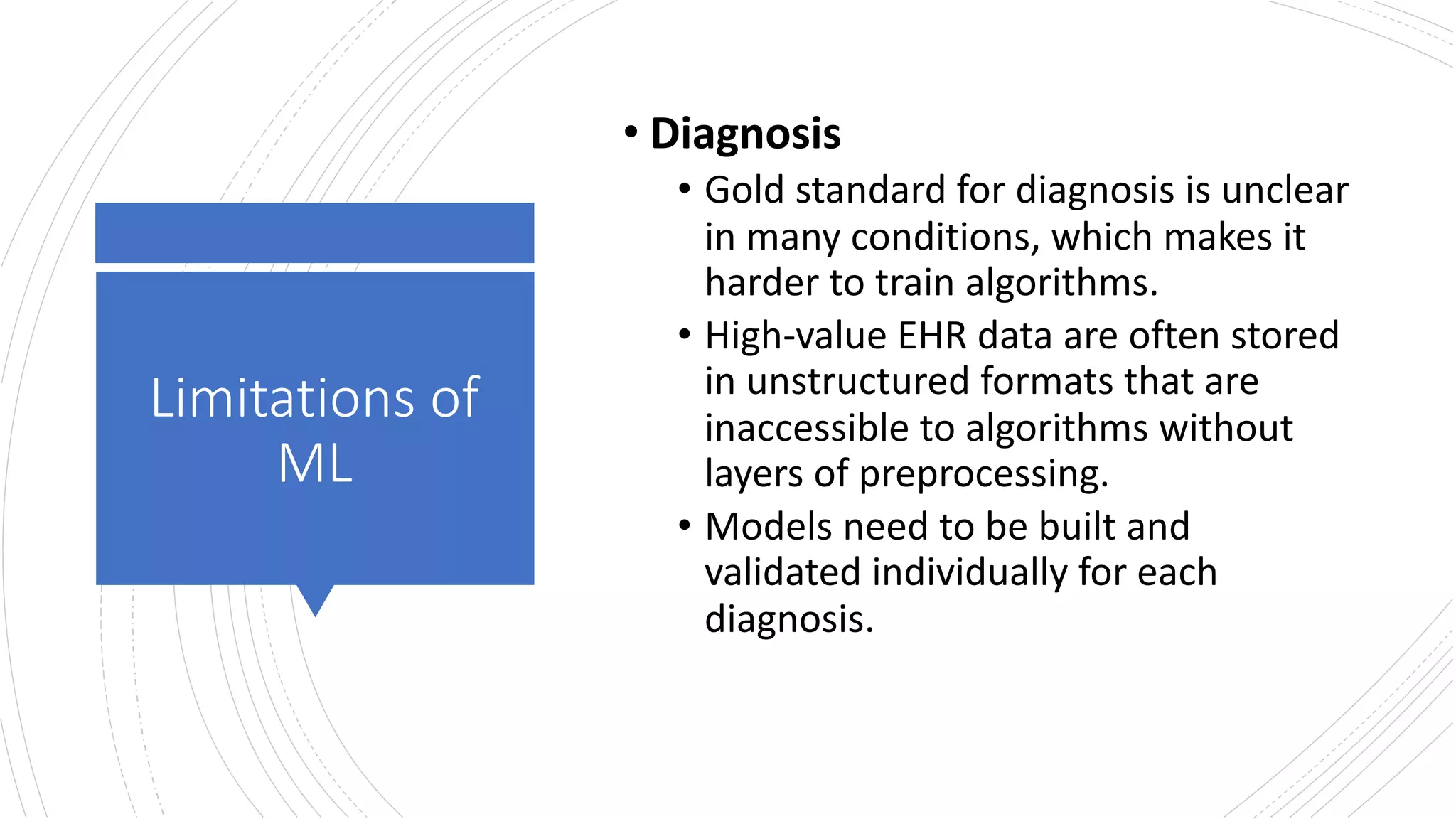
The document discusses the capabilities and limitations of machine learning (ML) in medicine, highlighting its potential to dramatically improve prognosis, diagnostic accuracy, and patient management by utilizing vast amounts of data. However, it also points out challenges such as unclear diagnostic standards, reliance on structured data, and limitations in predictive power without sufficient historical context. Solutions proposed include collecting diverse data types and reframing complex health questions to better inform predictions and interventions.