Embed presentation
Downloaded 13 times









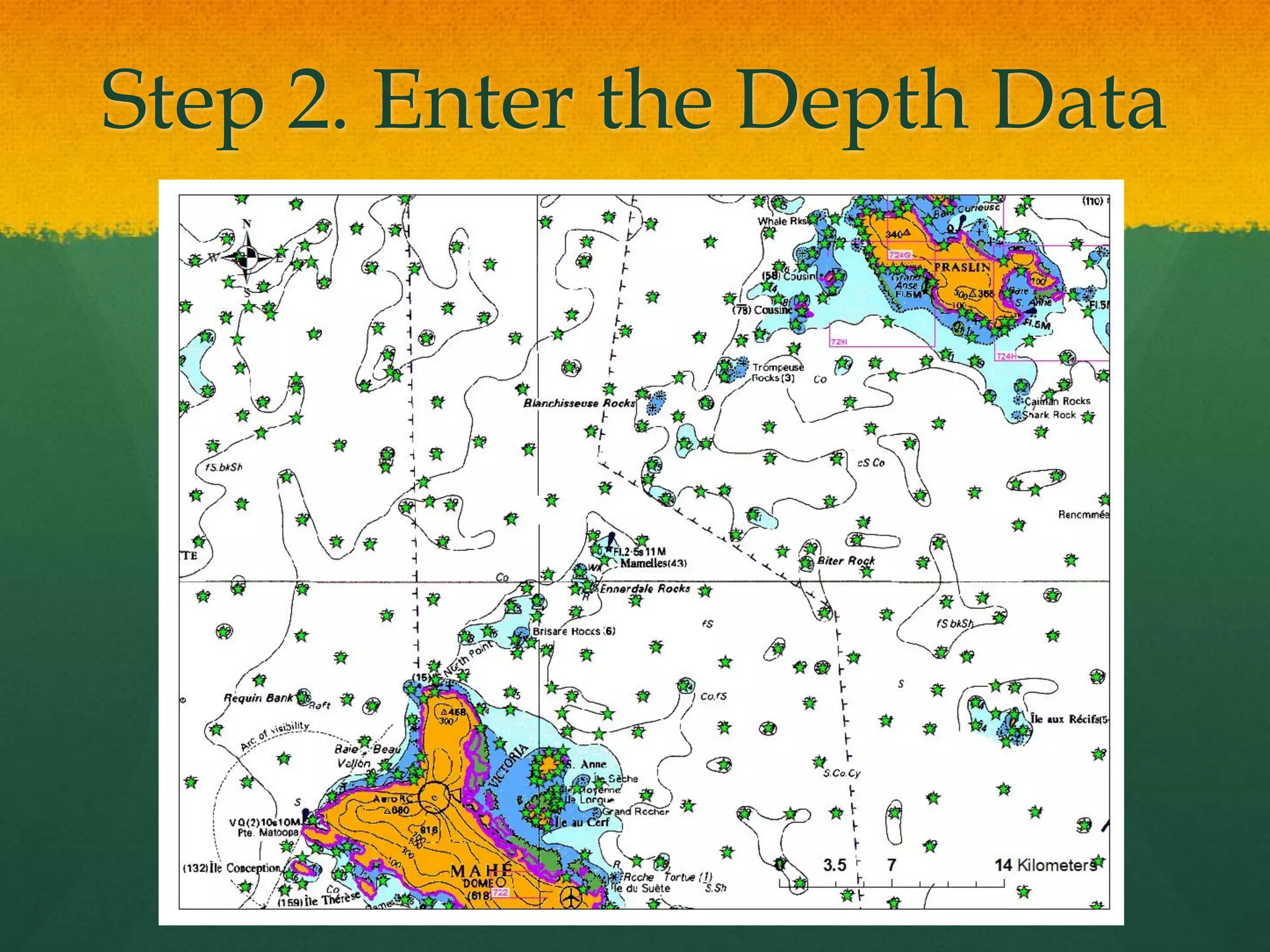

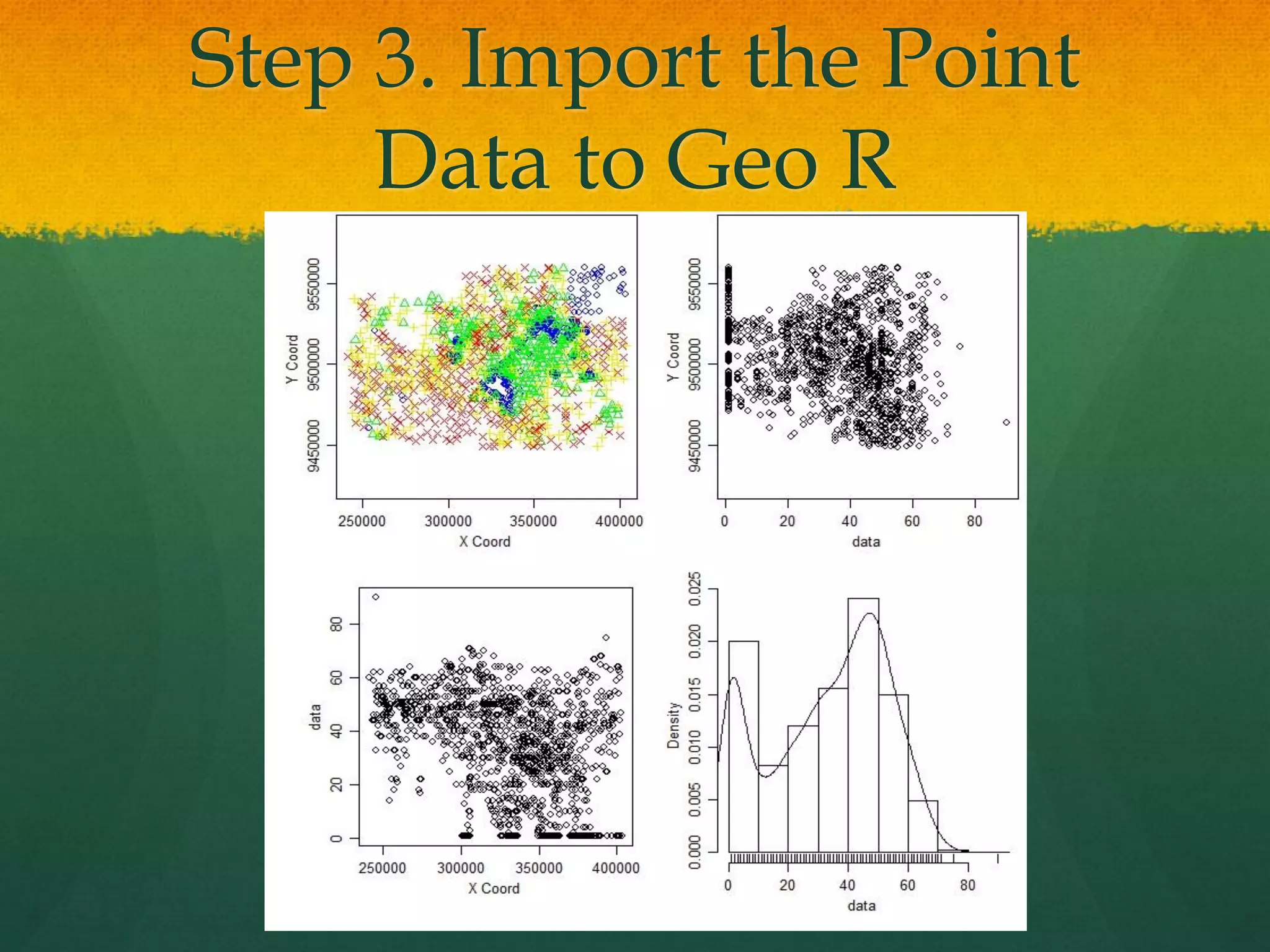
