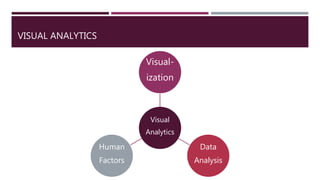
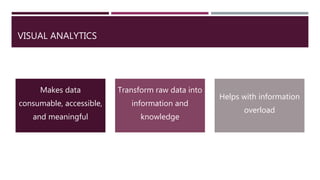
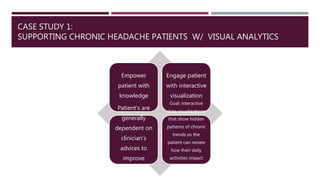
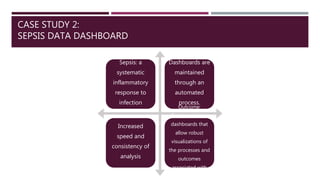
This document discusses the use of visual analytics in healthcare. It provides three case studies of using visual analytics: 1) supporting chronic headache patients by providing interactive visualizations of daily activities and their impact on conditions, 2) maintaining sepsis data dashboards through automated processes to allow robust visualizations of sepsis processes and outcomes, and 3) creating an interactive analytic injury dashboard to empower stakeholders to synthesize information to strengthen child injury surveillance, prevention and research. Visual analytics transforms raw data into meaningful information by making data accessible and helping address information overload.