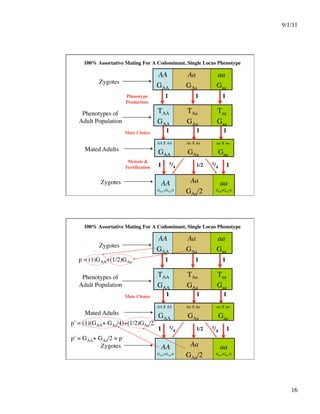
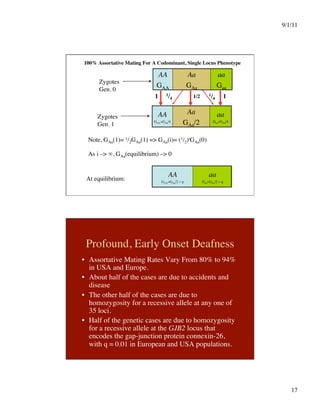
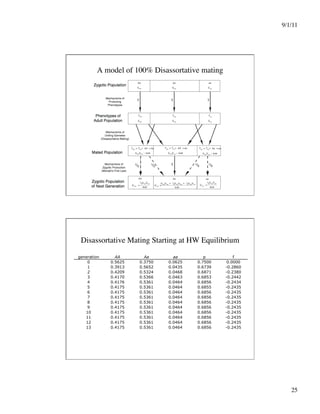
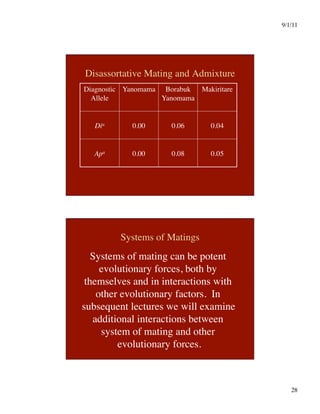
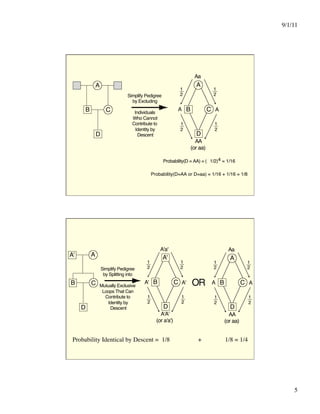
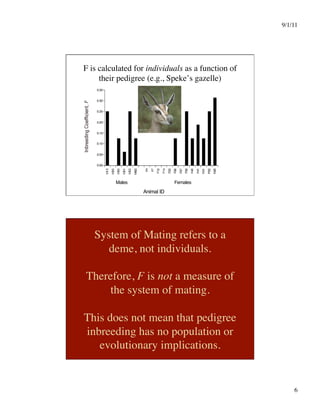
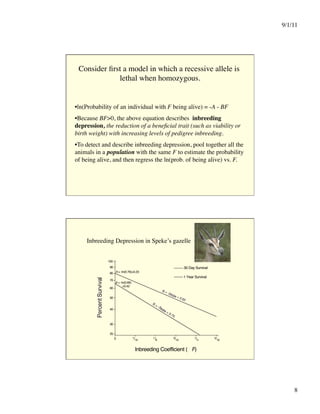
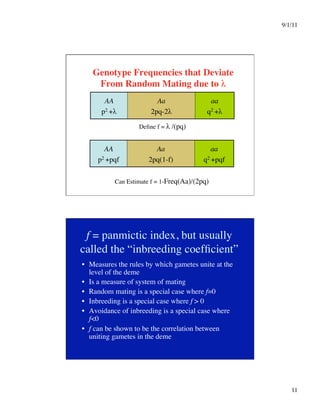
This document discusses different systems of mating and concepts related to inbreeding. It defines systems of mating as the rules by which gametes are chosen to form zygotes. Random mating is one system, while inbreeding occurs when relatives mate. Inbreeding can be measured at the individual level using the inbreeding coefficient (F), which represents an individual's probability of identity by descent. Inbreeding can also be measured at the population level using the inbreeding coefficient (f), which represents deviations from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. While F is calculated from pedigree data and ranges from 0 to 1, f is calculated from genotype frequencies and ranges from -1 to 1. The document contrasts F and f and provides examples of how different systems







![9/1/11
14
Impact of f
• Can greatly affect genotype frequencies,
particularly that of homozygotes for rare
alleles: e.g., let q =.001, then q2 = 0.000001
Now let f = 0.01, then q2+pqf = 0.000011
• f is NOT an evolutionary force by itself:
p’ = (1)(p2+pqf) + (.5)[2pq(1-f)]
= p2+pq + pqf - pqf
= p(p+q) = p
A contrast between F, the pedigree inbreeding coefficient,
and f, the system-of-mating inbreeding coefficient
Property
F
f
Data Used
Pedigree Data
Genotype
Frequency Data
Type of Measure
Probability
Correlation
Coefficient
Range
0 ≤ F ≤ 1
-1 ≤ f ≤ 1
Level
Individual
Deme
Biological
Meaning
Probability of
Identity–by–De-
scent
System of
Mating or HW
Deviation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hardy-weinberg-220304202025/85/Hardy-Weinberg-14-320.jpg)