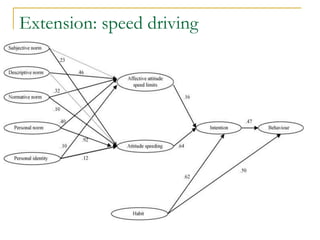
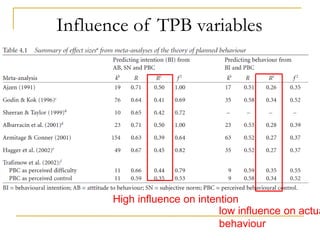
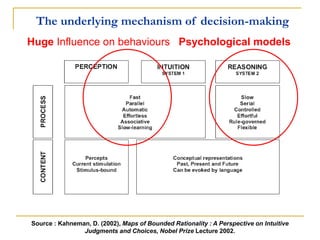
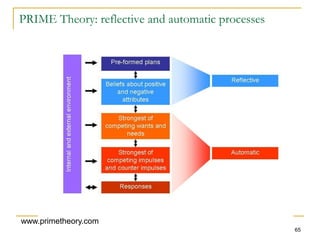
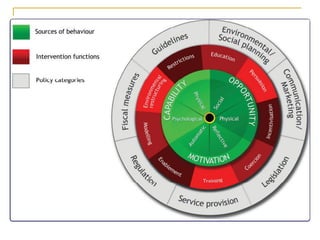
The document discusses several models of health behavior:
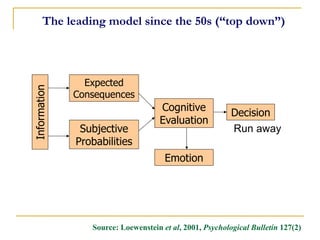
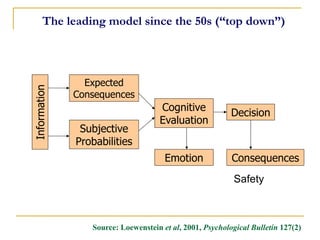
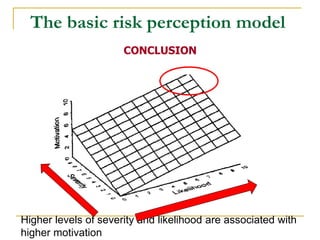
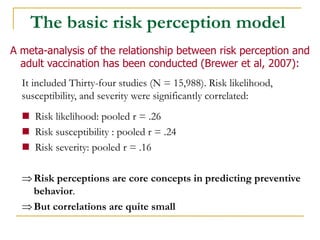
1) The Basic Risk Perception Model focuses on likelihood and severity of harm from not acting. Higher risk perception predicts greater motivation to act.
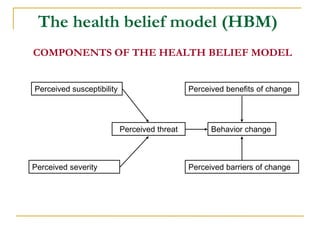
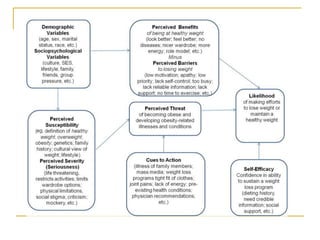
2) The Health Belief Model includes perceived susceptibility, severity, benefits, and barriers in predicting preventive health behaviors. Perceived barriers are the strongest predictor.
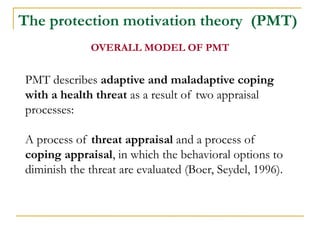
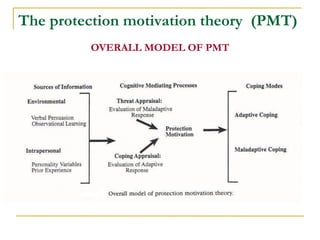
3) Protection Motivation Theory assesses threat and coping appraisal processes. Response costs have the strongest impact on health behaviors and attitudes.
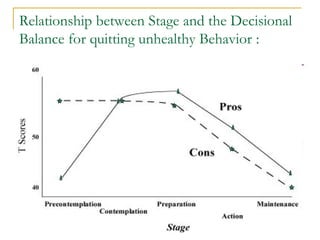
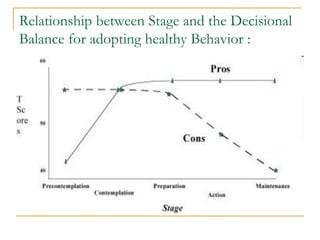
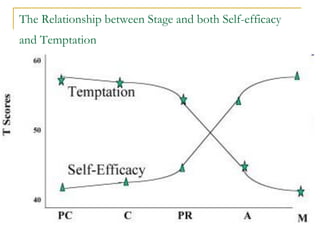
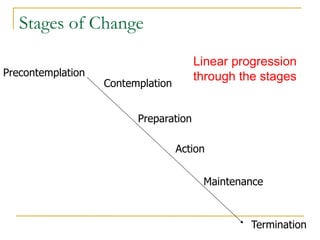
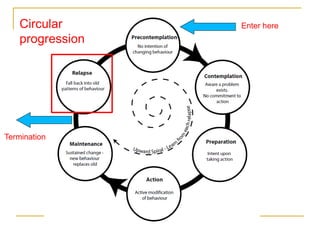
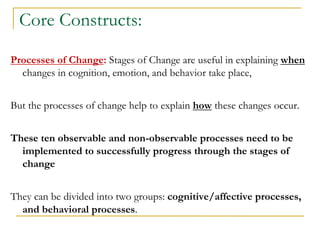
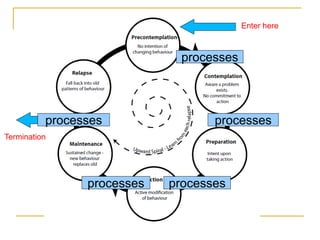
4) The Transtheoretical Model proposes stages of change and processes of change to explain behavior progression. Decisional balance and self-efficacy also predict stage of change.