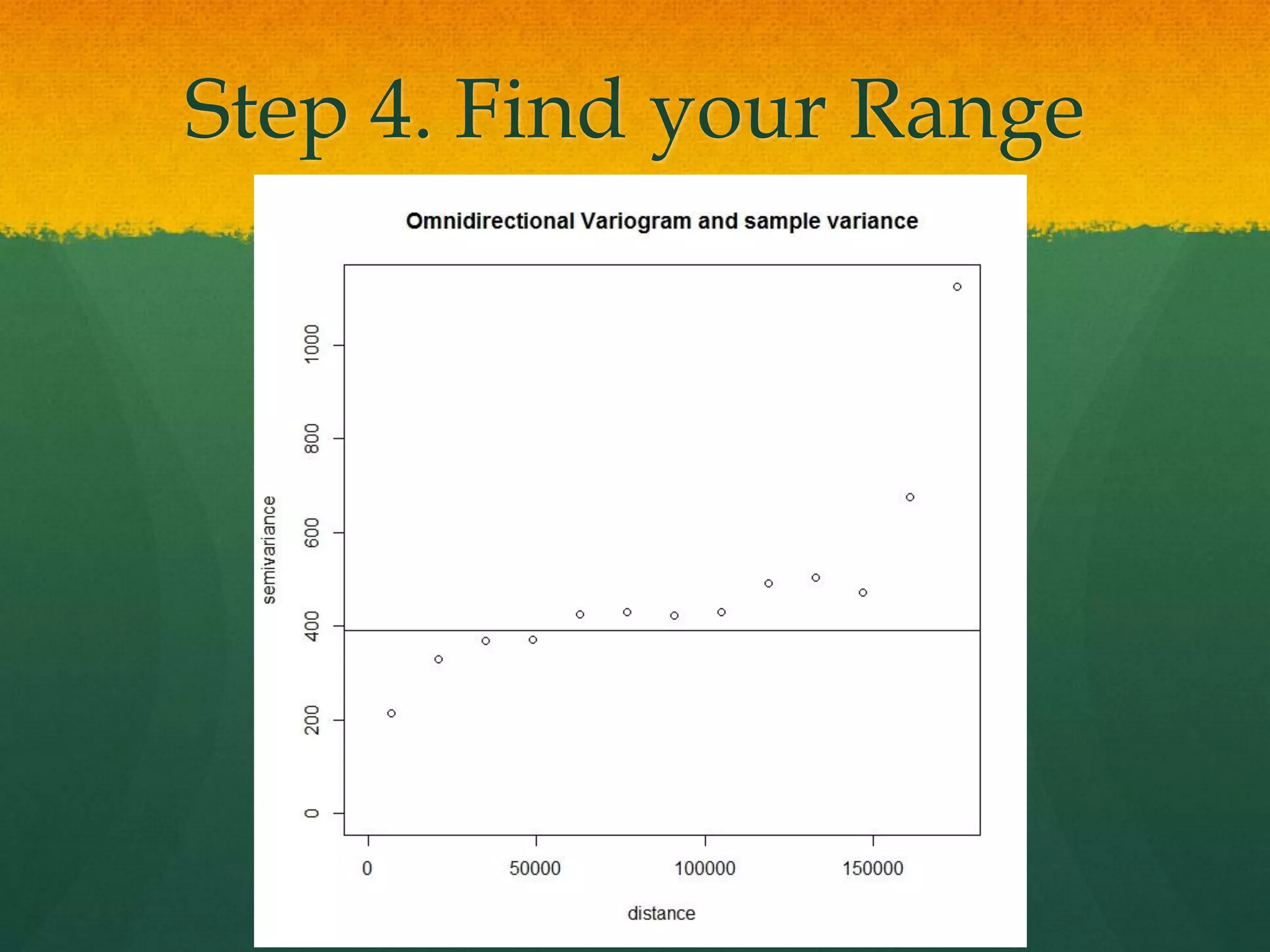

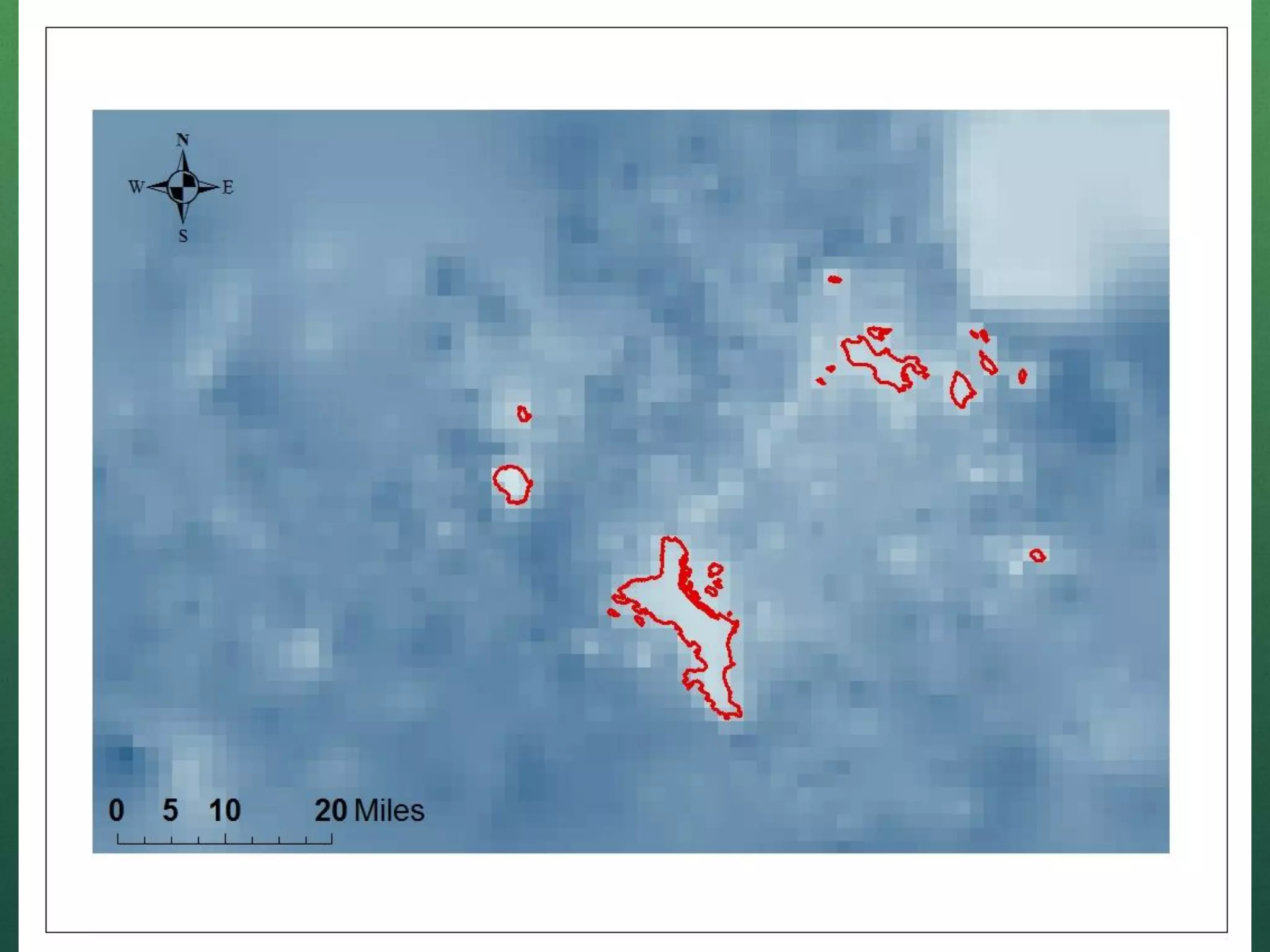
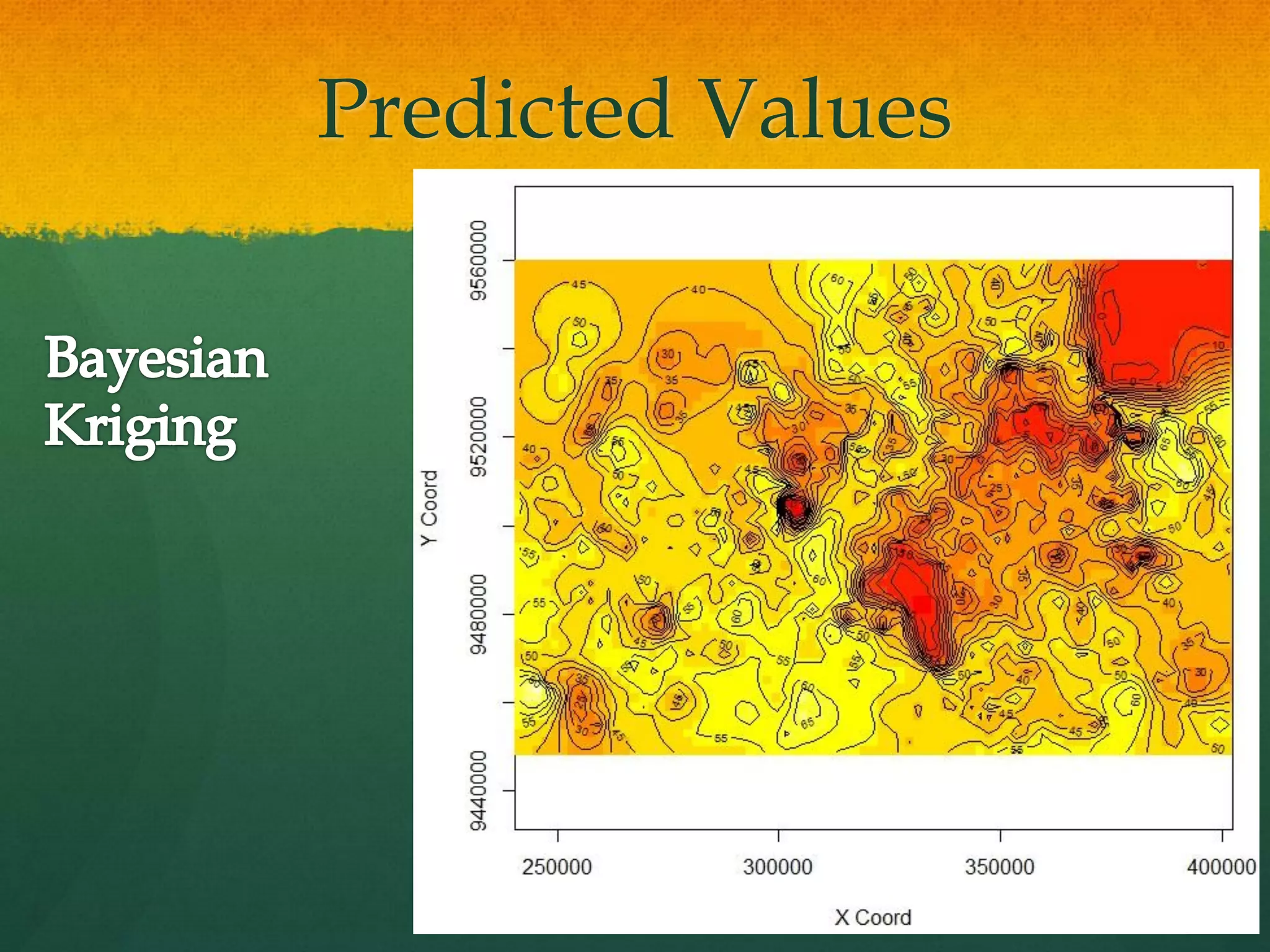
