Infections of the hand(maheswari)
- 1. Infections of the Hand
- 2. INTRODUCTION ANATOMY OF HAND CLASSIFICATION OF INFECTIONS AETIOPATHOGENESIS CLINICAL FEATURES TREATMENT COMPLICATIONS CARRY HOME MESSAGE
- 3. INTRODUCTION Hand is a compact actively functioning unit due to its mechanical and sensory functions. It is one of the most developed structures in the human evolution. Infection may be due to minor injuries or blood bone.
- 4. ANATOMY OF HAND The hand is the region of the upper limb distal to the wrist joint. It is subdivided into three parts: 1. Wrist 2.Metacarpus 3.Digits (five fingers including the thumb). The hand has an anterior surface (palm) and a dorsal surface (dorsum of hand).
- 7. CLASSIFICATION OF INFECTIONS 1. Spreading infections – spread to involve a large area of the hand. Eg: cellulitis and Lymphangitis. 2. Localized infections – localized to an area of the hand because of the anatomical factors. On the dorsum of the hand: subcutaneous infection Infection deep to the aponeurosis. On the palmar aspect of the hand: Superficial aponeurotic infection Deep aponeurotic infection Thenar space infection Mid-palmar space infection.
- 8. Others: Apical space of finger infection Terminal pulp space infection Middle volar space infection Proximal volar space infection Web space infection Tenosynovitis Space of parona’s infection
- 9. AETIOPATHOLOGY: Common in Manual workers & Housewives (Traumatic). Immunocompromised states like Diabetes Mellitus & HIV. Immunosuppression with Drugs like Steroids & CancerChemotherapy Vascular Diseases. Most common organism: Staphylococcus aureus. (80%). Other organisms like: Streptococcus; Gram Negative Bacillus Like E.coli, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas.
- 10. The organisms reach the tissues planes by direct implantation from outside or via the blood. Swelling, Erythema & Tenderness with progression to abscess formation. Spontaneous decompression can occur, (subungual abscess). Deeper infections can involve the nailbed, pulp space, and bone
- 11. GENERAL FEATURES: Infections spreads faster in all areas. Oedema develops – frog hand (oedema in Dorusm of hand). Restricted movements of fingers and hand. Loss of hook, pinch, grip and grasp. Severe pain and tenderness with fever. Tender palpable axillary lymphnodes.
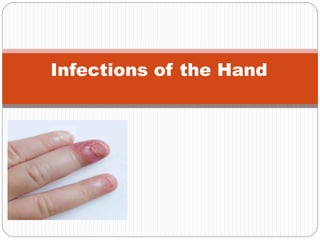
- 12. Acute Paronychium Infection of nail fold. It is the commonest infection of the hand. Results from careless nail paring or use of unsterile manicure instruments. Clinical Features: Pain, Tenderness, Redness and Swelling at one or both sides of the nail fold; and at base if suppuration extends till the base. Marked Tenderness on pressing the nail.
- 13. Clinical Presentation Initial swelling, erythema, tenderness with progression to fluctuance, and abscess formation are typical. Spontaneous decompression can occur, including tracking beneath the nail plate (subungual abscess). Deeper infections can involve the nailbed, pulp space, and bone, producing nailbed destruction, felon, or osteomyelitis
- 14. TREATMENT Early stage Oral antibiotics, Warm soaks Rest and observation Surgical decompression is the treatment of choice Decompression is performed by carefully entering the abscess cavity between the nail plate and nail fold with a scalpel blade . Asmall wick is placed for 24 to 48 hours to prevent the incision from closing and recurrence of the infection. The wick is removed, and saline warm soaks are begun.
- 15. • Depending on the extent of the infection, a partial or complete nail plate removal with or without lateral nail fold relief incision(s) is performed. • The incision should be made perpendicular to the edge of the nail fold. • Asingle or double incision is used depending on the location of the infection. • Subungual abscesses are treated with removal of a portion of or the
- 16. (A)Elevation of the eponychial fold with flat probe to expose the base of the nail. (B) Placement of an incision to drain the paronychium and to elevate the eponychial fold for excision of the proximal one-third of the nail. (C- E) Incisions and procedure for elevating the entire eponychial fold with excision of the proximal one-third of the nail. A gauze pack prevents premature closure of the cavity.
- 17. Complications: Extension of infection into pulp space. Chronic Paronychium. Chronic paronychia Chronic paronychia occurs more commonly in individuals constantly exposed to moist environments. Infections may be intermittent; clinically, the eponichial fold is thickened and painful Candidaalbicansis a frequent offending organism Topical antifungal ointments are generally used 4 to 6 weeks. Marsupialization; nail removal if deformed.
- 18. Apical Subungual Infection Infection of the tissues between the nail plate and the periosteum of the terminal phalynx. Results from a pin-prick or splinter beneath the nail. Excruciating pain with little swelling. Tenderness is maximum beneath the free edge of the nail. Pus comes to the surface at the free edge of the nail.
- 19. Treatment: In the early stage, conservative management. For suppuration – drainage of pus. A small V-Shaped piece if removed from the centre of the free edge of the nail along with a little wedge of the full thickness of the skin overlying the abscess. Complications: Chronic sinus due to pus spread. Extension of infection into tip of phalynx.
