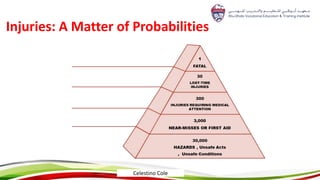
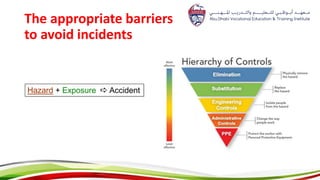
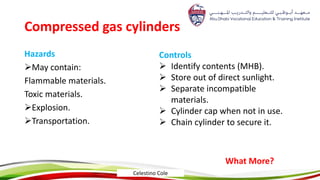
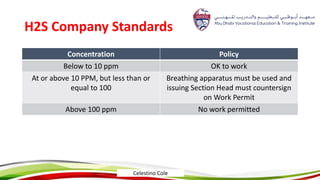
This document provides an overview of hazard recognition presented by Celestino Cole. It defines hazards and safety, outlines common workplace hazards like slips, trips, falls, tools, machines, ladders and scaffolds. It also discusses hazard controls and highlights specific hazards from cranes, forklifts, excavations, hazardous materials, compressed gas cylinders, and more. The document stresses that hazard recognition is everyone's responsibility and management must provide training to identify hazards.