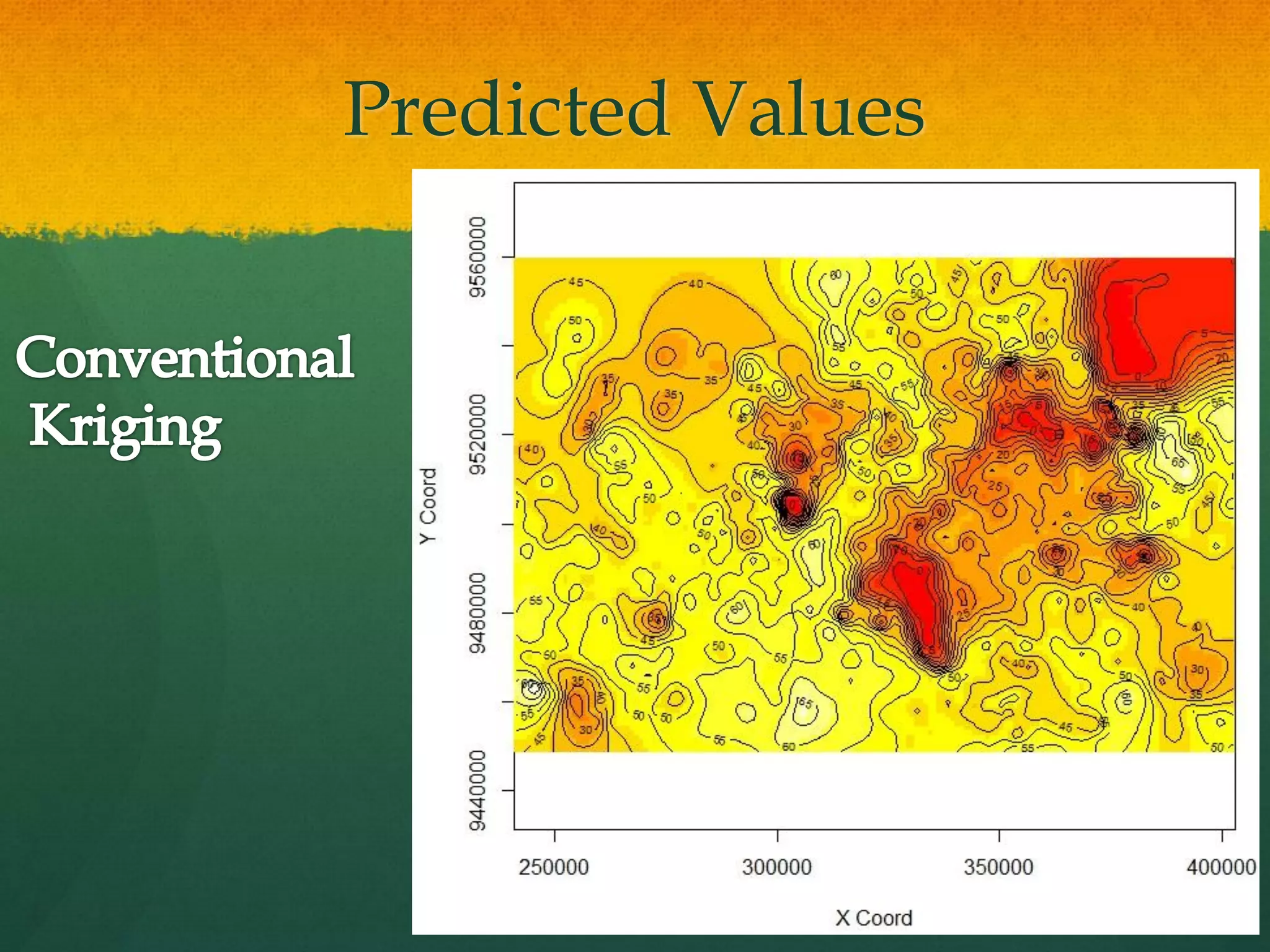
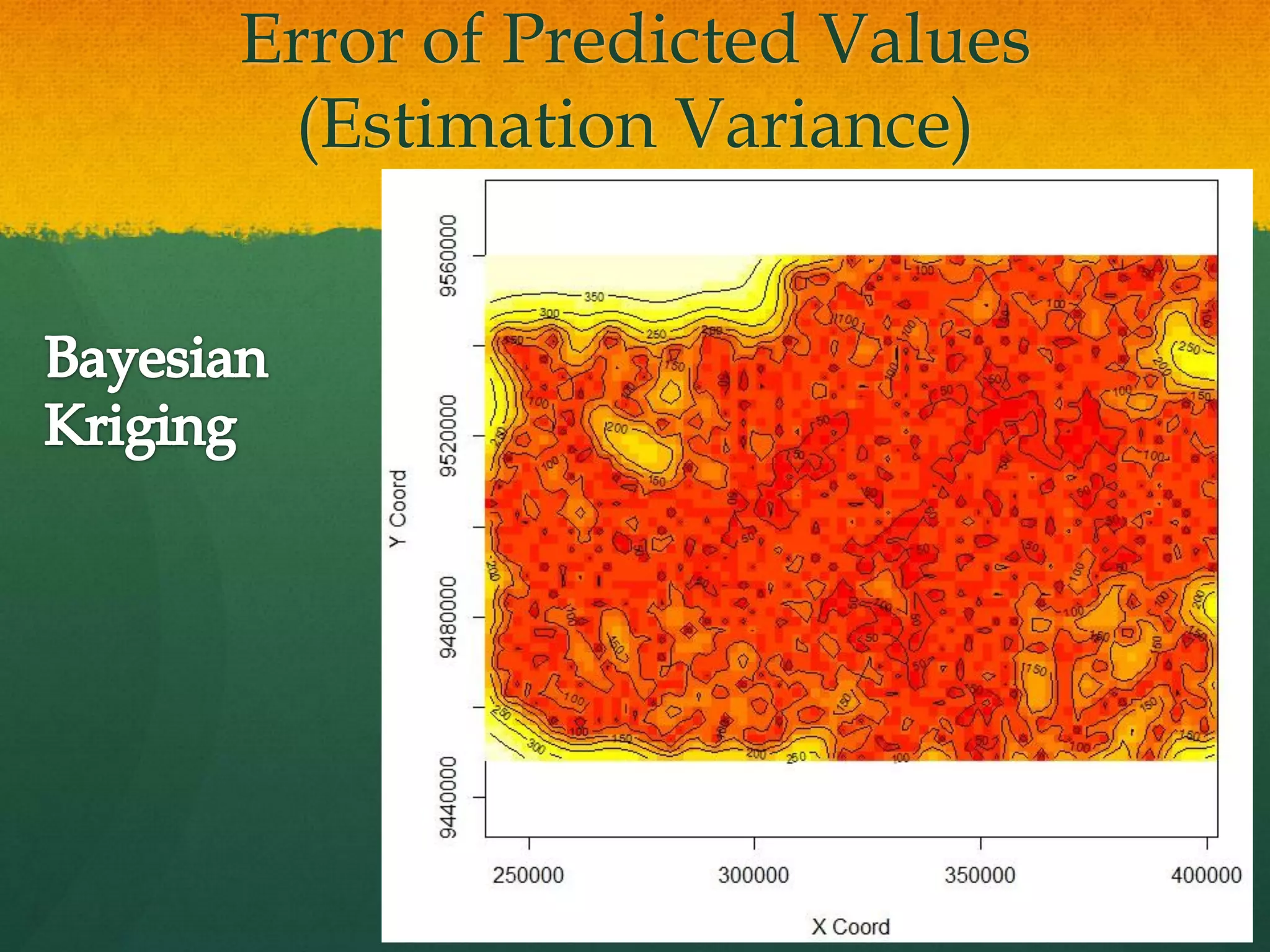
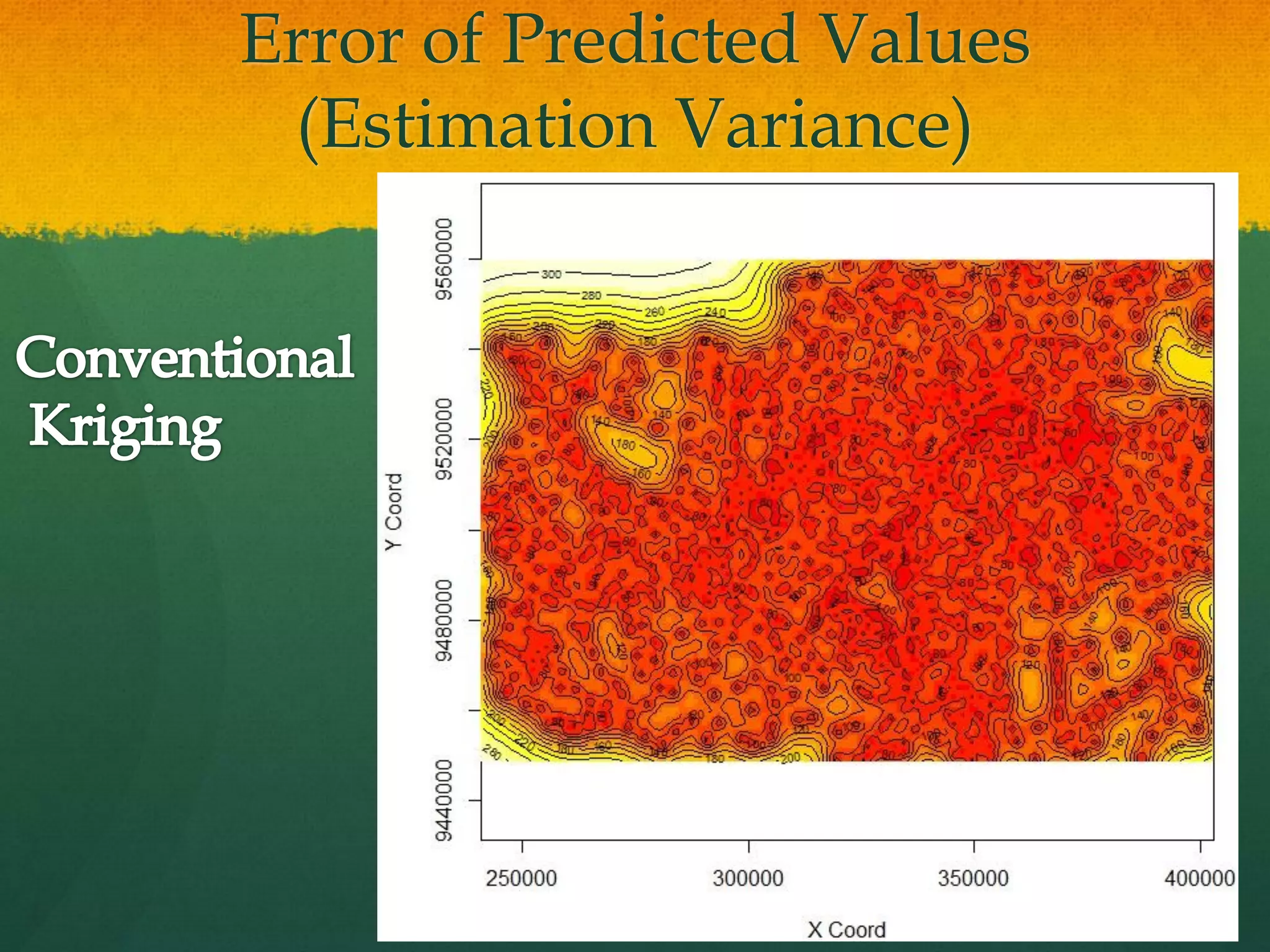
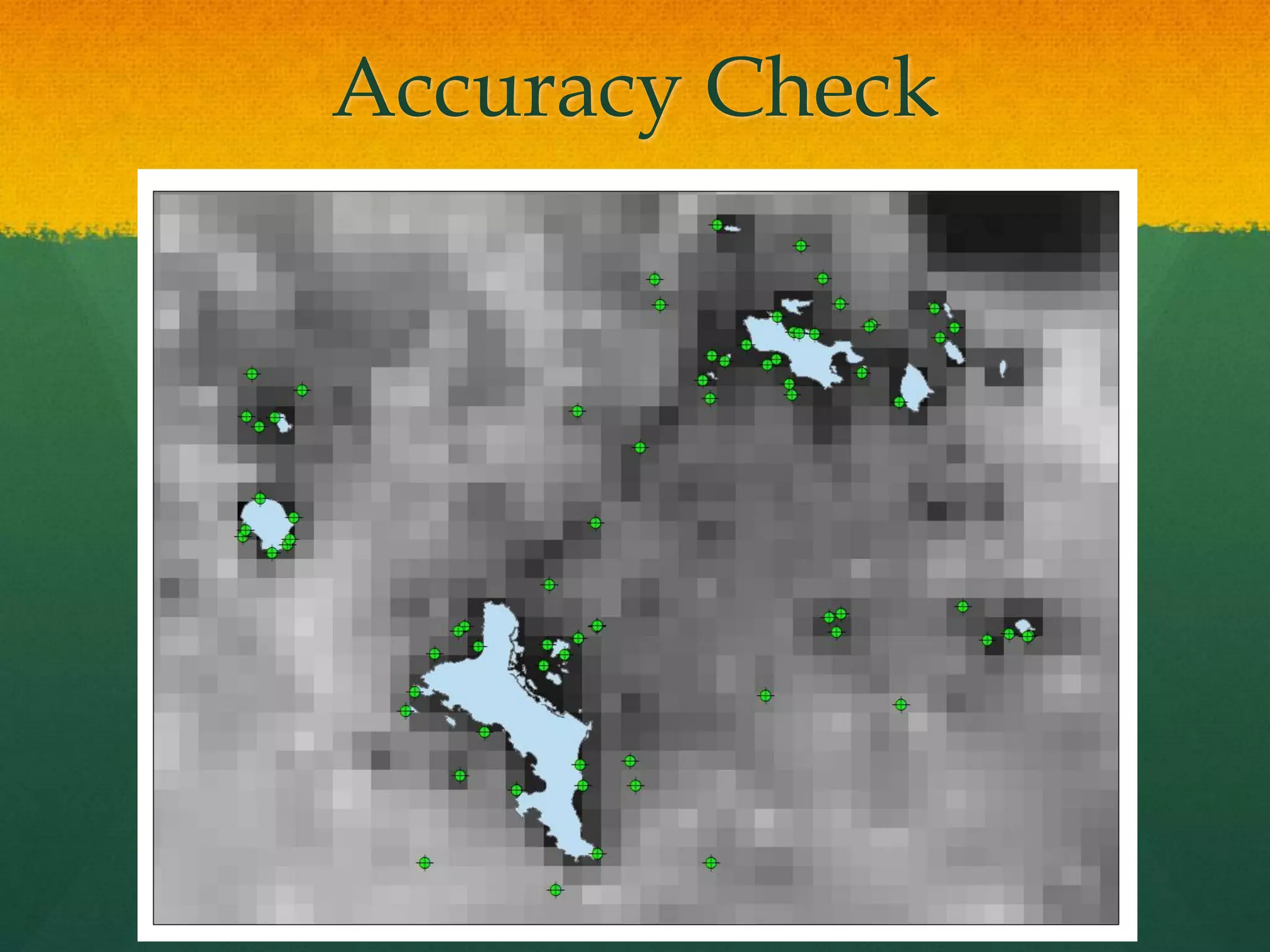