- 20. Terminal Pulp Space Infection Also known as “Whitlow” or “Felon”. SurgicalAnatomy: The terminal pulp space is the volar space of the distal digit. Filled with compact fat, feebly partitioned by multiple fibrous septae. At its proximal end, space closed by a septum of deep fascia connecting the distal flexor crease of the finger to the periosteum just distal to the insertion of the profundus flexor tendon.
- 21. 15-20 longitudonal septa anchoring skin to distal phalanx dividing the pulp into multiple closed compartments.
- 22. Pathophysiology Infection typically is due to direct inoculation of bacteria by penetrating trauma but may be caused by hematogenous spread local spread from an untreated paronychia. Most common in thumb and index finger. Clinical presentation Throbbing pain and Tense swelling localized to the pulp
- 23. “Don’t wait for fluctuation if tension is severe” Infection results in edema increased pressure within the closed compartment impaired venous outflow local compartment syndrome. Untreated felons can: extend toward the phalanx --> osteomyelitis toward the skin --> draining sinus obliterate vessels ---> skin slough or necrosis suppurative flexor tenosynovitis or septic arthritis of the DIPJ
- 24. Treatment If recognized early (mild cellulitis): soaks & Abx Later (abscess formation): surgical drainage Usually process has been going on > 48 hrs. Principles: Avoid injury to nerve and vessel structures Utilize an incision that won’t leave a disabling scar Do not violate flexor sheath (stay distal)
- 25. Complications Osteomyelitis of the terminal phalynx – with necrosis and sequestration of distal half due to thrombo- arteritis of digital vessels. Pyogenic arthritis of the distal interphalyngeal joint. Suppurative tenosynovitis of flexor tendon sheaths.
- 26. Web Space Infection Anatomy: A triangular space between the bases of adjacent fingers. Clinical features: Infection arises from skin crack; From a purulent blister; Proximal volar space infection through the lumbrical canal. Oedema over back of the hand. Swelling at the base of the finger, Fingers are seperated from the adjacent fingers. Tenderness maximum in web and
- 27. Treatment: In early stage – conservative treatment with antibiotics. In late stages – incision and drainage. Transverse incision on palmar surface; With constant probing pus drained, Edges of the wound are cut away with a diamond shaped opening. A conter incision given over dorsum of hand. Complications: Infection spreads to adjacent spaces and Tendon sheaths.
- 28. Deep Palmar Abscess A serious but rare infection. Infection in the thenar or mid-palmar space. Anatomy: Deep palmar spaces lie in the hollow of the palm, deep to the flexor tendons and their synovial sheaths. Space is divided into a medial mid-palmar space and a lateral thenar space. Posterior relation is formed by fascia covering the interossei and metacarpals on medial side & adductor pollicis muscle on the lateral side.
- 30. Clinical Features: Infection arises from penetrating wound via blood stream or complication of suppurative tenosynovitis. Severe swelling on dorsum of hand – frog hand. Extension at MCP Joints very painful & painless at IP Joints. Regional lymphadenopathy present.
- 31. Treatment: Needle aspiration to confirm pus. A central transverse incision in the line of flexor crease. Through deep probing, pus to be drained and skin edges & palmar fascia trimmed Complications: Discharging sinus. Stiffness of the hand.
- 32. Acute Suppurative Tenosynovitis It’s a rare but important infection; prompt treatment essential. Anatomy: Flexor sheaths are closed spaces Extend from the mid-palmar crease to the DIPJ (Prox edge of A1 pulley to distal edge of A5pulley). Flexor sheath of small finger is continuous proximally with the Ulnar Bursa, while the sheath of the thumb is continuous with the Radial Bursa. Radial & Ulnar bursae extend proximal to the TCL and connect with the Parona space (Potential space between FDP & PQ muscle).
- 33. Flexor sheath infections most often as a result of penetrating trauma More likelyat joint flexion creases Sheaths are separated from skin by only a small amount of subcutaneous tissue here Also, Felons can rupture into the distal flexor sheath Usual causative agent: S. Aureus Most commonly affected digits: Ring, long &index fingers Purulence within the sheath destroys the gliding mechanism, rapidly creating adhesions that lead to loss of function Destroys the blood supply producing tendon necrosis.
- 34. Kanavel’s 4 cardinal signs: Tenderness over & limited to the flexor sheath Symmetrical enlargement of the digit (“fusiform”) Severe pain on passive extension of the finger (> proximally) Flexed posture of the involved digit Not allfour signs may be present early on Most reliable sign: painw.passiveextension Cellulitis of the hand may appear similar, but swelling &tenderness is not usually isolated to a single digit
- 35. Early infection < 48 hrs (& usually lacking all 4 signs) may initially be treated with IV Abx, splinting & elevation Failure to respond within 24 hrs. should necessitate drainage Established pyogenic tenosynovitis is a Surgical Emergency. Requires prompt surgical drainage. Delay may result in skin/tendon necrosis.
- 36. Carry Home Messages: Careful history & examination. Anatomical area involved. Extent of spread. Empiric antibiotics till culture report. Prompt and adequate surgical treatment. Immobilization in position of function. Rehabilitation.
- 37. Thank you