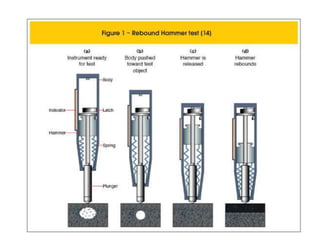
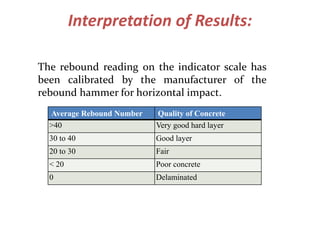
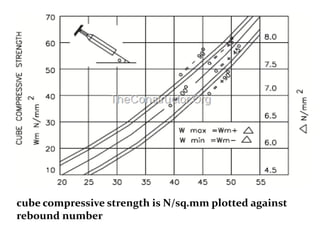
The document discusses the rebound hammer test, which is a non-destructive test used to estimate the compressive strength of hardened concrete. It works by measuring the rebound of a spring-loaded hammer after it impacts the concrete surface. A higher rebound number indicates higher compressive strength. The procedure involves firmly pressing the hammer plunger against the concrete surface to trigger the internal spring. The rebound reading can then be correlated to compressive strength using a calibration graph. Advantages are that it is simple, fast, and does not damage the structure. Limitations include only evaluating the surface layer and lack of direct relationship to other concrete properties.