1. The document discusses the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) established in 2000 and their progress and shortcomings.
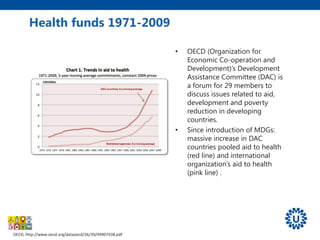
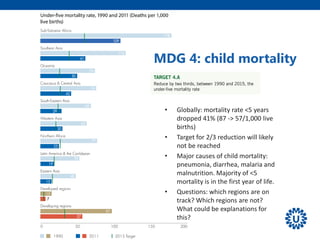
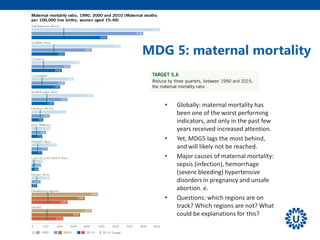
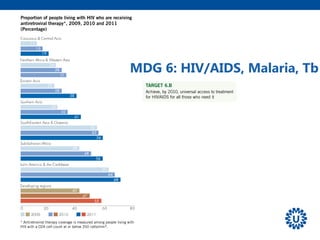
2. It provides an overview of the 8 MDGs and their targets and indicators. Overall progress on the health-related MDGs like reducing child mortality and improving maternal health was substantial but varied significantly across regions and countries.
3. Key shortcomings of the MDGs discussed are that important themes were missing, goals were narrowly defined without exploiting cross-links, and they did not sufficiently promote national ownership, equity, or multi-sectoral approaches within health systems.



![The UN Millennium Declaration
2000: UN Development Summit adopted UN
Millennium Declaration [A/Res/55/2]
• 6 values
• Freedom, equality, solidarity, tolerance, respect for nature, shared
responsibility.
• 7 key objectives
• Peace, security and disarmament, development and poverty eradication,
protection of the environment, human rights, democracy, good governance,
protection of vulnerable people, special needs Africa, strengthening UN.
• 11 development targets -> MDGs (2001)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lu9-140408032833-phpapp02/85/Health-Development-Strategies-2014-4-320.jpg)