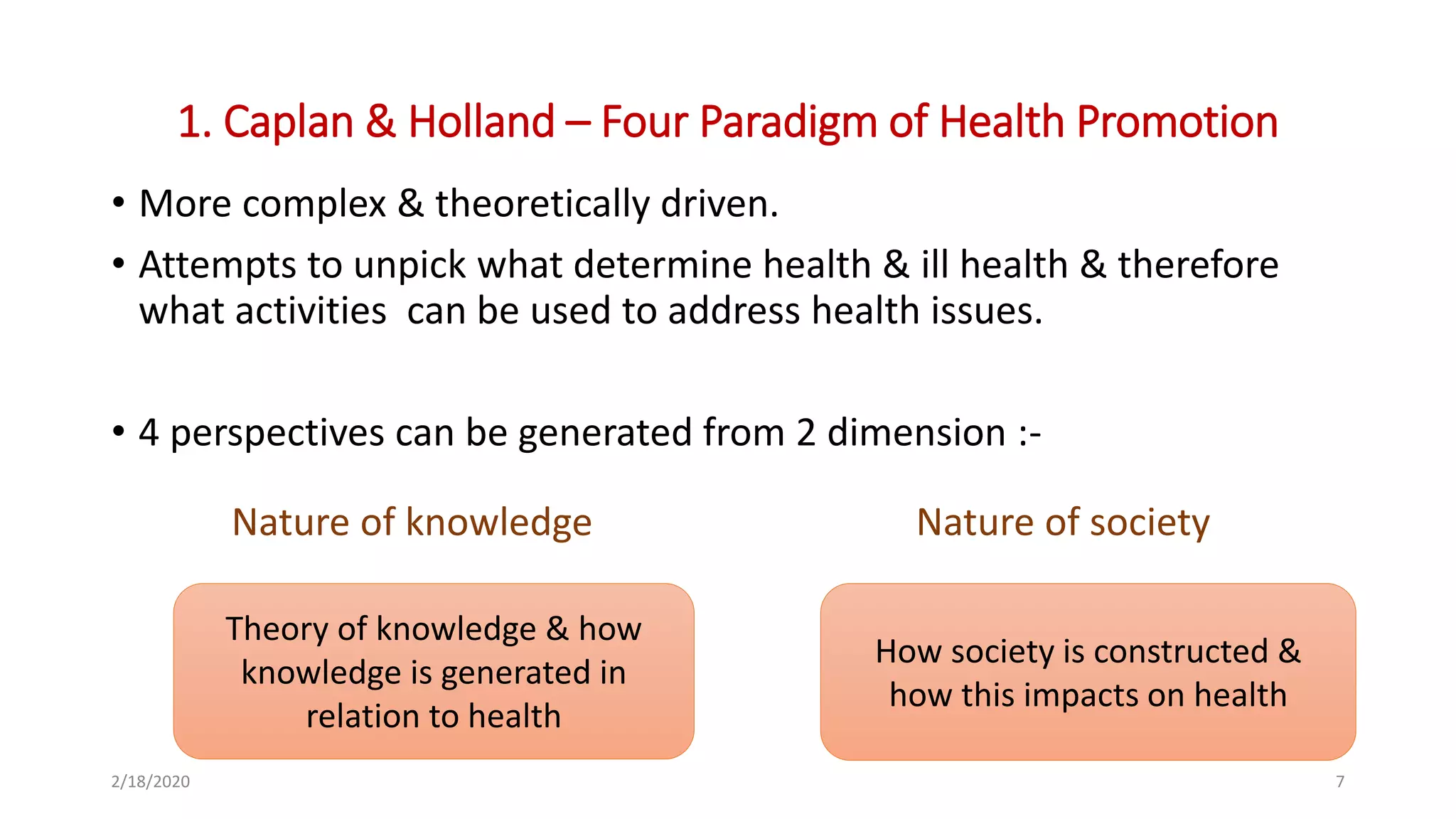
1) The document discusses several models of health promotion, including those proposed by Caplan & Holland, Beattie, Tones & Tilfors, and Tannahill.
2) Caplan & Holland's model categorizes health promotion into four paradigms based on theories of knowledge and the nature of society: traditional, humanist, radical humanist, and radical structuralist.
3) Beattie's model generates four health promotion strategies based on the mode of intervention (authoritarian vs negotiated) and focus of intervention (individual vs collective).