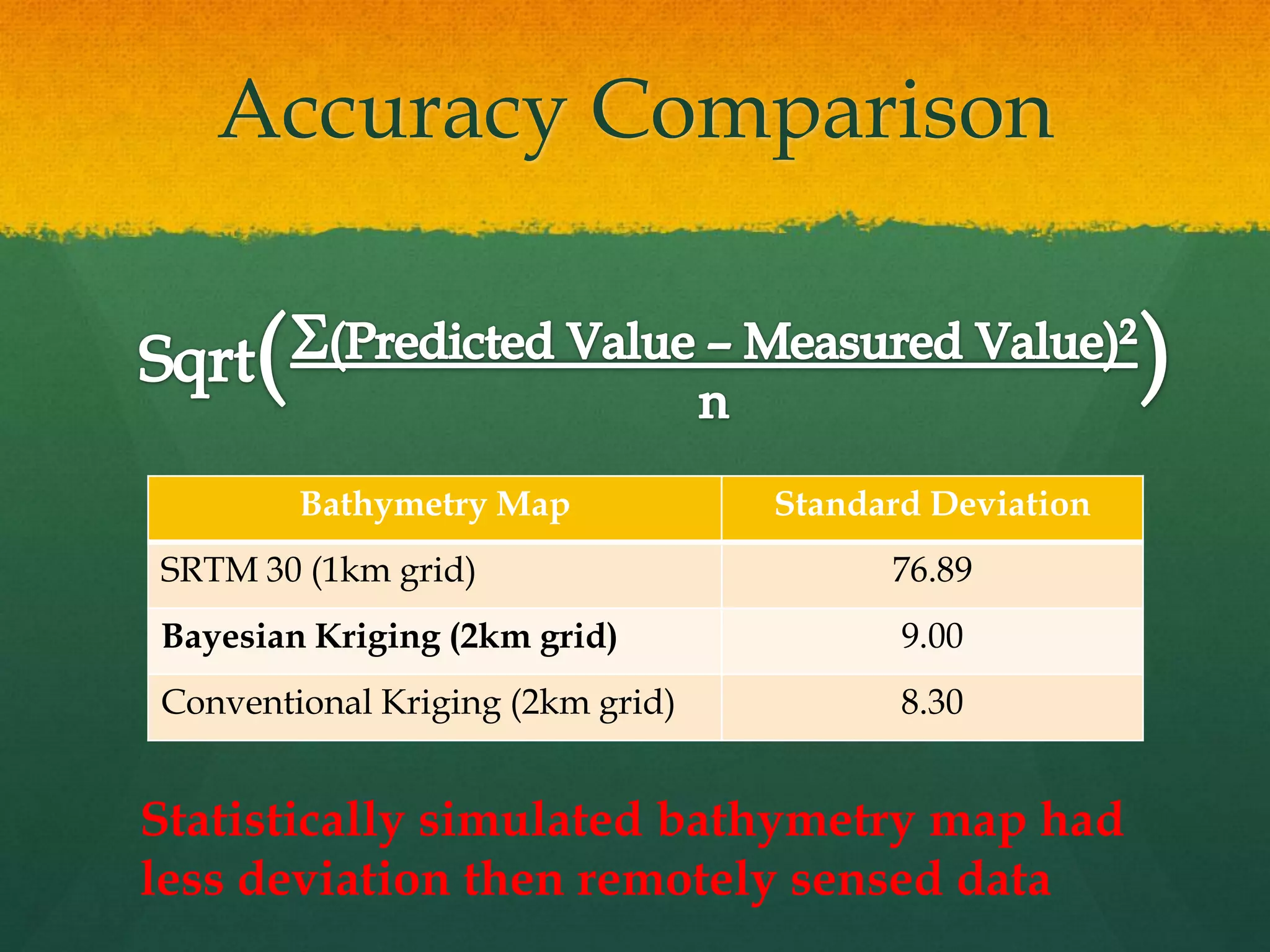

This document describes how to create a bathymetry map using Bayesian kriging with limited data. It involves georeferencing available depth data points, importing them into the open-source R package GeoR, using Bayesian kriging simulations to predict depth values on a regular grid, and checking the accuracy of the resulting pseudo-bathymetry map. The example presented used depth data from Seychelles to create a 2km resolution map that had lower standard deviation than other remotely sensed data, demonstrating how Bayesian kriging can generate useful bathymetry estimates with coarse input data.





















