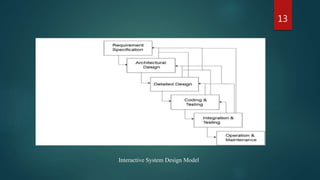
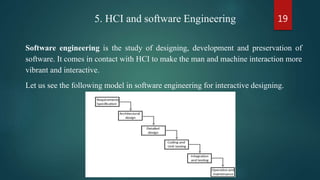
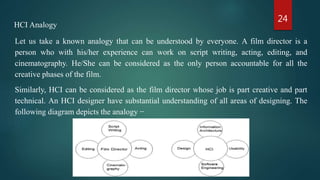
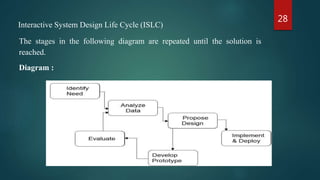
This document provides an overview of the subject of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI). It discusses the historical evolution of HCI from early computers to modern interfaces. It also covers key concepts like interactive system design, usability engineering, and the relationship between HCI and software engineering. The document outlines several topics that are important to HCI like GUI design, prototyping techniques, and research areas in HCI including ubiquitous computing and embedded systems.