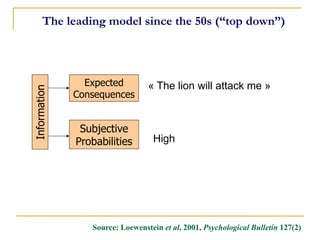
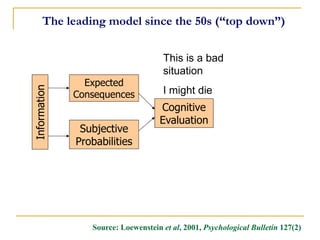
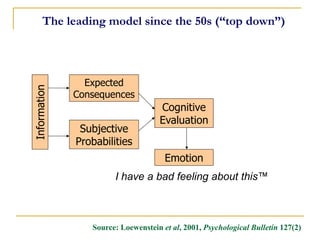












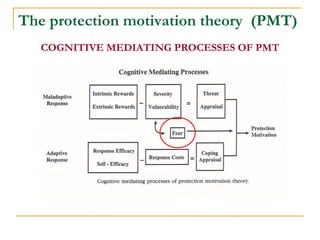
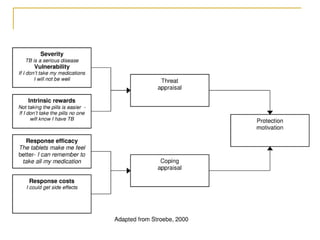


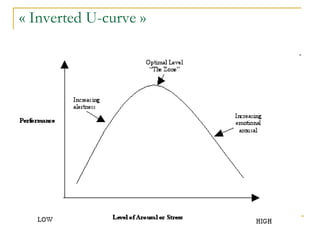



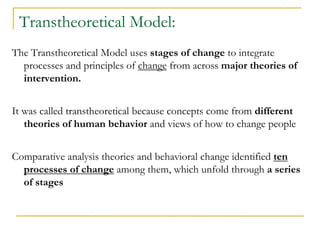



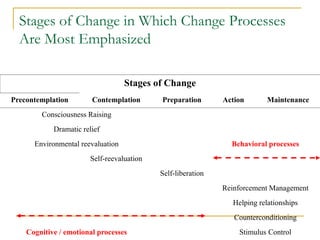
![Cognitive/Emotional Processes
Consciousness Raising [Increasing Awareness]
I recall information people had given me on how to stop smoking.
Dramatic Relief [Emotional Arousal]
I react emotionally to warnings about smoking cigarettes.
Environmental Reevaluation [Social Reappraisal]
I consider the view that smoking can be harmful to the people around me.
Social Liberation [Environmental Opportunities]
I find society changing in ways that make it easier for the nonsmoker.
Self Reevaluation [Self Reappraisal]
My dependency on cigarettes makes me feel disappointed in myself.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/healthbehaviourmodelscriticisims-141211042632-conversion-gate01/85/Health-behaviour-models-criticisims-44-320.jpg)
![Behavioral Processes
Stimulus Control [Re-Engineering]
I remove things from my home that remind me of smoking.
Helping Relationships [Supporting]
I have someone who listens to me when I need to talk about my smoking.
Counter Conditioning [Substituting]
I find that doing other things with my hands is a good substitute for
smoking.
Reinforcement Management [Rewarding]
I reward myself when I don’t smoke.
Self liberation [Committing]
I make commitments not to smoke.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/healthbehaviourmodelscriticisims-141211042632-conversion-gate01/85/Health-behaviour-models-criticisims-45-320.jpg)